
The basic structure/functional unit of the kidney is
A) Henle’s loop
B) Nephron
C) Nephridium
D) Pyramid
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: The kidneys are bean-shaped dark reddish colored organs present in the lower abdominal region. Both kidneys contain millions of microscopic units composed of renal tubules and renal corpuscle. These form the basic structural and functional units of the kidney that filters the blood.
Complete answer: The kidney is made up of the outer cortex called the renal cortex and the inner soft tissue called the renal medulla. The renal medulla contains several raised tissue portions called renal pyramids. Each of the renal medullae is made of millions of microscopic units of the kidney called nephrons. Nephrons are long tube-like structures having a length of around 35 to 55 mm long. The nephrons constitute the basic structural and functional units of the kidney. They consist of two units of filtering mechanisms. One of these components is the renal corpuscle which contains the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. The second component is called the renal tubule which is further made of three units.
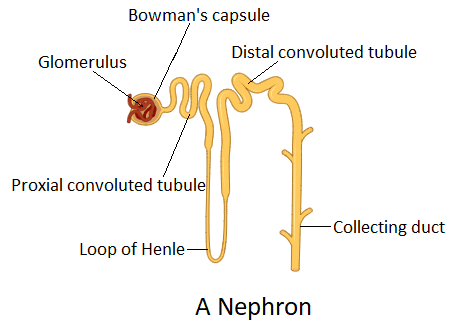
The glomerulus is a complex and dense network of capillaries through which impure blood is filtered. The thin vessels of the glomerulus do not allow large molecules to pass. The small impurity molecules pass through the glomerulus. This is called the filtrate. The filtrate is then passed to a cup-shaped cavity called Bowman’s capsule. The renal tubule is a convoluted structure that extends from the glomerulus. The initial part of the renal tubule is proximal convoluted tubule or PCT. The second region of the renal tubule is called the loop of Henle or Henle's loop. It is also called the nephritic loop as it forms a descending and ascending loop. The last part of the renal tubule is named the distal convoluted tubule or DCT. It is the last to receive the filtrate.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The filtration of blood occurs in the renal capsule, the renal tubules are for reabsorption from the filtrate. Both active and passive transport processes are used for this process. The secretions from the tubules add to filtrate and help in urine formation without altering electrolyte levels.
Complete answer: The kidney is made up of the outer cortex called the renal cortex and the inner soft tissue called the renal medulla. The renal medulla contains several raised tissue portions called renal pyramids. Each of the renal medullae is made of millions of microscopic units of the kidney called nephrons. Nephrons are long tube-like structures having a length of around 35 to 55 mm long. The nephrons constitute the basic structural and functional units of the kidney. They consist of two units of filtering mechanisms. One of these components is the renal corpuscle which contains the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. The second component is called the renal tubule which is further made of three units.

The glomerulus is a complex and dense network of capillaries through which impure blood is filtered. The thin vessels of the glomerulus do not allow large molecules to pass. The small impurity molecules pass through the glomerulus. This is called the filtrate. The filtrate is then passed to a cup-shaped cavity called Bowman’s capsule. The renal tubule is a convoluted structure that extends from the glomerulus. The initial part of the renal tubule is proximal convoluted tubule or PCT. The second region of the renal tubule is called the loop of Henle or Henle's loop. It is also called the nephritic loop as it forms a descending and ascending loop. The last part of the renal tubule is named the distal convoluted tubule or DCT. It is the last to receive the filtrate.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The filtration of blood occurs in the renal capsule, the renal tubules are for reabsorption from the filtrate. Both active and passive transport processes are used for this process. The secretions from the tubules add to filtrate and help in urine formation without altering electrolyte levels.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




