
Tangent and normal to the curve $y=2\sin x+\sin 2x$are drawn at $P\left( x=\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)$The area of the quadrilateral formed by the tangent, the normal and coordinate axes is \[\]
A. $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$\[\]
B. $3\pi $\[\]
C. $\dfrac{\pi \sqrt{3}}{2}$\[\]
D. $\pi $\[\]
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: We find the point of contact of the curve and the tangent by putting $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ in equation $y=2\sin x+\sin 2x$. We find the slope of tangent and by differentiating the equation with respect to $x$ and putting $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$. We obtain that tangent is a horizontal line, the normal is a vertical line the quadrilateral formed by them with the axes is a rectangle. We find the area of the rectangle.
Complete step by step answer:
We know from differential calculus that the slope of any curve at any point is given by the differentiation with respect to the independent variable. We also know that the slope of the curve at any point is the slope of the tangent at that point.
The given equation of the curve is
\[y=2\sin x+\sin 2x...(1)\]
We are given in the question that tangent and normal to the curve (1) are drawn at $P\left( x=\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)$. We first put $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ in equation (1) and find the point of contact of the curve and the tangent. We have,
\[\begin{align}
& y=2\sin x+\sin 2x. \\
& =2\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)+\sin \left( 2\times \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) \\
& =\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
So the point of contact is $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)$. We find the slope of the equation at the point of contact by differentiating equation (1) with respect to $x$ and putting $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$. We have
\[\begin{align}
& y=2\sin x+\sin 2x \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2\cos x+2\sin 2x \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}}}=2\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)+2\sin 2\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=1-1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
The obtained slope of the tangent is 0 . We know that the slope of every horizontal line is zero. So the tangent is horizontal line with equation $y=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}$. We also know that tangent and the normal are perpendicular to each other. So the normal line will be perpendicular to the tangent at the point $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)$ with equation $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}.$ So the area of the quadrilateral formed by the axes, the normal and the tangent will be a rectangle . \[\]
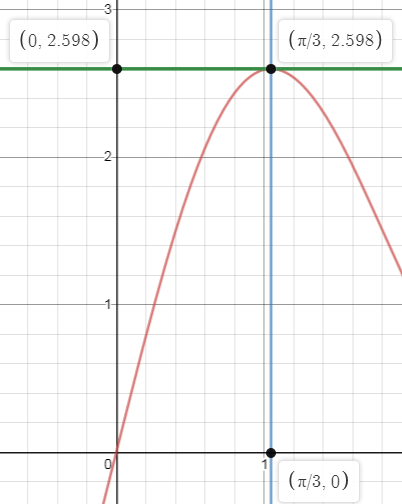
We have plotted the curve and shown vertices with $\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}=2.598.$We observe that lengths of the sides of the rectangle are equal to the abscissa and the ordinate of the point of contact $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)$ which are $\dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}$. So the area of the rectangle $A$ is
\[A=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{\pi \sqrt{3}}{2}\]
So the correct option is C. \[\]
Note: We can alternatively find the area $A$ enclosed by curve $f\left( x \right)$ and the vertical lines $x=a,x=b$ with definite integral using the formula $A=\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)}$. We see in this case the function is $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}$ and the vertical lines are $x=0,x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know from differential calculus that the slope of any curve at any point is given by the differentiation with respect to the independent variable. We also know that the slope of the curve at any point is the slope of the tangent at that point.
The given equation of the curve is
\[y=2\sin x+\sin 2x...(1)\]
We are given in the question that tangent and normal to the curve (1) are drawn at $P\left( x=\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)$. We first put $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ in equation (1) and find the point of contact of the curve and the tangent. We have,
\[\begin{align}
& y=2\sin x+\sin 2x. \\
& =2\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)+\sin \left( 2\times \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) \\
& =\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
So the point of contact is $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)$. We find the slope of the equation at the point of contact by differentiating equation (1) with respect to $x$ and putting $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$. We have
\[\begin{align}
& y=2\sin x+\sin 2x \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2\cos x+2\sin 2x \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}}}=2\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)+2\sin 2\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=1-1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
The obtained slope of the tangent is 0 . We know that the slope of every horizontal line is zero. So the tangent is horizontal line with equation $y=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}$. We also know that tangent and the normal are perpendicular to each other. So the normal line will be perpendicular to the tangent at the point $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)$ with equation $x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}.$ So the area of the quadrilateral formed by the axes, the normal and the tangent will be a rectangle . \[\]

We have plotted the curve and shown vertices with $\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}=2.598.$We observe that lengths of the sides of the rectangle are equal to the abscissa and the ordinate of the point of contact $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)$ which are $\dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}$. So the area of the rectangle $A$ is
\[A=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{\pi \sqrt{3}}{2}\]
So the correct option is C. \[\]
Note: We can alternatively find the area $A$ enclosed by curve $f\left( x \right)$ and the vertical lines $x=a,x=b$ with definite integral using the formula $A=\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)}$. We see in this case the function is $f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}$ and the vertical lines are $x=0,x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




