
The absolute configuration of:
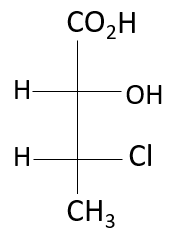
(1) (2R, 3R)
(2) (2R, 3S)
(3) (2S, 3R)
(4) (2S, R)

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint:When we move in a clockwise direction, it is called R configuration, and when we move in an anti-clockwise direction, it is called an S configuration. The letter R is Rectus and the S is Sinister..
Complete step by step answer:
The Atomic number is given the priority for selecting the direction, and hence the rotation. After numbering the compound
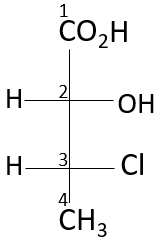
Here, the 2nd position and the 3rd carbon atom of this compound have chiral centers, looking at the third position, the highest atomic number containing atom in the compound is the chlorine atom (17), followed by the carbon (8), methyl group (8) and hydrogen (1). It is an anti-clockwise rotation, according to the rule, but the 4th priority is on the horizontal line, hence it is R configuration. Looking at the 2nd position, the hydroxyl group is given the most priority, followed by chlorine, carboxylic, and hydrogen. Due to the 4th priority being on the horizontal it is S configuration. Hence, the configuration at the second chiral position is S and at the third chiral position is R.
Thus, the absolute configuration of: 2-hydroxy-3- chloro butanoic acid is option (C), (2S, 3R).
Note:
The absolute configuration of chiral compounds was obtained after 1951. If a compound does not possess a chiral center, it does not show absolute configuration. The compounds such as (+) isoserine, (+) glyceraldehyde show absolute configuration. Alternative techniques are optical rotatory dispersion, vibrational circular dichroism, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, use of chiral shift reagents in proton NMR, and Coulomb explosion imaging.
Complete step by step answer:
The Atomic number is given the priority for selecting the direction, and hence the rotation. After numbering the compound

Here, the 2nd position and the 3rd carbon atom of this compound have chiral centers, looking at the third position, the highest atomic number containing atom in the compound is the chlorine atom (17), followed by the carbon (8), methyl group (8) and hydrogen (1). It is an anti-clockwise rotation, according to the rule, but the 4th priority is on the horizontal line, hence it is R configuration. Looking at the 2nd position, the hydroxyl group is given the most priority, followed by chlorine, carboxylic, and hydrogen. Due to the 4th priority being on the horizontal it is S configuration. Hence, the configuration at the second chiral position is S and at the third chiral position is R.
Thus, the absolute configuration of: 2-hydroxy-3- chloro butanoic acid is option (C), (2S, 3R).
Note:
The absolute configuration of chiral compounds was obtained after 1951. If a compound does not possess a chiral center, it does not show absolute configuration. The compounds such as (+) isoserine, (+) glyceraldehyde show absolute configuration. Alternative techniques are optical rotatory dispersion, vibrational circular dichroism, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, use of chiral shift reagents in proton NMR, and Coulomb explosion imaging.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




