
The adjoining figure represents a solid consisting of a cylinder mounted by a cone at one end and a hemisphere at the other end. Given that: common radius \[3.5\]cm, the height of the cylinder \[6.5\]cm and the total height \[12.8\]cm, calculate the volume of the solid? [Correct up to the nearest integer]
A. \[380{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
B. \[375{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
C. \[{\text{3750 }}c{m^3}\]
D. Does not exist
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: The given problem revolves around the concepts of ‘mensuration’ finding the desired measurement of solid geometries such as cylinder, cone, hemisphere, etc. First of all, draw the rough diagram from the given concept. Hence, calculating the remaining (required) values from the given parameters, and then substituting these values in the formula for the respective geometry like cylinder, hemisphere, cone, etc. i.e. \[\pi {r^2}h\], \[\dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\] respectively. As a result, finding the total volume of the entire solid, adding up all the volumes calculated individually, the desired volume is obtained.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, the given adjoining figure represents the solid which consists of three different geometric figures that are ‘Cylinder’, ‘Cone’ and ‘Hemisphere’ respectively.
Given that: common radius that is equal in all cases, \[r = 3.5{\text{ }}cm\],
Height of cylinder, \[h = 6.5{\text{ }}cm\],
Total height of the solid is \[ = 12.8{\text{ }}cm\]
\[\therefore \]Height of the cone \[ = \] Total height of the solid \[ - \] height of the cylinder \[ - \] height of hemisphere \[ = 12.8 - 6.5 - 3.5 = 2.8{\text{ }}cm\] … (\[\because \] height of hemisphere \[ = \] radius of hemisphere)
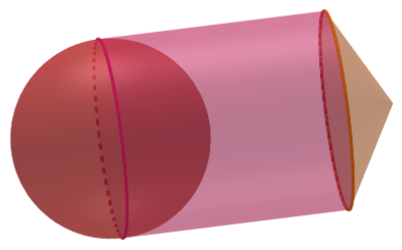
Drawing the rough figure for the given solid (here, we have taken the full sphere where the hemisphere is the half part of the sphere where it is shown on the outer side and other part inscribed in the cylinder, therefore we have considered the term ‘hemisphere’)
As a result, we have to calculate the entire volume of the above solid.
Since, as it consists of three different sections or solids particularly calculating the volume individually for the three different geometric solids
Hence, we have
Volume of hemisphere\[ = \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}\]
As a result, substituting the given values calculated above, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of hemisphere\[ = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( {3.5} \right)^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of hemisphere\[ = \dfrac{{44}}{{21}} \times 42.875\]
Hence, the required volume of the hemisphere is
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of hemisphere\[ = 89.8333{\text{ }}c{m^3}\] … (i)
Similarly,
Finding the volume for remaining two solid geometries that is ‘cylinder’ and ‘cone’, we get
Volume of cylinder\[ = \pi {r^2}h\]
As a result, substituting the given values calculated above, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cylinder \[ = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( {3.5} \right)^2} \times 6.5\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cylinder\[ = 20.4286 \times 12.25\]
Hence, the required volume of the cylinder is
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cylinder\[ = 250.2504{\text{ }}c{m^3}\] … (ii)
And,
Volume of cone\[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\]
As a result, substituting the given values calculated above, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( {3.5} \right)^2} \times 2.8\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cone \[ = 7.3333 \times 12.25 \times 0.4\]
Hence, the required volume of the cone is
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cone \[ = 35.9332{\text{ }}c{m^3}\] … (iii)
Now,
From (i), (ii) and (iii)
Total Volume of the solid \[ = \] Volume of hemisphere \[ + \] Volume of cylinder \[ + \] Volume of cone
Hence, substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total Volume of the solid \[ = 89.8333{\text{ }}c{m^3} + 250.2504{\text{ }}c{m^3} + 35.9332{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total Volume of the solid \[ = 376.0169{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
As a result, bearing the nearest that is approximate value of \[376.0169\] that is equal to \[375\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total Volume of the solid \[ = 375{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Remember as per as the calculations for mensuration is concerned be sure to consider the decimals up to four digits (while rounding-off the value add one to the left hand side of decimal if it exists the number/digit greater than five). Also, calculating the required parameters individually will ensure the required value/solution to the absolute answer. Consideration of the value of \[\pi \] that is \[\dfrac{{22}}{7}{\text{ or }}3.14\] matters, so as to be sure of our final answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, the given adjoining figure represents the solid which consists of three different geometric figures that are ‘Cylinder’, ‘Cone’ and ‘Hemisphere’ respectively.
Given that: common radius that is equal in all cases, \[r = 3.5{\text{ }}cm\],
Height of cylinder, \[h = 6.5{\text{ }}cm\],
Total height of the solid is \[ = 12.8{\text{ }}cm\]
\[\therefore \]Height of the cone \[ = \] Total height of the solid \[ - \] height of the cylinder \[ - \] height of hemisphere \[ = 12.8 - 6.5 - 3.5 = 2.8{\text{ }}cm\] … (\[\because \] height of hemisphere \[ = \] radius of hemisphere)

Drawing the rough figure for the given solid (here, we have taken the full sphere where the hemisphere is the half part of the sphere where it is shown on the outer side and other part inscribed in the cylinder, therefore we have considered the term ‘hemisphere’)
As a result, we have to calculate the entire volume of the above solid.
Since, as it consists of three different sections or solids particularly calculating the volume individually for the three different geometric solids
Hence, we have
Volume of hemisphere\[ = \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}\]
As a result, substituting the given values calculated above, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of hemisphere\[ = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( {3.5} \right)^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of hemisphere\[ = \dfrac{{44}}{{21}} \times 42.875\]
Hence, the required volume of the hemisphere is
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of hemisphere\[ = 89.8333{\text{ }}c{m^3}\] … (i)
Similarly,
Finding the volume for remaining two solid geometries that is ‘cylinder’ and ‘cone’, we get
Volume of cylinder\[ = \pi {r^2}h\]
As a result, substituting the given values calculated above, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cylinder \[ = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( {3.5} \right)^2} \times 6.5\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cylinder\[ = 20.4286 \times 12.25\]
Hence, the required volume of the cylinder is
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cylinder\[ = 250.2504{\text{ }}c{m^3}\] … (ii)
And,
Volume of cone\[ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\]
As a result, substituting the given values calculated above, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cone \[ = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times {\left( {3.5} \right)^2} \times 2.8\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cone \[ = 7.3333 \times 12.25 \times 0.4\]
Hence, the required volume of the cone is
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of cone \[ = 35.9332{\text{ }}c{m^3}\] … (iii)
Now,
From (i), (ii) and (iii)
Total Volume of the solid \[ = \] Volume of hemisphere \[ + \] Volume of cylinder \[ + \] Volume of cone
Hence, substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total Volume of the solid \[ = 89.8333{\text{ }}c{m^3} + 250.2504{\text{ }}c{m^3} + 35.9332{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total Volume of the solid \[ = 376.0169{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
As a result, bearing the nearest that is approximate value of \[376.0169\] that is equal to \[375\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total Volume of the solid \[ = 375{\text{ }}c{m^3}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Remember as per as the calculations for mensuration is concerned be sure to consider the decimals up to four digits (while rounding-off the value add one to the left hand side of decimal if it exists the number/digit greater than five). Also, calculating the required parameters individually will ensure the required value/solution to the absolute answer. Consideration of the value of \[\pi \] that is \[\dfrac{{22}}{7}{\text{ or }}3.14\] matters, so as to be sure of our final answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




