
Tangent ABC intersects circle O to B. Secant AFOD intersects the circle at F and D, and secant CGOE intersects the circle at G and E. If \[m\overset\frown{EFB}=m\overset\frown{DGB}\], prove that \[\Delta AOC\] is isosceles.
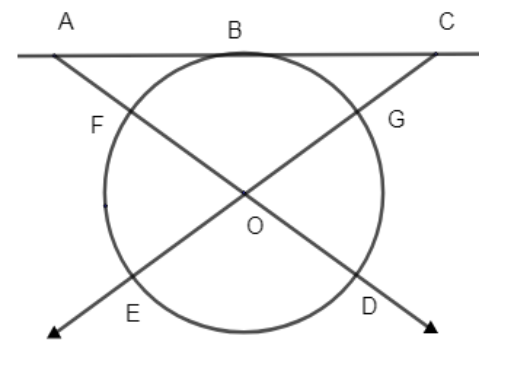

Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Join OB and use the property of tangent to a circle which says that “radius is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact”. Here, O is assumed as the center. Now, show that \[\angle AOB=\angle COB\], by first showing that, \[\angle EOF=\angle DOG\] using the rule of vertically opposite angles are equal. Finally, use A – S – A congruency criteria to prove \[\Delta AOB\] congruent to \[\Delta COB\] and hence, show that, AO = CO.
Complete step-by-step solution
Let us join OB where O is the center of the circle. So, the resultant figure will look like.
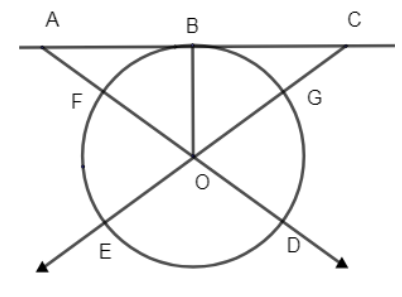
Now, we have to prove that AOC is an isosceles triangle. That means we have to prove, AO = CO.
We have been given that, \[m\overset\frown{EFB}=m\overset\frown{DGB}\], that means measure of arcs EFB and DGB are equal. We know that, equal angles at the center. Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow \angle EOB=\angle DOB\]
Now, \[\angle EOF=\angle DOG\] as they are vertically opposite angles and we know that such angles are equal.
\[\Rightarrow \angle EOB-\angle EOF=\angle DOG-\angle DOB\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle AOB=\angle COB\] - (i)
Let us consider \[\Delta AOB\] and \[\Delta COB\],
\[\Rightarrow \angle ABO=\angle CBO={{90}^{\circ }}\], since \[OB\bot ABC\].
\[\Rightarrow OB=OB\], common side in both triangles
\[\Rightarrow \angle AOB=\angle COB\], using relation (i)
\[\therefore \] We see that two angles and the included side of \[\Delta AOB\] are equal to the two angles and the included side of \[\Delta COB\]. Hence, \[\Delta AOB\] is congruent to \[\Delta COB\]. So, their corresponding sides must be equal.
\[\Rightarrow AO=CO\]
Now, in triangle AOC, we have proved that AO = CO.
Therefore, \[\Delta AOC\] is an isosceles triangle.
Note: One may note that in the above solution we have proved that the \[\Delta AOC\] is isosceles by proving that AO = CO. You may also prove \[\angle OAB=\angle OCB\] for the same. But first, we have to show that both the triangles are congruent which we did above using A – S – A congruency criteria. Here, the property of tangent and equal arcs are important things to remember.
Complete step-by-step solution
Let us join OB where O is the center of the circle. So, the resultant figure will look like.

Now, we have to prove that AOC is an isosceles triangle. That means we have to prove, AO = CO.
We have been given that, \[m\overset\frown{EFB}=m\overset\frown{DGB}\], that means measure of arcs EFB and DGB are equal. We know that, equal angles at the center. Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow \angle EOB=\angle DOB\]
Now, \[\angle EOF=\angle DOG\] as they are vertically opposite angles and we know that such angles are equal.
\[\Rightarrow \angle EOB-\angle EOF=\angle DOG-\angle DOB\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle AOB=\angle COB\] - (i)
Let us consider \[\Delta AOB\] and \[\Delta COB\],
\[\Rightarrow \angle ABO=\angle CBO={{90}^{\circ }}\], since \[OB\bot ABC\].
\[\Rightarrow OB=OB\], common side in both triangles
\[\Rightarrow \angle AOB=\angle COB\], using relation (i)
\[\therefore \] We see that two angles and the included side of \[\Delta AOB\] are equal to the two angles and the included side of \[\Delta COB\]. Hence, \[\Delta AOB\] is congruent to \[\Delta COB\]. So, their corresponding sides must be equal.
\[\Rightarrow AO=CO\]
Now, in triangle AOC, we have proved that AO = CO.
Therefore, \[\Delta AOC\] is an isosceles triangle.
Note: One may note that in the above solution we have proved that the \[\Delta AOC\] is isosceles by proving that AO = CO. You may also prove \[\angle OAB=\angle OCB\] for the same. But first, we have to show that both the triangles are congruent which we did above using A – S – A congruency criteria. Here, the property of tangent and equal arcs are important things to remember.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




