
What is the symbol of an element in group 4 and period 2?
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint:In the modern periodic table, columns represent groups and rows represent periods. An element in the same group exhibits similar properties. There are totally 18 groups and 7 periods with a separate place for inner transition elements.
Complete answer:Periodic table is a visual representation of the 118 chemical elements that have been discovered. It's organized into "periods" and "groups" in rows and columns, respectively. The elements are often organized by atomic number, which is the number of protons present in the nucleus of each atom of each element, from left to right and top to bottom. We can see that group 4 is the second group of transition metals present in the table. As the name suggests, these transition metals act as a bridge between metals and non-metal. The metallic character decreases from left to right of a period.
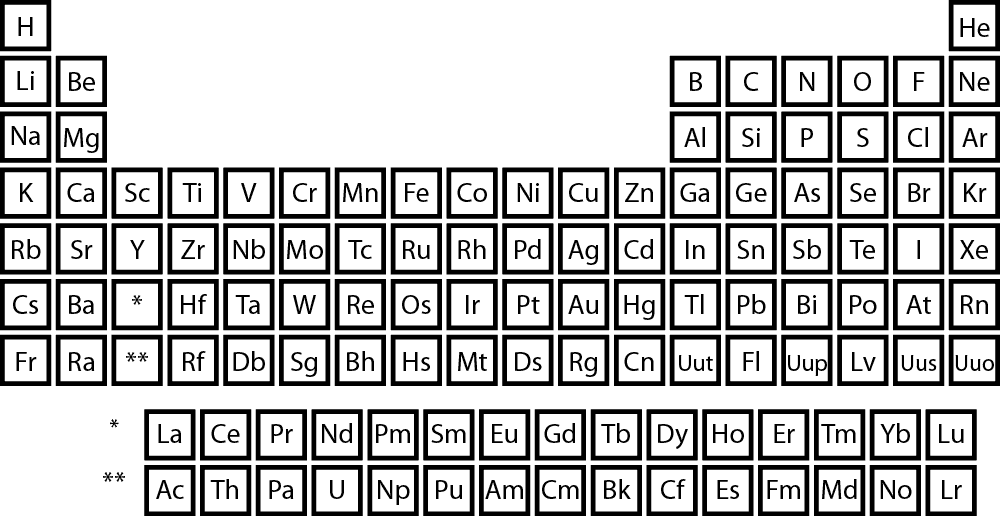
From the periodic table we can observe that the group 4 elements begin from the fourth period. In fact, there are no elements of group 4 in period 2. This is because the group 4 elements have an outer electronic configuration $(n - 1){d^2}n{s^2}$. And d orbitals are absent in the shell $n = 2$. Remember that periods denote the valence shell of an element. Since, an element with valence shell $n = 2$ cannot have d-orbitals, it cannot be a part of the group 4. So, technically there is no element in group 4 and period 2. But some use this kind of notation to represent the second element in the group 4, which is Zirconium ${Z^{40}}$.
Note:
It is more important to note the context in which such a question is raised. Some scientists when studying about the transition elements, refer to the first element of the group to be in period 1. Since, here the question is generally asked, we say that there is no element in the periodic table belonging to group 4 and period 2.
Complete answer:Periodic table is a visual representation of the 118 chemical elements that have been discovered. It's organized into "periods" and "groups" in rows and columns, respectively. The elements are often organized by atomic number, which is the number of protons present in the nucleus of each atom of each element, from left to right and top to bottom. We can see that group 4 is the second group of transition metals present in the table. As the name suggests, these transition metals act as a bridge between metals and non-metal. The metallic character decreases from left to right of a period.

From the periodic table we can observe that the group 4 elements begin from the fourth period. In fact, there are no elements of group 4 in period 2. This is because the group 4 elements have an outer electronic configuration $(n - 1){d^2}n{s^2}$. And d orbitals are absent in the shell $n = 2$. Remember that periods denote the valence shell of an element. Since, an element with valence shell $n = 2$ cannot have d-orbitals, it cannot be a part of the group 4. So, technically there is no element in group 4 and period 2. But some use this kind of notation to represent the second element in the group 4, which is Zirconium ${Z^{40}}$.
Note:
It is more important to note the context in which such a question is raised. Some scientists when studying about the transition elements, refer to the first element of the group to be in period 1. Since, here the question is generally asked, we say that there is no element in the periodic table belonging to group 4 and period 2.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




