
What will be the coefficient of restitution if a ball (v = 12 m/s) collides with another very heavy ball moving in the opposite direction with a speed of 3 m/s & the ball rebounds with a velocity of 12 m/s.
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: This is a question based on the concept of law of conservation of momentum. The law of conservation of momentum states that if no external force is acting then the linear momentum of an isolated system is always conserved. I.e the product of mass and velocity will remain the same before the collision as well as after the collision.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a ball of certain mass moving with a velocity of 12 m/s strikes a comparatively heavier ball which is moving with a velocity of 3 m/s. After the collision, this lighter ball rebounds with a velocity of 12 m/s, as shown in the figure.
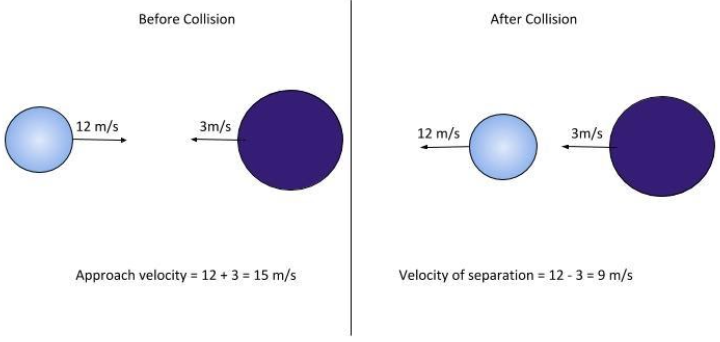
Now, the question is what will happen to the heavier ball, since there is no external force acting the momentum of the system will be conserved. Let. m & M be the masses of lighter and heavier balls respectively. Now the initial momentum (Pi) is given by,
${P_i} = 12m + 3M$
Assume v is the velocity with which the heavy ball is moving final momentum (Pf) or the momentum after the collision is given by,
${P_f} = 12m + vM$
Now according to the law of conservation of momentum, we can say that,
${P_i} = {P_f}$
Hence the final velocity of the heavy ball will be, v = 3 m/s and the ball will keep moving in the same direction.
We know that the coefficient of restitution is given by,
$e = \dfrac{{{\mathbf{Velocity}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{of}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{separation}}{\text{ }}}}{{{\mathbf{Velocity}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{of}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{approach}}}}$
From the figure put the values of the velocity of approach and velocity of separation in the above equation,
$e = \dfrac{9}{{15}}$
$e = 0.6$
Hence the coefficient of restitution for the given case will be 0.6.
Note: The coefficient of restitution is a parameter related to the collision of two bodies. The ratio of the velocity of approach to the velocity of separation is known as the coefficient of restitution. The value of the coefficient of restitution lies between 0 to 1 (0 < e < 1). For perfectly elastic collision e = 1.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a ball of certain mass moving with a velocity of 12 m/s strikes a comparatively heavier ball which is moving with a velocity of 3 m/s. After the collision, this lighter ball rebounds with a velocity of 12 m/s, as shown in the figure.

Now, the question is what will happen to the heavier ball, since there is no external force acting the momentum of the system will be conserved. Let. m & M be the masses of lighter and heavier balls respectively. Now the initial momentum (Pi) is given by,
${P_i} = 12m + 3M$
Assume v is the velocity with which the heavy ball is moving final momentum (Pf) or the momentum after the collision is given by,
${P_f} = 12m + vM$
Now according to the law of conservation of momentum, we can say that,
${P_i} = {P_f}$
Hence the final velocity of the heavy ball will be, v = 3 m/s and the ball will keep moving in the same direction.
We know that the coefficient of restitution is given by,
$e = \dfrac{{{\mathbf{Velocity}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{of}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{separation}}{\text{ }}}}{{{\mathbf{Velocity}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{of}}{\text{ }}{\mathbf{approach}}}}$
From the figure put the values of the velocity of approach and velocity of separation in the above equation,
$e = \dfrac{9}{{15}}$
$e = 0.6$
Hence the coefficient of restitution for the given case will be 0.6.
Note: The coefficient of restitution is a parameter related to the collision of two bodies. The ratio of the velocity of approach to the velocity of separation is known as the coefficient of restitution. The value of the coefficient of restitution lies between 0 to 1 (0 < e < 1). For perfectly elastic collision e = 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




