
The angle of incidence at which reflected light is totally polarized for reflection from air to glass (refractive index n), is:
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. }}{\sin ^{ - 1}}n \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. }}{\sin ^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{1}{n}) \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. ta}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{1}{n}) \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. ta}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}(n) \\
$

Answer
613.8k+ views
Hint: Find Brewster’s angle to get the required angle of incidence.
Formula used: Brewster’s angle for a material of refractive index $\mu $ is:
$\tan \theta = \mu $
Complete step-by-step solution -
Electromagnetic waves consist of electric field vectors and magnetic field vectors. These vectors are randomly oriented in any direction. Now, polarization is the phenomenon in which these randomly oriented field vectors get oriented in just one direction.
Polarization shows that a wave’s oscillations can have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave.
Polarization can occur either by reflection or by refraction.
When light strikes an interface such that there is $90^o$ between the reflected and refracted rays, the reflected portion of the light will be linearly polarized. The direction of polarization will be parallel to the plane of the interface.
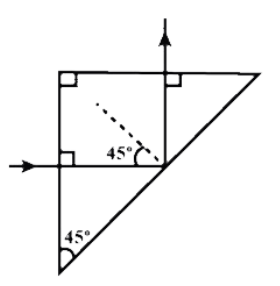
That particular angle of incidence producing a $90^o$ angle between the reflected and refracted ray is termed Brewster's angle.
As in the question, in the figure the angle shown is 450, it implies that the other angle is also 450 (from the law of reflection), and so the angle formed between the reflected and the refracted ray is a right angle. So, the polarization of the reflected portion occurs, and therefore, we can use Brewster’s angle to calculate the refractive index of the medium.
As refractive index here is n:
So,
$
\tan \theta = n \\
\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}(n) \\
$
The correct option is (C).
Note: To do this question, it was important to know the concept of polarization by reflection and use of Brewster’s angle.
Formula used: Brewster’s angle for a material of refractive index $\mu $ is:
$\tan \theta = \mu $
Complete step-by-step solution -
Electromagnetic waves consist of electric field vectors and magnetic field vectors. These vectors are randomly oriented in any direction. Now, polarization is the phenomenon in which these randomly oriented field vectors get oriented in just one direction.
Polarization shows that a wave’s oscillations can have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave.
Polarization can occur either by reflection or by refraction.
When light strikes an interface such that there is $90^o$ between the reflected and refracted rays, the reflected portion of the light will be linearly polarized. The direction of polarization will be parallel to the plane of the interface.
That particular angle of incidence producing a $90^o$ angle between the reflected and refracted ray is termed Brewster's angle.
As in the question, in the figure the angle shown is 450, it implies that the other angle is also 450 (from the law of reflection), and so the angle formed between the reflected and the refracted ray is a right angle. So, the polarization of the reflected portion occurs, and therefore, we can use Brewster’s angle to calculate the refractive index of the medium.
As refractive index here is n:
So,
$
\tan \theta = n \\
\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}(n) \\
$
The correct option is (C).
Note: To do this question, it was important to know the concept of polarization by reflection and use of Brewster’s angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




