
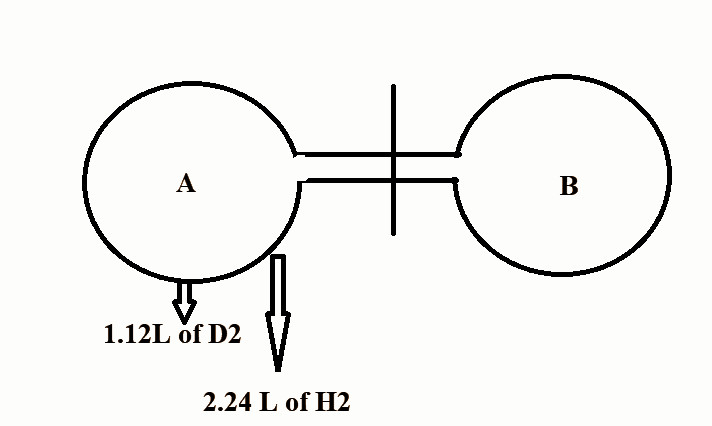
The above experiment is done at NTP. The stop cock is opened for a certain time and then closed. After effusion, the bulb A contains \[0.1{\text{g}}\] of \[{D_2}\] . Find out the number of moles of ${H_2}$ in bulb B.

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question you should know the concept of the ideal gas equation and Graham's law of diffusion. Use graham's law of diffusion to calculate the amount of gas diffused which can be used to calculate the leftover moles.
Formula used: ${\text{No}}{\text{. of moles = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Mass of the Substance in grams}}}}{{{\text{Molar mass of a Substance}}}}$
${\text{rate of effusion}} \propto \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{{\text{molar mass of gas}}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
In the question, we are given that the volume of \[{D_2}\] at NTP is \[1.12{\text{L}}\].
The number of moles of \[{D_2}\] will be $\dfrac{{1.12}}{{22.4}} = 0.05$ moles.
Now we can calculate the mass of \[{D_2}\] present
$ \Rightarrow 0.05 \times 4 = 0.2{\text{g}}$
Similarly, the mass of ${H_2}$ can be calculated to be \[0.1 \times 2 = 0.2{\text{g}}\]
After effusion bulb A contains \[{\text{0}}{\text{.1g}}\] of \[{D_2}\]
Therefore, the amount of \[{D_2}\] effused in bulb B is \[0.1{\text{g}}\].
According to Graham’s law:
${\text{rate of effusion}} \propto \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{{\text{molar mass of gas}}}}$
Therefore, the relation between rates and molar mass can be written as:
\[\dfrac{{{r_{{H_2}}}}}{{{r_{{D_2}}}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{M_{{D_2}}}}}{{{M_{{H_2}}}}}} = \dfrac{{{w_{{H_2}}}}}{{{w_{{D_2}}}}}\]
Substituting the appropriate values, we will get the value:
\[{w_{{H_{2}}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{4}{2}} \times 0.1 = 0.14{\text{g}}\]
This is the amount of ${H_2}$ in bulb B.
Now, the moles of ${H_2}$ will be \[\dfrac{{0.14}}{2} = 0.07\] moles.
Note: Make sure you remember that at conditions of high temperature and lower pressure, a real gas behaves like an ideal gas, because the potential energy due to intermolecular attractive forces becomes less significant compared with the particles’ kinetic energy, and the size of the molecules becomes less significant compared to the space between them. The five gas laws are:
1.Boyle’s Law establishes a relationship between the pressure and the volume of a gas.
2.Charles’s Law establishes a relationship between the volume occupied by a gas and the absolute temperature.
3.Gay-Lussac’s Law establishes a relationship between the pressure exerted by a gas on the walls of its container and the absolute temperature associated with the gas.
4.Avogadro’s Law establishes a relationship between the volume occupied by a gas and the amount of gaseous substance.
5.After combining these four aforementioned laws we arrive at the Combined Gas Law
Formula used: ${\text{No}}{\text{. of moles = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Mass of the Substance in grams}}}}{{{\text{Molar mass of a Substance}}}}$
${\text{rate of effusion}} \propto \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{{\text{molar mass of gas}}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
In the question, we are given that the volume of \[{D_2}\] at NTP is \[1.12{\text{L}}\].
The number of moles of \[{D_2}\] will be $\dfrac{{1.12}}{{22.4}} = 0.05$ moles.
Now we can calculate the mass of \[{D_2}\] present
$ \Rightarrow 0.05 \times 4 = 0.2{\text{g}}$
Similarly, the mass of ${H_2}$ can be calculated to be \[0.1 \times 2 = 0.2{\text{g}}\]
After effusion bulb A contains \[{\text{0}}{\text{.1g}}\] of \[{D_2}\]
Therefore, the amount of \[{D_2}\] effused in bulb B is \[0.1{\text{g}}\].
According to Graham’s law:
${\text{rate of effusion}} \propto \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{{\text{molar mass of gas}}}}$
Therefore, the relation between rates and molar mass can be written as:
\[\dfrac{{{r_{{H_2}}}}}{{{r_{{D_2}}}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{M_{{D_2}}}}}{{{M_{{H_2}}}}}} = \dfrac{{{w_{{H_2}}}}}{{{w_{{D_2}}}}}\]
Substituting the appropriate values, we will get the value:
\[{w_{{H_{2}}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{4}{2}} \times 0.1 = 0.14{\text{g}}\]
This is the amount of ${H_2}$ in bulb B.
Now, the moles of ${H_2}$ will be \[\dfrac{{0.14}}{2} = 0.07\] moles.
Note: Make sure you remember that at conditions of high temperature and lower pressure, a real gas behaves like an ideal gas, because the potential energy due to intermolecular attractive forces becomes less significant compared with the particles’ kinetic energy, and the size of the molecules becomes less significant compared to the space between them. The five gas laws are:
1.Boyle’s Law establishes a relationship between the pressure and the volume of a gas.
2.Charles’s Law establishes a relationship between the volume occupied by a gas and the absolute temperature.
3.Gay-Lussac’s Law establishes a relationship between the pressure exerted by a gas on the walls of its container and the absolute temperature associated with the gas.
4.Avogadro’s Law establishes a relationship between the volume occupied by a gas and the amount of gaseous substance.
5.After combining these four aforementioned laws we arrive at the Combined Gas Law
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




