
The basis of DNA fingerprinting is
(a) the double helix
(b) Error in the base sequence
(c) Polymorphism in sequence
(d) DNA replication
(e) DNA coiling
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: DNA, a short form of deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that contains the genetic code of organisms. DNA remains present in each cell of the organism and gives directions to the cells about the proteins to be synthesized.
Complete answer:
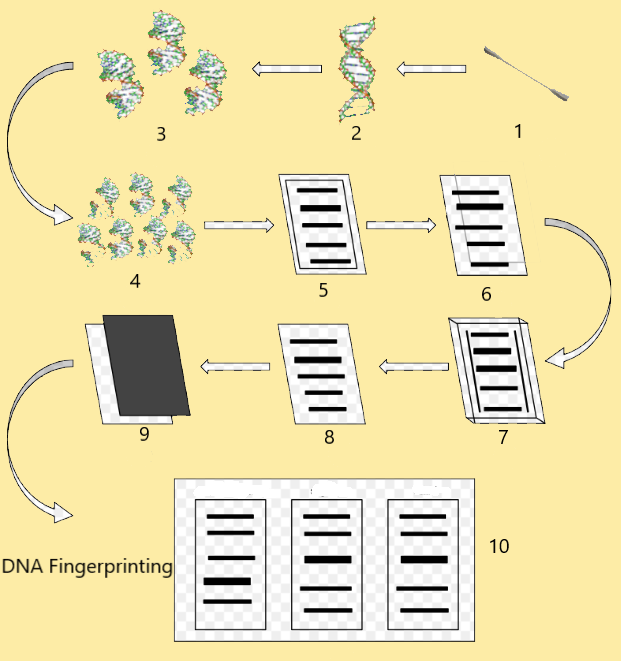
A technique that simultaneously detects lots of minisatellites in the genome to produce a pattern unique to an individual is called DNA fingerprinting. Sequence polymorphisms which are minor sequence differences (mostly single base-pair changes) between individuals are the basis of DNA fingerprinting.
The whole-genome can be digested by restriction enzymes into DNA fragments of specific lengths which are based on the location of restriction sites in the genome. Recognition sites for restriction enzymes are affected by sequence polymorphism which in turn causes variation in the size of DNA fragments produced by digestion with a particular restriction enzyme. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) are the variations which are detected by Southern blotting.
For this, DNA samples digested by restriction enzymes are sorted by gel electrophoresis followed by Southern blotting. Lastly, radioactive probes are washed over the nylon surface, allowing their joining to any DNA fragments of the same composition.
-DNA polymorphisms are responsible for the body design of an organism. Hence, DNA copying is very important for reproduction.
-During reproduction, additional copies of DNA are made so that each new daughter cell formed has its DNA. However, during DNA copying, some minor alterations occur. This results in bringing variations in the long run. DNA copying is essential for the inheritance of features from parents to the next generation.
So, the correct answer is,’ Polymorphism in sequence’.
Note:
-The chances of two people having the same 13-loci DNA profile is about one in one billion.
-A DNA fingerprint is a set of DNA markers that is different for each individual except with identical twins.
-Identical twins share about 100% of their genes. Siblings share about 50 percent of their genes.
Complete answer:
A technique that simultaneously detects lots of minisatellites in the genome to produce a pattern unique to an individual is called DNA fingerprinting. Sequence polymorphisms which are minor sequence differences (mostly single base-pair changes) between individuals are the basis of DNA fingerprinting.
The whole-genome can be digested by restriction enzymes into DNA fragments of specific lengths which are based on the location of restriction sites in the genome. Recognition sites for restriction enzymes are affected by sequence polymorphism which in turn causes variation in the size of DNA fragments produced by digestion with a particular restriction enzyme. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) are the variations which are detected by Southern blotting.
For this, DNA samples digested by restriction enzymes are sorted by gel electrophoresis followed by Southern blotting. Lastly, radioactive probes are washed over the nylon surface, allowing their joining to any DNA fragments of the same composition.
-DNA polymorphisms are responsible for the body design of an organism. Hence, DNA copying is very important for reproduction.
-During reproduction, additional copies of DNA are made so that each new daughter cell formed has its DNA. However, during DNA copying, some minor alterations occur. This results in bringing variations in the long run. DNA copying is essential for the inheritance of features from parents to the next generation.
So, the correct answer is,’ Polymorphism in sequence’.

Note:
-The chances of two people having the same 13-loci DNA profile is about one in one billion.
-A DNA fingerprint is a set of DNA markers that is different for each individual except with identical twins.
-Identical twins share about 100% of their genes. Siblings share about 50 percent of their genes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




