
The angles of a triangle are in A.P and the least angle is \[{{30}^{o}}\]. What is the greatest angle (in radian)?
(a) \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
(b) \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
(c) \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]
(d) \[\pi \]
Answer
625.8k+ views
Hint: First of all, we know that the general terms of A.P are like a, a + d, a + 2d…..So, first, assume the angles of the triangle as \[{{30}^{o}},\text{ }{{30}^{o}}+d,\text{ }{{30}^{o}}+2d\]. Equate the sum of these angles to \[{{180}^{o}}\] and get the value of d. Use the value of d to find the greatest angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that the angles of the triangle are in A.P and the least angle is \[{{30}^{o}}\]. We have to find the greatest angle (in radian). Let us first see what arithmetic progression is. Arithmetic Progression (A.P) is a sequence of numbers so that the difference of any two successive numbers is a constant value. For example, the series of natural numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6…. are in A.P with the first term as 1 and common difference as 1. Also, the nth term of A.P is \[{{a}_{n}}=a+\left( n-1 \right)d\] where ‘a’ is the first term, and ‘d’ is the common difference.
So, we know that the general terms of any arithmetic progression (A.P) are in the form a, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d…….Here, ‘a’ is the first term and ‘d’ is the common difference of A.P. We are given that the least angle of the triangle is \[{{30}^{o}}\] and all three angles are in A.P. So, let us assume the other two angles as \[{{30}^{o}}+d\] and \[{{30}^{o}}+2d\]. So, we get 3 angles of the triangle as, \[{{30}^{o}},\text{ }{{30}^{o}}+d,\text{ }{{30}^{o}}+2d\]
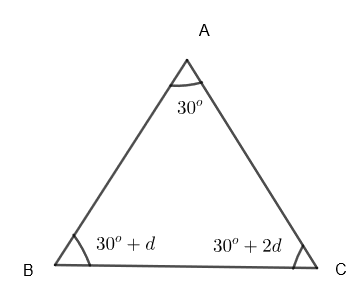
Also, we know that in any triangle, the sum of each of the angles is \[{{180}^{o}}\]. So, we get, \[\angle A+\angle B+\angle C={{180}^{o}}\]
By substituting the values of \[\angle A,\text{ }\angle B\text{ and }\angle C\], we get, \[{{90}^{o}}+3d={{180}^{o}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3d={{180}^{o}}-{{90}^{o}}\]
\[3d={{90}^{o}}\]
By dividing 3 on both the sides, we get, \[d=\dfrac{{{90}^{0}}}{3}={{30}^{o}}\]
So, we get 3 angles of the triangle as,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle A={{30}^{o}} \\
& \angle B={{30}^{o}}+d={{30}^{o}}+{{30}^{o}}={{60}^{o}} \\
& \angle C={{30}^{o}}+2d={{30}^{o}}+2\left( {{30}^{o}} \right)={{90}^{o}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the greatest angle as \[{{90}^{o}}\]. To get this angle in radian, we will multiply it with \[\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{o}}}\]. So, we get,
Greatest Angle \[={{90}^{o}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{o}}}=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Hence, option (a) is the right answer.
Note: In this question, students often take three angles in the arithmetic progression (A.P) as \[\left( {{30}^{o}}-d \right),{{30}^{o}},\left( {{30}^{o}}+d \right)\] but this is wrong because it is given in the question that the least angle is \[{{30}^{o}}\]. So we must start writing the terms with \[{{30}^{o}}\]. Also, the sum of all the angles of the triangle is \[{{180}^{o}}\], but in the above case, as we can see that \[\left( {{30}^{o}}-d \right)+\left( {{30}^{o}} \right)+\left( {{30}^{o}}+d \right)={{90}^{o}}\] which is incorrect. So, this point must be taken care of and take the 3 angles in A.P as \[\left( {{30}^{o}} \right),\left( {{30}^{o}}+d \right)\text{ and }\left( {{30}^{o}}+2d \right)\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that the angles of the triangle are in A.P and the least angle is \[{{30}^{o}}\]. We have to find the greatest angle (in radian). Let us first see what arithmetic progression is. Arithmetic Progression (A.P) is a sequence of numbers so that the difference of any two successive numbers is a constant value. For example, the series of natural numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6…. are in A.P with the first term as 1 and common difference as 1. Also, the nth term of A.P is \[{{a}_{n}}=a+\left( n-1 \right)d\] where ‘a’ is the first term, and ‘d’ is the common difference.
So, we know that the general terms of any arithmetic progression (A.P) are in the form a, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d…….Here, ‘a’ is the first term and ‘d’ is the common difference of A.P. We are given that the least angle of the triangle is \[{{30}^{o}}\] and all three angles are in A.P. So, let us assume the other two angles as \[{{30}^{o}}+d\] and \[{{30}^{o}}+2d\]. So, we get 3 angles of the triangle as, \[{{30}^{o}},\text{ }{{30}^{o}}+d,\text{ }{{30}^{o}}+2d\]

Also, we know that in any triangle, the sum of each of the angles is \[{{180}^{o}}\]. So, we get, \[\angle A+\angle B+\angle C={{180}^{o}}\]
By substituting the values of \[\angle A,\text{ }\angle B\text{ and }\angle C\], we get, \[{{90}^{o}}+3d={{180}^{o}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3d={{180}^{o}}-{{90}^{o}}\]
\[3d={{90}^{o}}\]
By dividing 3 on both the sides, we get, \[d=\dfrac{{{90}^{0}}}{3}={{30}^{o}}\]
So, we get 3 angles of the triangle as,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle A={{30}^{o}} \\
& \angle B={{30}^{o}}+d={{30}^{o}}+{{30}^{o}}={{60}^{o}} \\
& \angle C={{30}^{o}}+2d={{30}^{o}}+2\left( {{30}^{o}} \right)={{90}^{o}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the greatest angle as \[{{90}^{o}}\]. To get this angle in radian, we will multiply it with \[\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{o}}}\]. So, we get,
Greatest Angle \[={{90}^{o}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{o}}}=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Hence, option (a) is the right answer.
Note: In this question, students often take three angles in the arithmetic progression (A.P) as \[\left( {{30}^{o}}-d \right),{{30}^{o}},\left( {{30}^{o}}+d \right)\] but this is wrong because it is given in the question that the least angle is \[{{30}^{o}}\]. So we must start writing the terms with \[{{30}^{o}}\]. Also, the sum of all the angles of the triangle is \[{{180}^{o}}\], but in the above case, as we can see that \[\left( {{30}^{o}}-d \right)+\left( {{30}^{o}} \right)+\left( {{30}^{o}}+d \right)={{90}^{o}}\] which is incorrect. So, this point must be taken care of and take the 3 angles in A.P as \[\left( {{30}^{o}} \right),\left( {{30}^{o}}+d \right)\text{ and }\left( {{30}^{o}}+2d \right)\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




