
Statement 1: Para-dichlorobenzene has a higher melting point and solubility than that of ortho and meta forms
Statement 2: Para isomer has symmetrical structure and can easily pack closely in the crystal structure.
A.Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation for Statement 1.
B.Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are correct and Statement 2 is not the correct explanation for Statement 1.
C.Statement 1 is correct and Statement 2 is wrong.
D.Statement 1 is wrong and Statement 2 is correct.
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:Para-dichlorobenzene, ortho-dichlorobenzene, and meta-dichlorobenzene are organic halogen compounds. These are examples of different isomeric forms of haloalkanes. The boiling point, melting point, and solubility depend on the symmetry of the compounds. For symmetric compounds, higher energy is needed to break them.
Complete step by step answer:
p-dichlorobenzene, o-dichlorobenzene and m-dichlorobenzene are organic halogen compounds.
Para, ortho, and meta forms of dichlorobenzene are the different isomeric forms of dichlorobenzene where the position of the halogen chlorine is different in the three isomers.
First, let’s draw the structures of these three compounds.
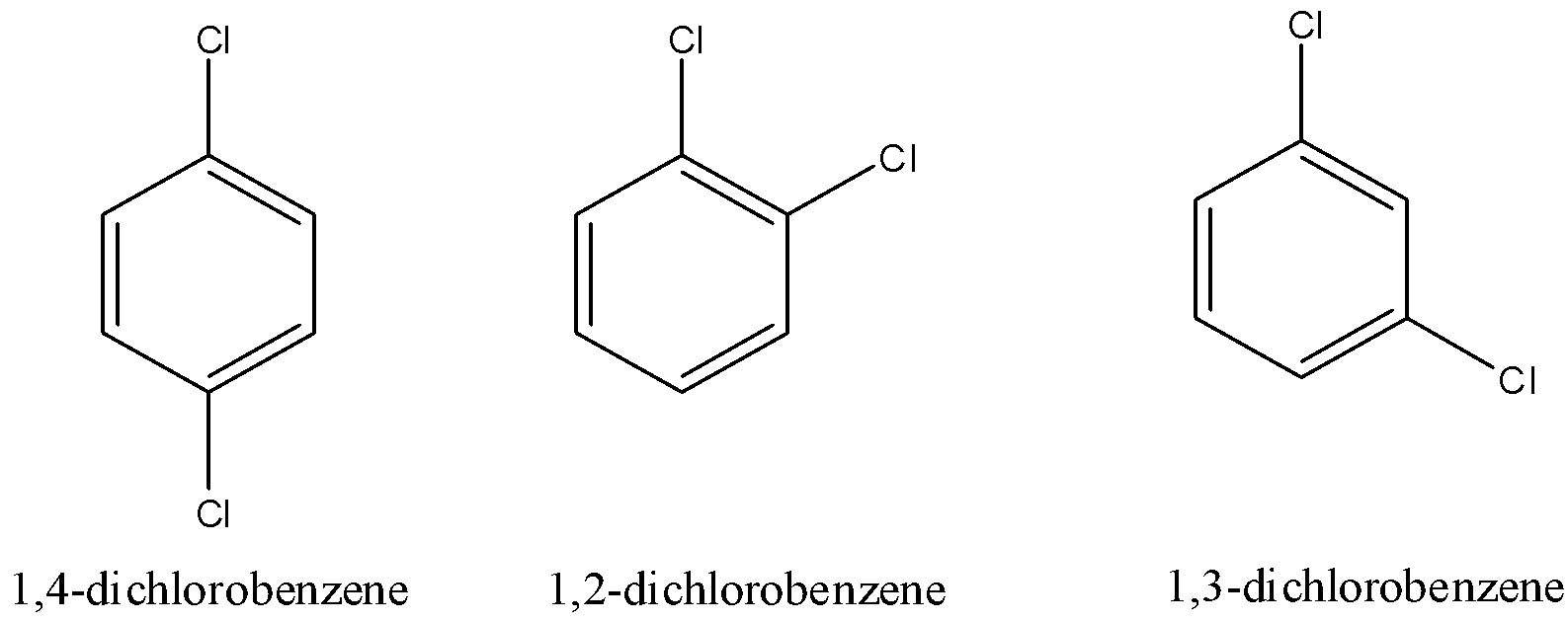
Para-dichlorobenzene is also known as $1,4 - $ dichlorobenzene where chlorine is in $1,4$ positions of benzene.
Ortho-dichlorobenzene is $1,2 - $ dichlorobenzene where chlorine is in $1$ and $2$ positions of benzene rings.
$1,3 - $ Dichlorobenzene is meta-dichlorobenzene where chlorine is in $1,3$ positions of the benzene ring.
When we consider the structures of para-dichlorobenzene, ortho-dichlorobenzene, and meta-dichlorobenzene, we could see that para-dichlorobenzene has a symmetric structure compared to ortho and meta- forms of dichlorobenzene. Since both the chlorine atoms are in opposite positions in para-dichlorobenzene, this gives symmetric structure to paradichlorobenzene.
Because of the symmetric structure of para-dichlorobenzene, it fits in the crystal structure better than the ortho and meta-dichlorobenzene.
Thus para-dichlorobenzene has a closed packed crystal structure.
So more energy is needed to break the crystal lattice of para-dichlorobenzene than ortho and meta isomers.
Therefore melting point and solubility of para-dichloro benzene is higher than ortho and meta- isomers of dichlorobenzene.
Thus we can say that the structure of the para isomer is symmetrical and can easily pack closely in the crystal structure. Due to this reason, para-dichlorobenzene has higher solubility and a higher melting point than ortho and meta- isomer.
Both statement $1$ and statement $2$ are correct and the statement $2$ is the correct explanation for the statement $1$.
Thus the answer is an option (A) .
Note:
In para, ortho, and meta- isomers of dichlorobenzene, the chemical formula is the same and all these isomers contain the same halogen atom chlorine which is present equally in all these isomers. The only difference is in the position of the chlorine atom in the benzene ring. The para isomer is closely packed in the crystal lattice than other isomers due to its symmetry. So more energy is needed to break the para isomer.
Complete step by step answer:
p-dichlorobenzene, o-dichlorobenzene and m-dichlorobenzene are organic halogen compounds.
Para, ortho, and meta forms of dichlorobenzene are the different isomeric forms of dichlorobenzene where the position of the halogen chlorine is different in the three isomers.
First, let’s draw the structures of these three compounds.

Para-dichlorobenzene is also known as $1,4 - $ dichlorobenzene where chlorine is in $1,4$ positions of benzene.
Ortho-dichlorobenzene is $1,2 - $ dichlorobenzene where chlorine is in $1$ and $2$ positions of benzene rings.
$1,3 - $ Dichlorobenzene is meta-dichlorobenzene where chlorine is in $1,3$ positions of the benzene ring.
When we consider the structures of para-dichlorobenzene, ortho-dichlorobenzene, and meta-dichlorobenzene, we could see that para-dichlorobenzene has a symmetric structure compared to ortho and meta- forms of dichlorobenzene. Since both the chlorine atoms are in opposite positions in para-dichlorobenzene, this gives symmetric structure to paradichlorobenzene.
Because of the symmetric structure of para-dichlorobenzene, it fits in the crystal structure better than the ortho and meta-dichlorobenzene.
Thus para-dichlorobenzene has a closed packed crystal structure.
So more energy is needed to break the crystal lattice of para-dichlorobenzene than ortho and meta isomers.
Therefore melting point and solubility of para-dichloro benzene is higher than ortho and meta- isomers of dichlorobenzene.
Thus we can say that the structure of the para isomer is symmetrical and can easily pack closely in the crystal structure. Due to this reason, para-dichlorobenzene has higher solubility and a higher melting point than ortho and meta- isomer.
Both statement $1$ and statement $2$ are correct and the statement $2$ is the correct explanation for the statement $1$.
Thus the answer is an option (A) .
Note:
In para, ortho, and meta- isomers of dichlorobenzene, the chemical formula is the same and all these isomers contain the same halogen atom chlorine which is present equally in all these isomers. The only difference is in the position of the chlorine atom in the benzene ring. The para isomer is closely packed in the crystal lattice than other isomers due to its symmetry. So more energy is needed to break the para isomer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




