
Steps in noncyclic photophosphorylation include passage of electrons along
(A) ${ FRS\rightarrow { FD\rightarrow { Cytb6 } } }\rightarrow { Cytf }\rightarrow { PC }\rightarrow { Chla }\\ $
(B) ${ Chla\rightarrow { Cytb6\rightarrow { Cytf } } }\rightarrow { PC }\rightarrow { PSI }{ \rightarrow FRS }\rightarrow { FD }\\ \\ $
(C) ${ Chla\rightarrow { PQ\rightarrow { Cytb6 } } }\rightarrow { Cytf }\rightarrow { PC }{ \rightarrow PS1 }\rightarrow { FRS\rightarrow }{ FD }\\ \\ \\ $
(D) ${ { PQ\rightarrow { Cytb6 } } }\rightarrow { Cytf }\rightarrow { PC }{ \rightarrow PS1 }\rightarrow { FRS\rightarrow }{ FD }\\ \\ \\ \\ \\ $
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, the electrons which are released by ${ P 680 }$( photosystem II) after absorbing light are first accepted by the primary electron acceptor and finally reach the NADP at the end.
Complete answer:
In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are excited by PSII and then first accepted by the primary electron acceptor which transfers electrons to PQ.PQ transfer electrons to the cytochrome complex in which ${ Cyt b6 }$ is followed by Cyt f. Further electrons are passed to PC which transfers electrons to PSI and further helps in the excitation of electrons. Those excited electrons are again accepted by the primary electron acceptor and passed to FD.
In Non-cyclic photophosphorylation, when electrons are accepted by the primary electron acceptor, the chlorophyll molecules which are present in PSII are oxidized and an electron-hole is created which is to be filled. So, the electrons are extracted from water and passed to the PSII in order to fill the electron-hole. This splits water molecules into two hydrogen ions and one oxygen atom. This single oxygen atom combines with another oxygen atom to form ${ O }_{ 2 }$.
When at last the electron reaches $NAD{ P }^{ + }$ reductase, it results in the formation of NADPH. NADPH is further used in the production of glucose in the Calvin cycle.
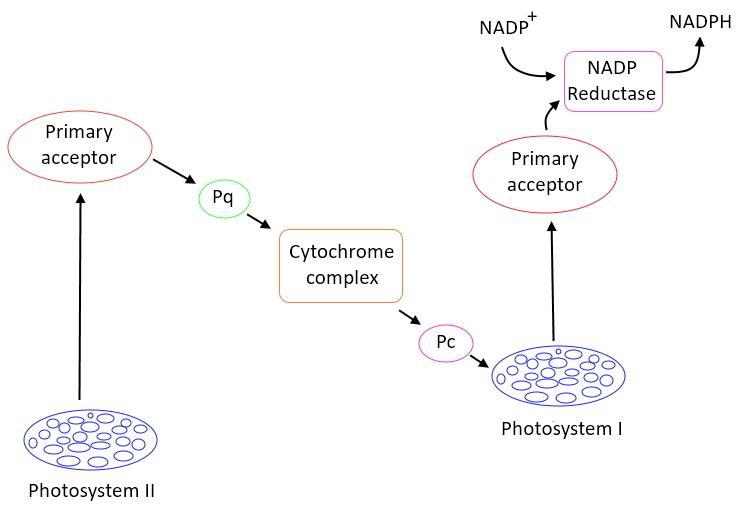
So, the correct answer is ‘${ { PQ\rightarrow { Cytb6 } } }\rightarrow { Cytf }\rightarrow { PC }{ \rightarrow PS1 }\rightarrow { FRS\rightarrow }{ FD }\\ \\ \\ \\ \\ $’.
Note: Non-cyclic photophosphorylation is also known as a Z-scheme. The name Z- scheme was coined because the redox diagram represents the Z. The movement of electrons from different sites leads to the formation of the characteristic shape of the alphabet Z.
Complete answer:
In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are excited by PSII and then first accepted by the primary electron acceptor which transfers electrons to PQ.PQ transfer electrons to the cytochrome complex in which ${ Cyt b6 }$ is followed by Cyt f. Further electrons are passed to PC which transfers electrons to PSI and further helps in the excitation of electrons. Those excited electrons are again accepted by the primary electron acceptor and passed to FD.
In Non-cyclic photophosphorylation, when electrons are accepted by the primary electron acceptor, the chlorophyll molecules which are present in PSII are oxidized and an electron-hole is created which is to be filled. So, the electrons are extracted from water and passed to the PSII in order to fill the electron-hole. This splits water molecules into two hydrogen ions and one oxygen atom. This single oxygen atom combines with another oxygen atom to form ${ O }_{ 2 }$.
When at last the electron reaches $NAD{ P }^{ + }$ reductase, it results in the formation of NADPH. NADPH is further used in the production of glucose in the Calvin cycle.

So, the correct answer is ‘${ { PQ\rightarrow { Cytb6 } } }\rightarrow { Cytf }\rightarrow { PC }{ \rightarrow PS1 }\rightarrow { FRS\rightarrow }{ FD }\\ \\ \\ \\ \\ $’.
Note: Non-cyclic photophosphorylation is also known as a Z-scheme. The name Z- scheme was coined because the redox diagram represents the Z. The movement of electrons from different sites leads to the formation of the characteristic shape of the alphabet Z.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




