
What is the steric number for the O atom in water?
Answer
487.8k+ views
Hint: Water (\[{{H}_{2}}O\]) is an inorganic, clear, tasteless, odourless, and virtually colourless chemical substance that is the primary ingredient of the Earth's hydrosphere and all known living species' fluids (in which it acts as a solvent). Even though it contains no calories or organic nutrients, it is necessary for all known forms of life. Each of its molecules has one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms linked by covalent bonds, as indicated by its chemical formula \[{{H}_{2}}O\].
Complete answer:
The number of atoms bound to a central atom of a molecule plus the number of lone pairs connected to the core atom is known as the steric number. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion) theory uses a molecule's steric number to predict its molecular geometry. The VSEPR theory uses simpler ideas than the more complicated original methods to calculate the form of a molecule, or its geometry. It's beneficial for predicting the shapes of molecules with a core atom that's bonded to numerous other atoms on all sides. It's also used to figure out which of several products will be the end result of an organic process.
This means that all you have to do to determine an atom's steric number is count how many lone pairs of electrons it has and how many bonds it makes with other atoms.
Drawing the Lewis structure of water, \[{{H}_{2}}O\], is an excellent place to start.
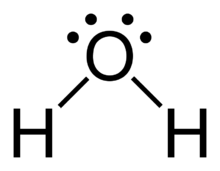
Each water molecule has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. There will be a total of 8 valence electrons in the molecule.
one atom of hydrogen from each of the two hydrogen atoms
six from the presence of oxygen
The centre atom will be the oxygen atom. It will make two single bonds, one with each hydrogen atom, accounting for four valence electrons, and it will have two lone pairs of electrons accounting for the remaining four.
The oxygen atom is surrounded by four electron density areas, two single bonds, and two lone pairs of electrons, as shown.
As a result, the steric number of the atom will be equal to 4.
Note:
The assumption of VSEPR is that the valence electron pairs around an atom resist each other and, as a result, would organise themselves in a way that minimises this repulsion. This reduces the energy of the molecule and enhances its stability, determining the molecular shape. The electron-electron repulsion caused by the Pauli exclusion principle is more significant than the electrostatic repulsion in defining molecule geometry, according to Gillespie.
Complete answer:
The number of atoms bound to a central atom of a molecule plus the number of lone pairs connected to the core atom is known as the steric number. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion) theory uses a molecule's steric number to predict its molecular geometry. The VSEPR theory uses simpler ideas than the more complicated original methods to calculate the form of a molecule, or its geometry. It's beneficial for predicting the shapes of molecules with a core atom that's bonded to numerous other atoms on all sides. It's also used to figure out which of several products will be the end result of an organic process.
This means that all you have to do to determine an atom's steric number is count how many lone pairs of electrons it has and how many bonds it makes with other atoms.
Drawing the Lewis structure of water, \[{{H}_{2}}O\], is an excellent place to start.

Each water molecule has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. There will be a total of 8 valence electrons in the molecule.
one atom of hydrogen from each of the two hydrogen atoms
six from the presence of oxygen
The centre atom will be the oxygen atom. It will make two single bonds, one with each hydrogen atom, accounting for four valence electrons, and it will have two lone pairs of electrons accounting for the remaining four.
The oxygen atom is surrounded by four electron density areas, two single bonds, and two lone pairs of electrons, as shown.
As a result, the steric number of the atom will be equal to 4.
Note:
The assumption of VSEPR is that the valence electron pairs around an atom resist each other and, as a result, would organise themselves in a way that minimises this repulsion. This reduces the energy of the molecule and enhances its stability, determining the molecular shape. The electron-electron repulsion caused by the Pauli exclusion principle is more significant than the electrostatic repulsion in defining molecule geometry, according to Gillespie.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




