
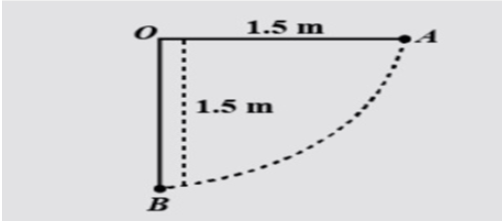
The bob of a pendulum is released from a horizontal position A as shown in the figure. If the length of the pendulum is 1.5m, what is the speed with which the bob arrives at the lower most point B, given that it dissipated 5% of its initial energy against air resistance?
(A) 5m/s
(B) 5.5m/s
(C) 5.3m/s
(D) 4.4m/s

Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint- An object possesses kinetic energy due to the motion. The work or energy needed to accelerate an object or body to move from its initial rest position is known as kinetic energy. The kinetic energy plays an important role in the field of mechanics.
Formula used: To solve this type of problems we use the following formula.
Potential energy $ = mgh$
Kinetic energy $ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Here, m is mass, g is acceleration due to gravity, h is the height of the object and v is the velocity of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
Following is the given information in the question: length of pendulum (l) = 1.5m, energy dissipated = 5%, let the mass of bob be m.
Now, we know about the law of conservation of energy, according to which energy of the system must remain constant.
Let us apply the law of conservation at horizontal position;
Here potential energy, P.E.=mgl and kinetic energy, K.E.= 0.
Therefore, total energy is given below.
T.E.=P.E.+K.E.=mgl (1)
Similarly, applying law of conservation of energy at the mean position;
P.E.=0 and K.E. $ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Therefore, total energy is given below.
T.E.=P.E.+K.E. $ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ (2)
According to the question, as bob moves from horizontal position to mean position 5% energy is dissipated. That means total energy at mean position is 95% if the total energy at horizontal position.
Mathematically we can write it as below.
$\dfrac{{95}}{{100}} \times $ mgl$ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Let us substitute the values in the above equation.
$\dfrac{{95 \times 1.5 \times 9.8}}{{100}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2}$
Let us now simplify the expression.
${v^2} = 27.93m/s \Rightarrow v = 5.28m/s$
Hence, option (C) “5.3m/s” is the correct option.
Note:
Total mechanical energy of a system is always equal to its potential energy plus kinetic energy.
For conservative system, total energy is constant, always.
Formula used: To solve this type of problems we use the following formula.
Potential energy $ = mgh$
Kinetic energy $ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Here, m is mass, g is acceleration due to gravity, h is the height of the object and v is the velocity of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
Following is the given information in the question: length of pendulum (l) = 1.5m, energy dissipated = 5%, let the mass of bob be m.
Now, we know about the law of conservation of energy, according to which energy of the system must remain constant.
Let us apply the law of conservation at horizontal position;
Here potential energy, P.E.=mgl and kinetic energy, K.E.= 0.
Therefore, total energy is given below.
T.E.=P.E.+K.E.=mgl (1)
Similarly, applying law of conservation of energy at the mean position;
P.E.=0 and K.E. $ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Therefore, total energy is given below.
T.E.=P.E.+K.E. $ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ (2)
According to the question, as bob moves from horizontal position to mean position 5% energy is dissipated. That means total energy at mean position is 95% if the total energy at horizontal position.
Mathematically we can write it as below.
$\dfrac{{95}}{{100}} \times $ mgl$ = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Let us substitute the values in the above equation.
$\dfrac{{95 \times 1.5 \times 9.8}}{{100}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2}$
Let us now simplify the expression.
${v^2} = 27.93m/s \Rightarrow v = 5.28m/s$
Hence, option (C) “5.3m/s” is the correct option.
Note:
Total mechanical energy of a system is always equal to its potential energy plus kinetic energy.
For conservative system, total energy is constant, always.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




