
The areas of three adjacent faces of a rectangular box which meet in a point are known. The product of these areas is equal to \[\]
A. the volume of the box \[\]
B. twice the volume of the box \[\]
C. the square of the volume of the box \[\]
D. the cube root of the volume of the box \[\]
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: We denote the denote the vertices of the cuboid shaped rectangular box as A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and three different sides length, breadth and height denoted $l,$$b$ and $h$. We find surface area of any three adjacent surfaces using the formula for area of a rectangle and find their product. We compare the product with volume of the cuboid box $V=lbh$ to choose the correct option. \[\]
Complete step by step answer:
We know that a cuboid is a three dimensional object with six rectangular faces joined by 8 vertices. It has three different types of sides called length, breadth and height denoted $l,$$b$ and $h$. \[\]
The amount of space contained by a three dimensional object is measured by the quantity called volume. The amount of space that is occupied by a cuboid is the product of length, breadth and height. Mathematically, volume denoted as $V$of a cuboid is
\[V=l\times b\times h=lbh....\left( 1 \right)\]
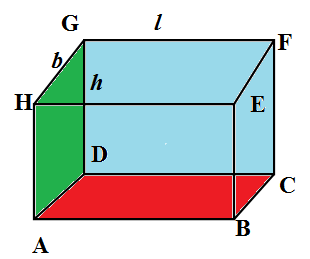
Let us denote the vertices of the cuboid as A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H. We are going to call two rectangular surfaces adjacent when they share a common vertex. We have the rectangular surfaces ABCD, DCFG and ADGH share the common vertex D. Let us assign
\[\begin{align}
& AB=HE=GF=CD=l \\
& AD=BC=EF=GH=b \\
& AH=GD=BE=CF=h \\
\end{align}\]
We are given the question that the areas of three adjacent faces of a rectangular box which meet in a point are known. The rectangular face is the product of its different sides. So the areas of three adjacent faces are
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Area of }ABCD=AB\times BC=l\times b=lb \\
& \text{Area of }DCFG=DC\times GD=h\times l=hl \\
& \text{Area of }ADGH=GH\times GD=l\times b=lb \\
\end{align}\]
So the product surface areas of the three adjacent faces is
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD \\
& =lb\times bh\times hl={{l}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}={{\left( lbh \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
.We use value for equation (1) and have;
\[\text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD={{\left( lbh \right)}^{2}}={{V}^{2}}\]
The product of these areas is equal to the square of the volume.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: A cube is cuboid with all sides of equal length which means $l=b=h=a$ and unlike the areas of the faces of a cuboid , the areas of faces of the cube are equal. The total surface area of the rectangular box will be $2\left( lb+bh+hl \right)$and length of the space diagonal will be $\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$.The total surface of cube is $6{{a}^{2}}$ and the volume is ${{a}^{3}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that a cuboid is a three dimensional object with six rectangular faces joined by 8 vertices. It has three different types of sides called length, breadth and height denoted $l,$$b$ and $h$. \[\]
The amount of space contained by a three dimensional object is measured by the quantity called volume. The amount of space that is occupied by a cuboid is the product of length, breadth and height. Mathematically, volume denoted as $V$of a cuboid is
\[V=l\times b\times h=lbh....\left( 1 \right)\]

Let us denote the vertices of the cuboid as A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H. We are going to call two rectangular surfaces adjacent when they share a common vertex. We have the rectangular surfaces ABCD, DCFG and ADGH share the common vertex D. Let us assign
\[\begin{align}
& AB=HE=GF=CD=l \\
& AD=BC=EF=GH=b \\
& AH=GD=BE=CF=h \\
\end{align}\]
We are given the question that the areas of three adjacent faces of a rectangular box which meet in a point are known. The rectangular face is the product of its different sides. So the areas of three adjacent faces are
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Area of }ABCD=AB\times BC=l\times b=lb \\
& \text{Area of }DCFG=DC\times GD=h\times l=hl \\
& \text{Area of }ADGH=GH\times GD=l\times b=lb \\
\end{align}\]
So the product surface areas of the three adjacent faces is
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD \\
& =lb\times bh\times hl={{l}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}={{\left( lbh \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
.We use value for equation (1) and have;
\[\text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD\times \text{Area of }ABCD={{\left( lbh \right)}^{2}}={{V}^{2}}\]
The product of these areas is equal to the square of the volume.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: A cube is cuboid with all sides of equal length which means $l=b=h=a$ and unlike the areas of the faces of a cuboid , the areas of faces of the cube are equal. The total surface area of the rectangular box will be $2\left( lb+bh+hl \right)$and length of the space diagonal will be $\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$.The total surface of cube is $6{{a}^{2}}$ and the volume is ${{a}^{3}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




