
The bond angle around B in \[BC{{l}_{3}}\] and\[B{{F}_{3}}\] is the same. Explain.
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Boron is the element of group 13. It has 3 valence electrons in its outer shell. On the basis of hybridization, the structure is estimated. The structure helps in finding the bond angle. The number of lone pairs should also be considered.
Complete answer:
Boron is the first element of the group 13.
Its outer electronic configuration is \[2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}\]
It means that it has 3 valence electrons in its outer shell. Hence, it can form 3 bonds.
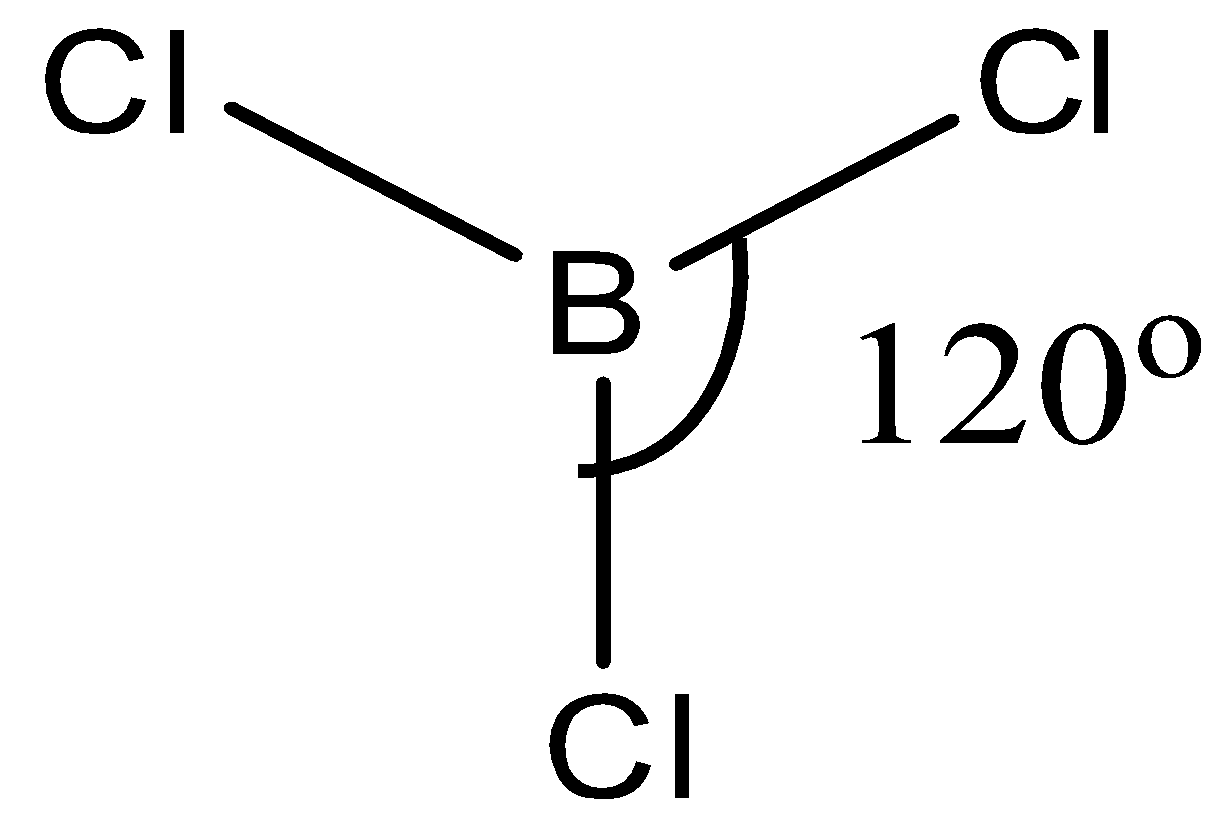
Now, in \[BC{{l}_{3}}\], boron is surrounded by 3 atoms of chlorine. Chlorine atom belongs to the group of halogens (group 17), which requires only one electron to complete its octet.
Hence, the chlorine forms a single bond with the boron atom.
Now, all the 3 valence electrons of boron form a bond with the chlorine atom hence there are no lone pairs present in the compound.
Since there are 3 bonds in the compound the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{2}}\]
And we know that \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridization forms trigonal planar geometry.
The trigonal planar has \[{{120}^{\circ }}\] bond angle around the central atom.
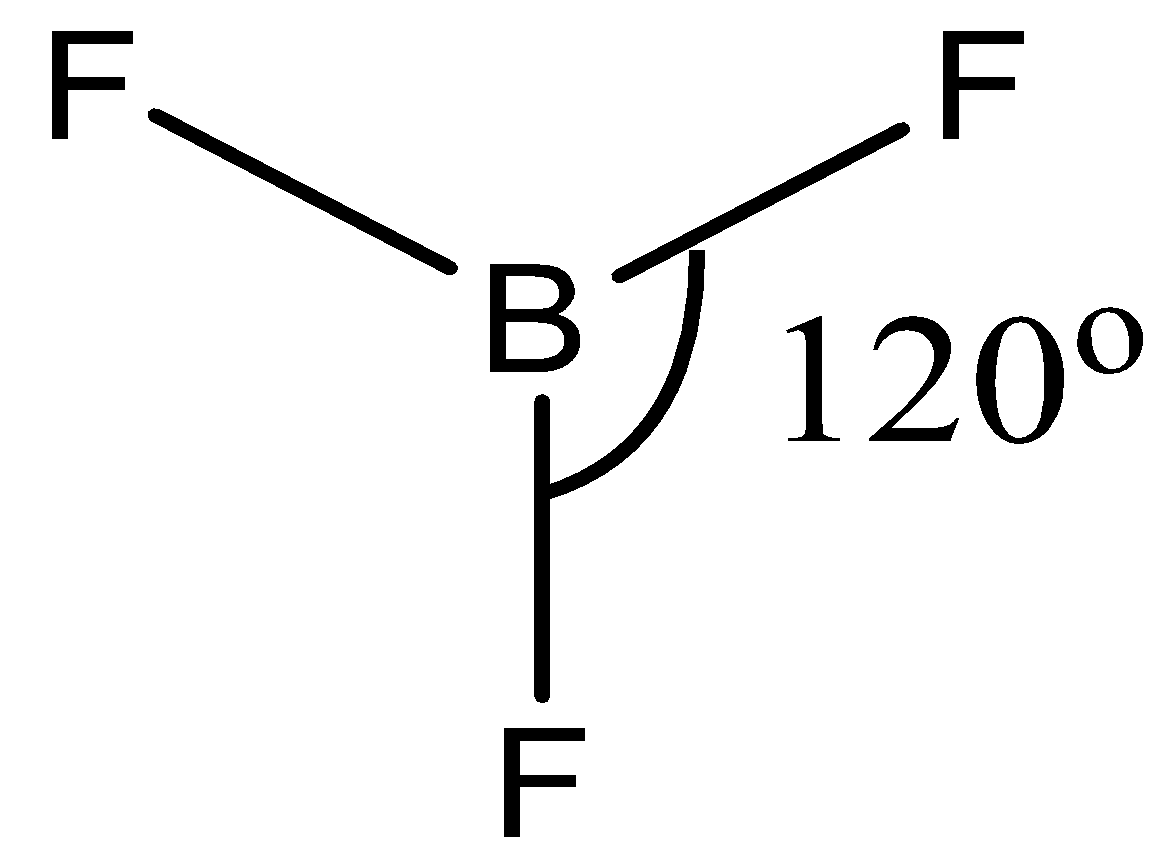
Now, in \[B{{F}_{3}}\], boron is surrounded by 3 atoms of Fluorine. Fluorine atoms also belong to the group of halogens (group 17), which requires only one electron to complete its octet.
Hence, the chlorine forms a single bond with the boron atom.
Now, all the 3 valence electrons of boron form a bond with the Fluorine atom hence there is no lone pair present in the compound.
Since there are 3 bonds in the compound the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{2}}\]
And we know that \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridization forms trigonal planar geometry.
The trigonal planar has \[{{120}^{\circ }}\] bond angle around the central atom.
Hence the bond angle is the same in both cases.
Note: You may get confused that fluorine is a more electronegative atom so it would make a bond angle different from boron trichloride. The structure and bond angle depends on the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs around the central atom.
Complete answer:
Boron is the first element of the group 13.
Its outer electronic configuration is \[2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}\]
It means that it has 3 valence electrons in its outer shell. Hence, it can form 3 bonds.
Now, in \[BC{{l}_{3}}\], boron is surrounded by 3 atoms of chlorine. Chlorine atom belongs to the group of halogens (group 17), which requires only one electron to complete its octet.
Hence, the chlorine forms a single bond with the boron atom.
Now, all the 3 valence electrons of boron form a bond with the chlorine atom hence there are no lone pairs present in the compound.
Since there are 3 bonds in the compound the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{2}}\]
And we know that \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridization forms trigonal planar geometry.
The trigonal planar has \[{{120}^{\circ }}\] bond angle around the central atom.

Now, in \[B{{F}_{3}}\], boron is surrounded by 3 atoms of Fluorine. Fluorine atoms also belong to the group of halogens (group 17), which requires only one electron to complete its octet.
Hence, the chlorine forms a single bond with the boron atom.
Now, all the 3 valence electrons of boron form a bond with the Fluorine atom hence there is no lone pair present in the compound.
Since there are 3 bonds in the compound the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{2}}\]
And we know that \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridization forms trigonal planar geometry.
The trigonal planar has \[{{120}^{\circ }}\] bond angle around the central atom.

Hence the bond angle is the same in both cases.
Note: You may get confused that fluorine is a more electronegative atom so it would make a bond angle different from boron trichloride. The structure and bond angle depends on the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs around the central atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




