
Suppose that, the acceleration due to gravity is $10\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-2}}$ and at the surface of the mars is $4\cdot 0\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-2}}$ . A 60 kg passenger goes from the earth to mars in a spaceship moving with constant velocity. Neglect all other objects in the sky which part of the figure best represents the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time?
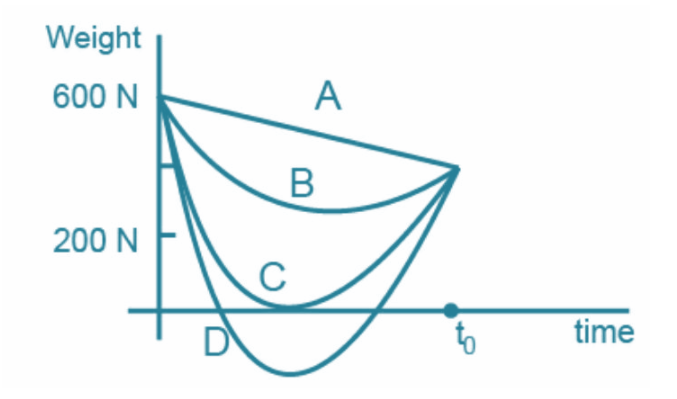
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D

Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: As the passenger is moving from earth to the mars, at some point the net force experienced by it would be zero. So its weight will also be zero. After passing that point, it will experience gravitational pull of mars and so force increases and hence weight increases.
Complete step by step solution: We know that acceleration due to gravity is given by:
$\text{g}=\dfrac{\text{GM}}{{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
Where G = gravitational constant
r = radius of massive body
M = mass of massive body
Now as we can see that $\text{g }\alpha \frac{1}{2}$ . So the graph cannot be a straight line.
Also, now the passenger is going from earth to mars, there will be a point in the path of passenger
Where it will experience equal force from earth and mars. So at that position, the net force on the body would be zero
F = 0 and so weight = 0
After passing this point, the passenger comes under the gravitational field of mars, so the force and hence weight of the passenger starts increasing.
So the correct option is C.
Note: The gravitational pull of the earth is an attraction the earth exerts on an object or the object exerts on the earth. It is proportional to the product of the masses of the earth and the object and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between object and the earth’s center. The mathematical formula for gravitational force is
$\text{F}=\dfrac{\text{G M m}}{{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
Where G = gravitational constant
Complete step by step solution: We know that acceleration due to gravity is given by:
$\text{g}=\dfrac{\text{GM}}{{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
Where G = gravitational constant
r = radius of massive body
M = mass of massive body
Now as we can see that $\text{g }\alpha \frac{1}{2}$ . So the graph cannot be a straight line.
Also, now the passenger is going from earth to mars, there will be a point in the path of passenger
Where it will experience equal force from earth and mars. So at that position, the net force on the body would be zero
F = 0 and so weight = 0
After passing this point, the passenger comes under the gravitational field of mars, so the force and hence weight of the passenger starts increasing.
So the correct option is C.
Note: The gravitational pull of the earth is an attraction the earth exerts on an object or the object exerts on the earth. It is proportional to the product of the masses of the earth and the object and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between object and the earth’s center. The mathematical formula for gravitational force is
$\text{F}=\dfrac{\text{G M m}}{{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
Where G = gravitational constant
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




