
The area of the triangle with the vertices A \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] , B \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] , and C \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] is
(A) 14
(B) 28
(C) 8
(D) 6
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: First of all, plot the vertices of the \[\Delta ABC\] in XY plane. Now, draw a line from the vertex C to meet at point D which is perpendicular to the base AB and mark its coordinates on the XY plane. Now, using the distance formula get the lengths of the base AB and the perpendicular CD. Then put the lengths of the base AB and the perpendicular CD in the formula of the area of a triangle, \[\text{Area=}\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{length of the perpendicular}\] and solve it further.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, it is given that we have the coordinates of the three vertices of the triangle.
The coordinate of the vertex A = \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] …………………………(1)
The coordinate of the vertex B = \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] …………………………(2)
The coordinate of the vertex C = \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] …………………………(3)
We have to find the area of this triangle.
Plotting the coordinates of these vertex in the XY plane we get,
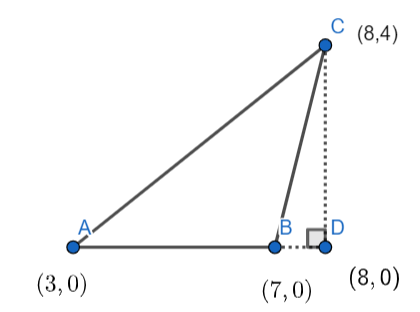
We have \[\Delta ABC\] in which the points A, B, and C are the vertex and the line CD is perpendicular to the line AD. The base AB of \[\Delta ABC\] is a part of the line AD.
Since the perpendicular is drawn from the point C and it is touching the base AB at point D and the base AB is lying on the x-axis. So, the x coordinate of point D will be the same as of the x-coordinate of point C. As the point D is on the x-axis, the y-coordinate of point D is equal to 0.
The coordinate of the point D = \[\left( 8,0 \right)\] ………………………….(4)
Since CD is perpendicular to AD, so CD is also perpendicular to the base AB of the \[\Delta ABC\] .
From equation (3) and equation (4), we have the coordinates of the point C and point D.
The coordinate of the vertex C = \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the point D = \[\left( 8,0 \right)\] .
Now, using distance formula and the coordinates of the points C and D to find the length of the perpendicular CD.
\[\text{Distance=}\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
The coordinate of the vertex C = \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the point D = \[\left( 8,0 \right)\] .
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow CD=\sqrt{{{\left( 8-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4-0 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow CD=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow CD=\sqrt{{{4}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow CD=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have the length of the perpendicular CD which is equal to 4 units.
From equation (1) and equation (2), we have the coordinates of point A and point B.
The coordinate of the vertex A = \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the vertex B = \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] .
Now, using distance formula and the coordinates of the points A and B to find the length of the perpendicular AB.
\[\text{Distance=}\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
The coordinate of the vertex A = \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the vertex B = \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] .
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{\left( 3-7 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{\left( -4 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{16} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have the length of the base AB which is equal to 4 units.
In \[\Delta ABC\] , we have
The base AB = 4 units.
The length of the perpendicular = 4 units.
We know the formula of the area of a triangle, \[\text{Area=}\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{length of the perpendicular}\] .
Now, putting the value of the base and length of the perpendicular in the formula, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Area=}\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{length of the perpendicular} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Area=}\dfrac{1}{2}\times 4\times 4 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Area=}8 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the area of the triangle \[\Delta ABC\] is \[8\,\text{uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\] .
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: We can also solve this question using a determinant method.
We know the formula, the area of the triangle having vertex \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] , \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] , and \[\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)\] ,
\[Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left| \begin{align}
& \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{1}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{2}} & {{y}_{2}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{3}} & {{y}_{3}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
\end{align} \right|\] …………………..(1)
We have to find the area of the triangle with the vertices A \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] , B \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] , and C \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] .
Replacing \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] by \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] , \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] by \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] , and \[\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)\] by \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] in equation (1), we get
\[Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left| \begin{align}
& \begin{matrix}
3 & 0 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
7 & 0 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
8 & 4 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
\end{align} \right|\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 3\left\{ 0\left( 1 \right)-4\left( 1 \right) \right\}-0\left\{ 7\left( 1 \right)-8\left( 1 \right) \right\}+1\left\{ 7\left( 4 \right)-0\left( 8 \right) \right\} \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 3\left\{ -4 \right\}-0\left\{ -1 \right\}+1\left\{ 28 \right\} \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ -12-0+28 \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ -12+28 \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 16\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=8\]
Therefore, the area of the triangle \[\Delta ABC\] is 8.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, it is given that we have the coordinates of the three vertices of the triangle.
The coordinate of the vertex A = \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] …………………………(1)
The coordinate of the vertex B = \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] …………………………(2)
The coordinate of the vertex C = \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] …………………………(3)
We have to find the area of this triangle.
Plotting the coordinates of these vertex in the XY plane we get,

We have \[\Delta ABC\] in which the points A, B, and C are the vertex and the line CD is perpendicular to the line AD. The base AB of \[\Delta ABC\] is a part of the line AD.
Since the perpendicular is drawn from the point C and it is touching the base AB at point D and the base AB is lying on the x-axis. So, the x coordinate of point D will be the same as of the x-coordinate of point C. As the point D is on the x-axis, the y-coordinate of point D is equal to 0.
The coordinate of the point D = \[\left( 8,0 \right)\] ………………………….(4)
Since CD is perpendicular to AD, so CD is also perpendicular to the base AB of the \[\Delta ABC\] .
From equation (3) and equation (4), we have the coordinates of the point C and point D.
The coordinate of the vertex C = \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the point D = \[\left( 8,0 \right)\] .
Now, using distance formula and the coordinates of the points C and D to find the length of the perpendicular CD.
\[\text{Distance=}\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
The coordinate of the vertex C = \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the point D = \[\left( 8,0 \right)\] .
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow CD=\sqrt{{{\left( 8-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4-0 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow CD=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow CD=\sqrt{{{4}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow CD=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have the length of the perpendicular CD which is equal to 4 units.
From equation (1) and equation (2), we have the coordinates of point A and point B.
The coordinate of the vertex A = \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the vertex B = \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] .
Now, using distance formula and the coordinates of the points A and B to find the length of the perpendicular AB.
\[\text{Distance=}\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
The coordinate of the vertex A = \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] .
The coordinate of the vertex B = \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] .
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{\left( 3-7 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{\left( -4 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{16} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have the length of the base AB which is equal to 4 units.
In \[\Delta ABC\] , we have
The base AB = 4 units.
The length of the perpendicular = 4 units.
We know the formula of the area of a triangle, \[\text{Area=}\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{length of the perpendicular}\] .
Now, putting the value of the base and length of the perpendicular in the formula, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Area=}\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{length of the perpendicular} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Area=}\dfrac{1}{2}\times 4\times 4 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Area=}8 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the area of the triangle \[\Delta ABC\] is \[8\,\text{uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\] .
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: We can also solve this question using a determinant method.
We know the formula, the area of the triangle having vertex \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] , \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] , and \[\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)\] ,
\[Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left| \begin{align}
& \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{1}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{2}} & {{y}_{2}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{3}} & {{y}_{3}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
\end{align} \right|\] …………………..(1)
We have to find the area of the triangle with the vertices A \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] , B \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] , and C \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] .
Replacing \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] by \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] , \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] by \[\left( 7,0 \right)\] , and \[\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)\] by \[\left( 8,4 \right)\] in equation (1), we get
\[Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left| \begin{align}
& \begin{matrix}
3 & 0 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
7 & 0 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
8 & 4 & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \\
\end{align} \right|\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 3\left\{ 0\left( 1 \right)-4\left( 1 \right) \right\}-0\left\{ 7\left( 1 \right)-8\left( 1 \right) \right\}+1\left\{ 7\left( 4 \right)-0\left( 8 \right) \right\} \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ 3\left\{ -4 \right\}-0\left\{ -1 \right\}+1\left\{ 28 \right\} \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ -12-0+28 \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left[ -12+28 \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 16\]
\[\Rightarrow Area=8\]
Therefore, the area of the triangle \[\Delta ABC\] is 8.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




