
The angular shape of ozone molecule \[\left( {{O_3}} \right)\] consists of:
A. $1$ sigma and $2$ pi bonds
B. $2$ sigma and $2$ pi bonds
C. $1$ sigma and $1$ pi bonds
D. $2$ sigma and $1$ pi bonds
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, we must first understand some basic concepts about ozone and its structure. Then we need to assess the properties of bonding between the atoms of the ozone molecule and then only we can conclude the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts:
Ozone: Ozone or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula \[\left( {{O_3}} \right)\] . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope \[{O_2}\] , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to \[{O_2}\] (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Step 1: Structure of Ozone:
Ozone is a bent molecule, with ${C_{2V}}$ symmetry (similar to the water molecule). The central atom is hybridized with one lone pair. Ozone is a polar molecule with a dipole moment of \[0.53{\text{ }}D\] . The molecule can be represented as a resonance hybrid with two contributing structures, each with a single bond on one side and double bond on the other. The arrangement possesses an overall bond order of \[1.5\] for both sides.
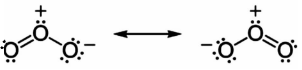
Step 2: From the above structure, we can clearly conclude that there is a double bond (which means $1$ sigma and $1$ pi bond) and a single bond (which means $1$ sigma bond). And hence overall there are $2$ sigma and pi bonds in the structure.
So, clearly we can conclude that the correct answer is Option D.
Note:Multiple studies have been conducted to determine the mechanism behind ozone's harmful effects, particularly in the lungs. These studies have shown that exposure to ozone causes changes in the immune response within the lung tissue, resulting in disruption of both the innate and adaptive immune response, as well as altering the protective function of lung epithelial cells.
Complete step-by-step answer:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts:
Ozone: Ozone or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula \[\left( {{O_3}} \right)\] . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope \[{O_2}\] , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to \[{O_2}\] (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Step 1: Structure of Ozone:
Ozone is a bent molecule, with ${C_{2V}}$ symmetry (similar to the water molecule). The central atom is hybridized with one lone pair. Ozone is a polar molecule with a dipole moment of \[0.53{\text{ }}D\] . The molecule can be represented as a resonance hybrid with two contributing structures, each with a single bond on one side and double bond on the other. The arrangement possesses an overall bond order of \[1.5\] for both sides.

Step 2: From the above structure, we can clearly conclude that there is a double bond (which means $1$ sigma and $1$ pi bond) and a single bond (which means $1$ sigma bond). And hence overall there are $2$ sigma and pi bonds in the structure.
So, clearly we can conclude that the correct answer is Option D.
Note:Multiple studies have been conducted to determine the mechanism behind ozone's harmful effects, particularly in the lungs. These studies have shown that exposure to ozone causes changes in the immune response within the lung tissue, resulting in disruption of both the innate and adaptive immune response, as well as altering the protective function of lung epithelial cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




