
Tangents are drawn from the point $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ to the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ touching the ellipse at points A and B. The orthocentre of the $ \Delta PAB $ is
A. $ \left( 5,\dfrac{8}{7} \right) $
B. $ \left( \dfrac{7}{5},\dfrac{25}{8} \right) $
C. $ \left( \dfrac{11}{5},\dfrac{8}{5} \right) $
D. $ \left( \dfrac{8}{25},\dfrac{7}{5} \right) $
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:
We first describe the general condition of two tangents from a fixed point on an ellipse. We put the values for the point $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ to the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ . We get the equations of the tangents. These lines touch the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ at points A and B. we find the intersecting points. Then using the vertical line of AP, we find the y-coordinate of the orthocentre.
Complete step by step answer:
Tangents are drawn from the point $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ to the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ touching the ellipse at points A and B.
From a fixed point $ \left( m,n \right) $ in general two tangents can be drawn to an ellipse. The equation of pair of tangents drawn to the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is given by
$ \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{{{m}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{n}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{mx}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{ny}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)}^{2}} $ .
In symbol we write $ S{{S}_{1}}={{T}^{2}} $ , where \[S=\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right),{{S}_{1}}=\left( \dfrac{{{m}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{n}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right),T=\left( \dfrac{mx}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{ny}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)\].
For our given ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ and the point $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ , the pair of tangents will be
$ \begin{align}
& \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{4}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{3x}{9}+\dfrac{4y}{4}-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 4\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{x}{3}+y-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align} $
We solve the equations to get the lines
$ \begin{align}
& 4\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{x}{3}+y-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4{{x}^{2}}}{9}+{{y}^{2}}-4=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+{{y}^{2}}+1+\dfrac{2xy}{3}-2y-\dfrac{2x}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{9}-\dfrac{2xy}{3}+2y+\dfrac{2x}{3}-5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2xy+6y+2x-15=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x-3 \right)\left( x-2y+5 \right)=0 \\
\end{align} $
We have multiplication of two equations as 0.
So, the lines are $ \left( x-3 \right)=0;\left( x-2y+5 \right)=0 $ . These lines are the tangents.
These lines touch the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ at points A and B. We find the points.
For the line $ \left( x-3 \right)=0 $ , we have $ x=3 $ . Therefore, $ \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1\Rightarrow y=0 $ .
So, one point is $ A\equiv \left( 3,0 \right) $ .
For the line $ \left( x-2y+5 \right)=0 $ , we have $ x=2y-5 $ . Therefore,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\left( 2y-5 \right)}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow 25{{y}^{2}}-80y+64=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{80\pm \sqrt{{{80}^{2}}-4\times 25\times 64}}{2\times 25}=\dfrac{8}{5} \\
\end{align} $ .
Putting value of y, we get $ x=\dfrac{2\times 8}{5}-5=-\dfrac{9}{5} $
So, the other point is $ B\equiv \left( -\dfrac{9}{5},\dfrac{8}{5} \right) $ .
The points are $ \left( 3,0 \right) $ and $ \left( -\dfrac{9}{5},\dfrac{8}{5} \right) $ .
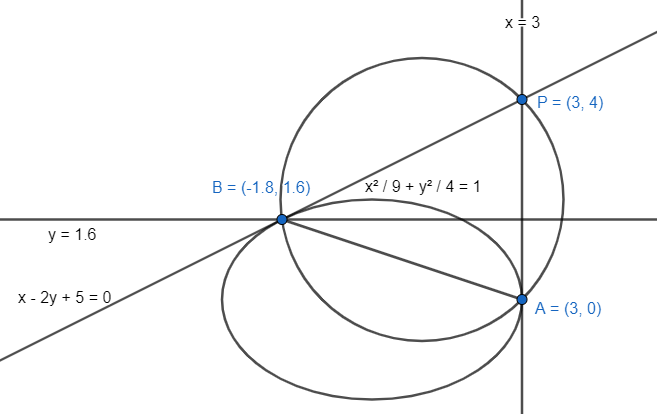
Now we find the orthocentre of the $ \Delta PAB $ .
As the line AP is vertical, the altitude through B is $ y=\dfrac{8}{5} $ . The orthocentre lies on the line $ y=\dfrac{8}{5} $ . The orthocentre of the $ \Delta PAB $ is $ \left( \dfrac{11}{5},\dfrac{8}{5} \right) $ as that is the only possible option of the given options.The correct option is C.
Note:
We need to remember that we can also solve this from the chord of contact points. We have the equation of chord of contact from the endpoints which are on the ellipse. We find the tangent equations from those points. Their intersecting point will be $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ . The orthocentre is the point where all the three altitudes of the triangle cut or intersect each other.
We first describe the general condition of two tangents from a fixed point on an ellipse. We put the values for the point $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ to the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ . We get the equations of the tangents. These lines touch the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ at points A and B. we find the intersecting points. Then using the vertical line of AP, we find the y-coordinate of the orthocentre.
Complete step by step answer:
Tangents are drawn from the point $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ to the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ touching the ellipse at points A and B.
From a fixed point $ \left( m,n \right) $ in general two tangents can be drawn to an ellipse. The equation of pair of tangents drawn to the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is given by
$ \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{{{m}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{n}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{mx}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{ny}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)}^{2}} $ .
In symbol we write $ S{{S}_{1}}={{T}^{2}} $ , where \[S=\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right),{{S}_{1}}=\left( \dfrac{{{m}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{n}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right),T=\left( \dfrac{mx}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{ny}{{{b}^{2}}}-1 \right)\].
For our given ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ and the point $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ , the pair of tangents will be
$ \begin{align}
& \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{4}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{3x}{9}+\dfrac{4y}{4}-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 4\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{x}{3}+y-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align} $
We solve the equations to get the lines
$ \begin{align}
& 4\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-1 \right)={{\left( \dfrac{x}{3}+y-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4{{x}^{2}}}{9}+{{y}^{2}}-4=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+{{y}^{2}}+1+\dfrac{2xy}{3}-2y-\dfrac{2x}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{9}-\dfrac{2xy}{3}+2y+\dfrac{2x}{3}-5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2xy+6y+2x-15=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x-3 \right)\left( x-2y+5 \right)=0 \\
\end{align} $
We have multiplication of two equations as 0.
So, the lines are $ \left( x-3 \right)=0;\left( x-2y+5 \right)=0 $ . These lines are the tangents.
These lines touch the ellipse $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 $ at points A and B. We find the points.
For the line $ \left( x-3 \right)=0 $ , we have $ x=3 $ . Therefore, $ \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1\Rightarrow y=0 $ .
So, one point is $ A\equiv \left( 3,0 \right) $ .
For the line $ \left( x-2y+5 \right)=0 $ , we have $ x=2y-5 $ . Therefore,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\left( 2y-5 \right)}^{2}}}{9}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow 25{{y}^{2}}-80y+64=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{80\pm \sqrt{{{80}^{2}}-4\times 25\times 64}}{2\times 25}=\dfrac{8}{5} \\
\end{align} $ .
Putting value of y, we get $ x=\dfrac{2\times 8}{5}-5=-\dfrac{9}{5} $
So, the other point is $ B\equiv \left( -\dfrac{9}{5},\dfrac{8}{5} \right) $ .
The points are $ \left( 3,0 \right) $ and $ \left( -\dfrac{9}{5},\dfrac{8}{5} \right) $ .

Now we find the orthocentre of the $ \Delta PAB $ .
As the line AP is vertical, the altitude through B is $ y=\dfrac{8}{5} $ . The orthocentre lies on the line $ y=\dfrac{8}{5} $ . The orthocentre of the $ \Delta PAB $ is $ \left( \dfrac{11}{5},\dfrac{8}{5} \right) $ as that is the only possible option of the given options.The correct option is C.
Note:
We need to remember that we can also solve this from the chord of contact points. We have the equation of chord of contact from the endpoints which are on the ellipse. We find the tangent equations from those points. Their intersecting point will be $ P\left( 3,4 \right) $ . The orthocentre is the point where all the three altitudes of the triangle cut or intersect each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




