
The compound formed as a result of oxidation of ethylbenzene by ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is:
A. acetophenone
B. benzophenone
C. benzoic acid
D. benzaldehyde
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: Any aliphatic carbon with hydrogen attached to it, in combination with a benzene ring will be oxidized to benzoic acid regardless of the length of the entire side chain as ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is a strong oxidizing agent.
Complete step by step answer:
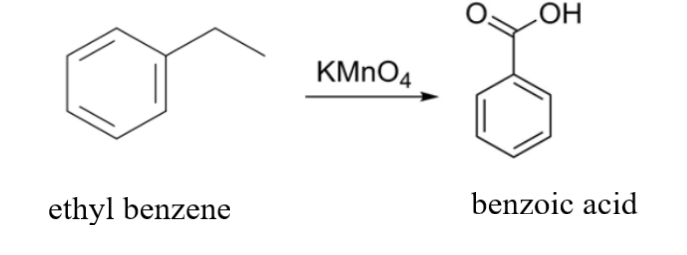
Here, we are provided with ethyl benzene i.e. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$that has to be oxidized with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$. ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is a strong oxidizing reagent. What it does is it will oxidize the carbon that is attached to the benzene ring because the hydrogen attached to that carbon will be the most acidic hydrogen. The two hydrogens attached to the carbon get replaced by two ${\text{ - OH}}$ groups. Similarly, in the place of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ an ${\text{ - OH}}$ group will get attached. As a result, three ${\text{ - OH}}$ groups will get attached to the benzene ring. The attachment of three ${\text{ - OH}}$ groups will make the product highly unstable due to which it will tend to lose water ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ and the reaction will end with the formation of benzoic acid ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH}}$ as an end product.
The reaction is as follows:
Another example can be:
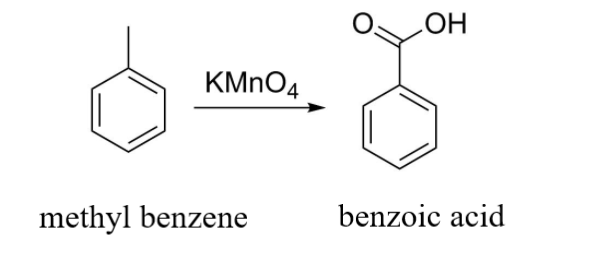
In this example, the result of oxidation of methyl benzene with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is benzoic acid.
From the above two cases, we infer that the reaction does not depend on the length of the side chain attached to the benzene ring. Irrespective of the side chain, the ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ will always oxidize it to benzoic acid.
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note:
Keep in mind the trick that no matter how long the side chain is, the result of this reaction will always be benzoic acid as explained above that the reaction does not depend on the length of the side chain attached to the ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we are provided with ethyl benzene i.e. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$that has to be oxidized with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$. ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is a strong oxidizing reagent. What it does is it will oxidize the carbon that is attached to the benzene ring because the hydrogen attached to that carbon will be the most acidic hydrogen. The two hydrogens attached to the carbon get replaced by two ${\text{ - OH}}$ groups. Similarly, in the place of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ an ${\text{ - OH}}$ group will get attached. As a result, three ${\text{ - OH}}$ groups will get attached to the benzene ring. The attachment of three ${\text{ - OH}}$ groups will make the product highly unstable due to which it will tend to lose water ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ and the reaction will end with the formation of benzoic acid ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH}}$ as an end product.
The reaction is as follows:

Another example can be:

In this example, the result of oxidation of methyl benzene with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is benzoic acid.
From the above two cases, we infer that the reaction does not depend on the length of the side chain attached to the benzene ring. Irrespective of the side chain, the ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ will always oxidize it to benzoic acid.
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note:
Keep in mind the trick that no matter how long the side chain is, the result of this reaction will always be benzoic acid as explained above that the reaction does not depend on the length of the side chain attached to the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




