
The angle of elevation of the top of a vertical tower AB from a point X on the ground is $60{}^\circ $ . At a point Y, 40m vertically above X, the angle of elevation of the top is $45{}^\circ $ . Calculate the height of the tower.
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint: First draw a rough diagram of the given conditions. Now, assume that the height of the pole is ‘h’ and its distance from the tower is ‘d’. Form two equations in ‘h’ and ‘d’ using the information provided and solve these two equations to get the value of ‘h’ and ‘d’. Use $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{base}}$ to form the equations in the right angle triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume that X is the bottom of the pole and Y is the top of the pole. It is given that the top of the tower is denoted by B and bottom as A. So, let us draw the diagram of the given situation.
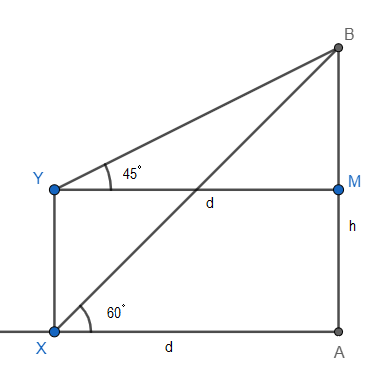
From the above figure, we have,
In right angle triangle XAB,
AX = d, AB = h
\[\angle AXB=60{}^\circ \]
Therefore, using $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{base}}$, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{AB}{AX} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{h}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow h=d\tan 60{}^\circ ........................(i) \\
\end{align}$
Now, in right angle triangle BYM,
YM = AX = d, as they are the opposite sides of the rectangle PAMQ.
BM = AB – AM = h-AM , because it is given that the height of the tower is h m and here we have assumed the tower as AB.
Also, \[\angle BYM=45{}^\circ \] , as from the figure we can see that angle of depression of the top of the pole are alternate interior angles, and alternate interior angles are equal.
Therefore, using $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{base}}$, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{BM}{YM} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{h-AM}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow h-AM=d\tan 45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow h=d\tan 45{}^\circ +AM$
From equations (i) and (ii) we get,
$d\tan 60{}^\circ =d\tan 45{}^\circ +AM$
We know that $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}\text{ and tan45}{}^\circ \text{=1}$ .
$\therefore \sqrt{3}d=d+AM$
As AMXY is a rectangle. AM=XY=40
$\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)d=40$
$\Rightarrow d=\dfrac{40}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)}$
Substituting the value of d in equation (i), we get,
$h=\dfrac{40}{\sqrt{3}-1}\tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{40\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}$
Therefore, the height of the tower is $\dfrac{40\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}meters$ .
Note: We must substitute and eliminate the variables properly otherwise we may get confused while solving the equations. Here, in the above question we have used the tangent of the given angle because we have to find both, height of the tower and its distance from the post. So, the function relating these two variables is tangent of the angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume that X is the bottom of the pole and Y is the top of the pole. It is given that the top of the tower is denoted by B and bottom as A. So, let us draw the diagram of the given situation.

From the above figure, we have,
In right angle triangle XAB,
AX = d, AB = h
\[\angle AXB=60{}^\circ \]
Therefore, using $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{base}}$, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{AB}{AX} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{h}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow h=d\tan 60{}^\circ ........................(i) \\
\end{align}$
Now, in right angle triangle BYM,
YM = AX = d, as they are the opposite sides of the rectangle PAMQ.
BM = AB – AM = h-AM , because it is given that the height of the tower is h m and here we have assumed the tower as AB.
Also, \[\angle BYM=45{}^\circ \] , as from the figure we can see that angle of depression of the top of the pole are alternate interior angles, and alternate interior angles are equal.
Therefore, using $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{base}}$, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{BM}{YM} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{h-AM}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow h-AM=d\tan 45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow h=d\tan 45{}^\circ +AM$
From equations (i) and (ii) we get,
$d\tan 60{}^\circ =d\tan 45{}^\circ +AM$
We know that $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}\text{ and tan45}{}^\circ \text{=1}$ .
$\therefore \sqrt{3}d=d+AM$
As AMXY is a rectangle. AM=XY=40
$\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)d=40$
$\Rightarrow d=\dfrac{40}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)}$
Substituting the value of d in equation (i), we get,
$h=\dfrac{40}{\sqrt{3}-1}\tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{40\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}$
Therefore, the height of the tower is $\dfrac{40\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}meters$ .
Note: We must substitute and eliminate the variables properly otherwise we may get confused while solving the equations. Here, in the above question we have used the tangent of the given angle because we have to find both, height of the tower and its distance from the post. So, the function relating these two variables is tangent of the angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




