
What is the structural difference between high density polythene (HDP) and low density polythene (LDP)?
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: . Polythene is a type of polymer whose monomer is ethene or ethylene. The two polymers have different structures because the temperature, pressure and catalysts used for their formation are different.
Complete answer:
Polythene is homopolymer which is formed with only one monomer which is Ethene$(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{=C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{)}$. It is obtained by a free radical polymerization mechanism.
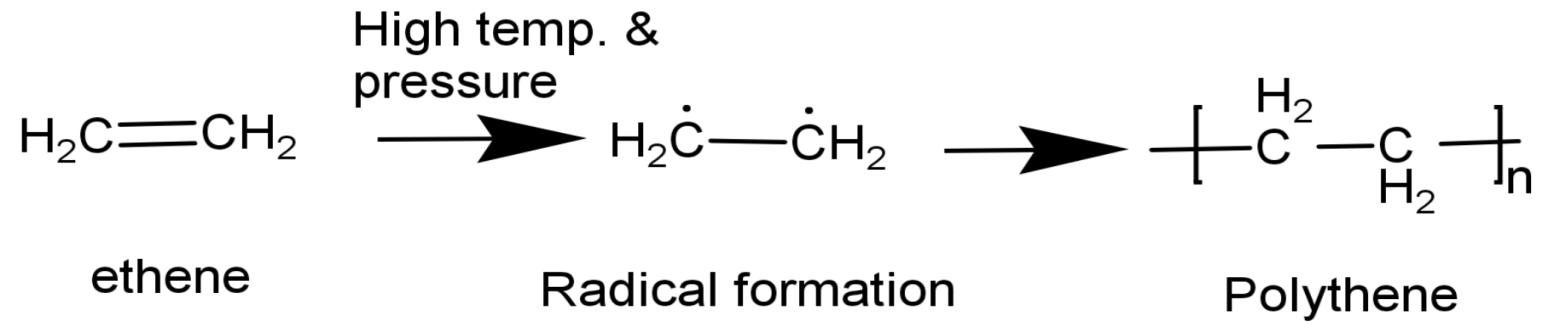
Polythenes are slightly branched or linear long chain molecules. Polythenes have the ability to harden on cooling and soften on heating, because of which they are called as thermoplastics. There are two types of Polythenes:
(1) Low density Polythene (2) High density Polythene
Let us discuss the differences between the two types of Polythenes.
Note: There is no such structural major difference between low density polythene and high density polythene. As the type of formation, the mechanism of formation is the same and the formula with which it is represented is also the same for both. But the reagents used are different. So, it is easier to see these Polythenes in tabular form. Such complex topics are easily learnt through tables. .
Complete answer:
Polythene is homopolymer which is formed with only one monomer which is Ethene$(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{=C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{)}$. It is obtained by a free radical polymerization mechanism.

Polythenes are slightly branched or linear long chain molecules. Polythenes have the ability to harden on cooling and soften on heating, because of which they are called as thermoplastics. There are two types of Polythenes:
(1) Low density Polythene (2) High density Polythene
Let us discuss the differences between the two types of Polythenes.
| LOW DENSITY POLYTHENE | HIGH DENSITY POLYTHENE |
| The temperature and pressure required for the formation of low density polythene is 350K to 570K and 1000 atmosphere to 2000 atmosphere respectively. | The temperature and pressure required for the formation of high density polythene is 333K-343K and 6-7 atmospheres respectively. |
| Catalyst required is a peroxide initiator or traces of dioxygen. | Catalysts are triethylaluminium and titanium tetrachloride (Ziegler-Natta catalyst). |
| It has a highly branched structure. | It has linear structure, and has high density due to close packing, that is why it is also called linear polymer. |
| Are chemically inert, tough but flexible. | Are chemically inert, more tough but hard. |
| Used in insulation of electric wires and in manufacturing of toys and pipes. | Used in manufacturing of buckets, bottles and dustbins. |
| Cannot resist high temperature. | Can resist high temperatures. |
| Have weaker intermolecular forces. | Have stronger intermolecular forces. |
Note: There is no such structural major difference between low density polythene and high density polythene. As the type of formation, the mechanism of formation is the same and the formula with which it is represented is also the same for both. But the reagents used are different. So, it is easier to see these Polythenes in tabular form. Such complex topics are easily learnt through tables. .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




