
The by-product obtained during the production of phenol from Cummene industrially is:
A. acetaldehyde
B. acetic acid
C. acetone
D. acetyl halide
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: In a chemical reaction, the products other than the desirable one are called by-products.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that phenol can be prepared by various methods using different precursors. For example, chlorobenzene on treatment with ${\rm{NaOH}}$ under the conditions of \[{\rm{623 K and 320 atm}}\] gives sodium phenoxide that gives phenol on treatment with acid. Another example is diazonium salt of benzene, $\left( {{\rm{Ph}} - {\rm{N}}_2^ + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }} \right)$ which can give phenol upon hydrolysis as per the following reaction:
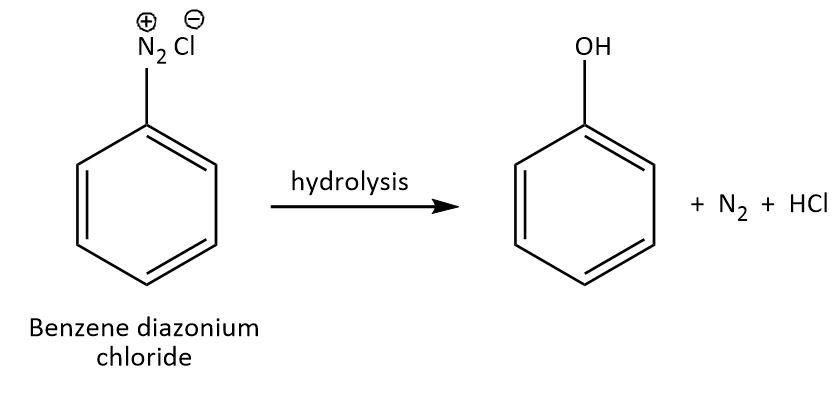
As we can see that in addition to phenol, ${{\rm{N}}_2}\;{\rm{and}}\;{\rm{HCl}}$are also produced. We can say that in this reaction, phenol is the main product as it was desired and all the additional products are the by-products of this reaction as they were not specifically desired.
Now let’s discuss the industrial production of phenol from cummeneIsopropylbenzene, commonly known as cummene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is usually found in crude oils and is significant for its varied applications including being used as solvent or blending component. The most important use of cumene is its use in phenol production.
We know that cummene upon getting oxidized in the presence of air givescummenehydroperoxide which can be shown as follows:
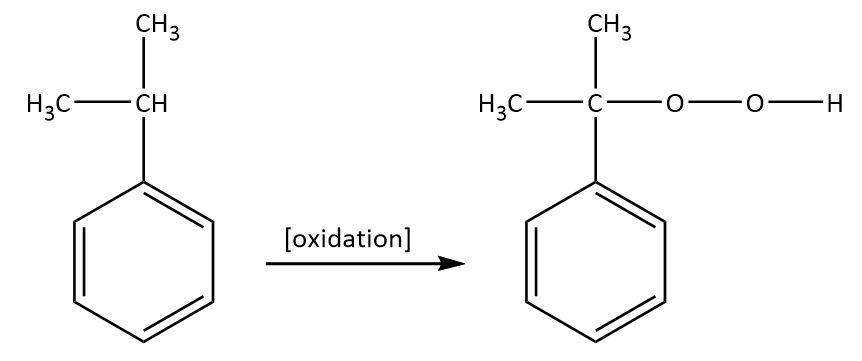
Cummenehydroperoxide gives phenol when treated with dilute acid which can be shown as follows:
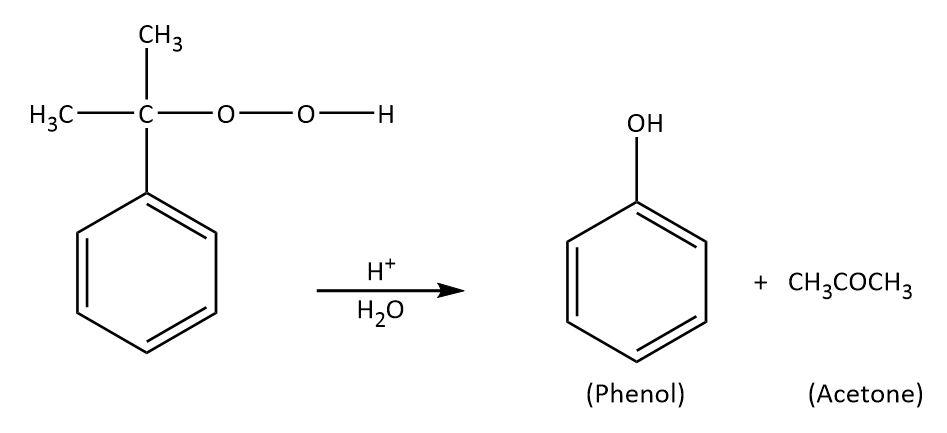
As we can see that we are getting a byproduct as well which is acetone${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
We have to be careful while using the terminology as main product and by-product and while writing the reactions for not just the number of atoms but the structure of the compound is very significant.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that phenol can be prepared by various methods using different precursors. For example, chlorobenzene on treatment with ${\rm{NaOH}}$ under the conditions of \[{\rm{623 K and 320 atm}}\] gives sodium phenoxide that gives phenol on treatment with acid. Another example is diazonium salt of benzene, $\left( {{\rm{Ph}} - {\rm{N}}_2^ + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }} \right)$ which can give phenol upon hydrolysis as per the following reaction:

As we can see that in addition to phenol, ${{\rm{N}}_2}\;{\rm{and}}\;{\rm{HCl}}$are also produced. We can say that in this reaction, phenol is the main product as it was desired and all the additional products are the by-products of this reaction as they were not specifically desired.
Now let’s discuss the industrial production of phenol from cummeneIsopropylbenzene, commonly known as cummene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is usually found in crude oils and is significant for its varied applications including being used as solvent or blending component. The most important use of cumene is its use in phenol production.
We know that cummene upon getting oxidized in the presence of air givescummenehydroperoxide which can be shown as follows:

Cummenehydroperoxide gives phenol when treated with dilute acid which can be shown as follows:

As we can see that we are getting a byproduct as well which is acetone${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
We have to be careful while using the terminology as main product and by-product and while writing the reactions for not just the number of atoms but the structure of the compound is very significant.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




