
What is the surface area formula of a 3-dimensional rectangle?
Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: We surface area is always calculated for 2-dimensional figures, and so we can visualize a cuboid as a combination of rectangles, and add these areas to get the total surface area of a 3-dimensional rectangle.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a rectangle is a 2-dimensional figure. We have shown a rectangle of length l and breadth b in the following figure,
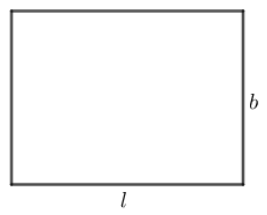
We know that in a rectangle, the opposite sides are equal and parallel. Also, we are aware that each one of the angles of a rectangle is a right angle.
To convert this 2-dimensional shape into 3-dimensional, let us put similar rectangles on the top of this one, in similar orientation. We will see that we get a heap of rectangles, shaped like a box. This shape is called a cuboid. We have shown a cuboid of length l, breadth b and height h in the figure below,
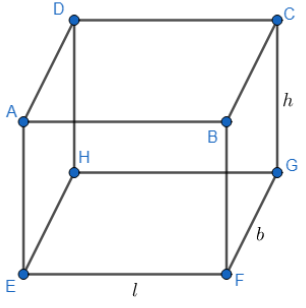
Here, in this figure, we can see that ABCDEFGH is a cuboid. We need to find the surface area of this cuboid. This surface area will be equal to the sum of individual surface areas of each rectangle.
We also know that the opposite faces of a cuboid have the same dimensions, and so the same area.
So, we can write,
Area of face ABCD = Area of face EFGH
Area of face BCGF = Area of face ADHE
Area of face ABFE = Area of face DCGH
Thus, from the figure, we can write,
Surface area of cuboid ABCDEFGH
= $2\times $Surface area of ABCD + $2\times $Surface area of BCGF + $2\times $Surface area of ABFE
Thus, the surface area S,
$S=2\left( lb \right)+2\left( bh \right)+2\left( lh \right)$
Thus, the surface area of the 3-dimensional rectangle is $S=2\left( lb+bh+lh \right)$.
Note: We must remember that as all squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are square, similarly, all cubes are cuboids, but all cuboids are not cubes. Cuboids are also sometimes referred to as closed boxes.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a rectangle is a 2-dimensional figure. We have shown a rectangle of length l and breadth b in the following figure,

We know that in a rectangle, the opposite sides are equal and parallel. Also, we are aware that each one of the angles of a rectangle is a right angle.
To convert this 2-dimensional shape into 3-dimensional, let us put similar rectangles on the top of this one, in similar orientation. We will see that we get a heap of rectangles, shaped like a box. This shape is called a cuboid. We have shown a cuboid of length l, breadth b and height h in the figure below,

Here, in this figure, we can see that ABCDEFGH is a cuboid. We need to find the surface area of this cuboid. This surface area will be equal to the sum of individual surface areas of each rectangle.
We also know that the opposite faces of a cuboid have the same dimensions, and so the same area.
So, we can write,
Area of face ABCD = Area of face EFGH
Area of face BCGF = Area of face ADHE
Area of face ABFE = Area of face DCGH
Thus, from the figure, we can write,
Surface area of cuboid ABCDEFGH
= $2\times $Surface area of ABCD + $2\times $Surface area of BCGF + $2\times $Surface area of ABFE
Thus, the surface area S,
$S=2\left( lb \right)+2\left( bh \right)+2\left( lh \right)$
Thus, the surface area of the 3-dimensional rectangle is $S=2\left( lb+bh+lh \right)$.
Note: We must remember that as all squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are square, similarly, all cubes are cuboids, but all cuboids are not cubes. Cuboids are also sometimes referred to as closed boxes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




