
State the De Morgan's Law.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: This theorem is particularly a powerful tool in digital design and electronics.
It explains that the complement of the product of all the terms is equal to the sum of complement of each term. Similarly, the complement of the sum of all the terms is equal to the product of the complement of each term.
Complete step by step answer:
1. De Morgan's theorem are basically two sets of rules or laws developed from Boolean expressions for AND, OR and NOT gates using two input variables, A and B. These two rules or theorems allow the input variables to be negated and converted from one form of a Boolean function into an opposite form.
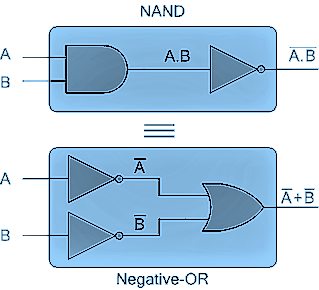
2. De Morgan’s first theorem proves that –when two (or more) input variables are first AND'ed and then negated giving a NAND gate, they are equivalent to the OR of the complement of the individual variables.
Thus, the equivalent NAND function will be negative OR function,
providing that $\overline {A \cdot B} = \overline A + \overline B $ .
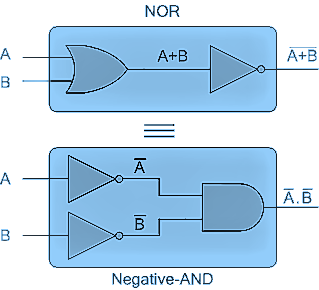
3. De Morgan’s second theorem proves that – when two (or more) input variables are first OR'ed and then negated giving a NOR gate, they are equivalent to the AND of the complements of the individual variables.
Thus, the equivalent of the NOR function is a negative AND function,
proving that $\overline {A + B} = \overline A \cdot \overline B $ .
So, from above discussion it could be concluded that a NAND gate is equivalent to a OR gate with inverted inputs. And similarly, a NOR gate is equivalent to a AND gate with inverted inputs.
Note:Do not confuse with De Morgan’s theorem, also present in Sets (Mathematics).
While solving problems on Boolean algebra it is often easier to approach the problem by breaking the longest (uppermost) bar before breaking any bars under it. You must never attempt to break two bars in one step.
It explains that the complement of the product of all the terms is equal to the sum of complement of each term. Similarly, the complement of the sum of all the terms is equal to the product of the complement of each term.
Complete step by step answer:
1. De Morgan's theorem are basically two sets of rules or laws developed from Boolean expressions for AND, OR and NOT gates using two input variables, A and B. These two rules or theorems allow the input variables to be negated and converted from one form of a Boolean function into an opposite form.
2. De Morgan’s first theorem proves that –when two (or more) input variables are first AND'ed and then negated giving a NAND gate, they are equivalent to the OR of the complement of the individual variables.
Thus, the equivalent NAND function will be negative OR function,
providing that $\overline {A \cdot B} = \overline A + \overline B $ .
3. De Morgan’s second theorem proves that – when two (or more) input variables are first OR'ed and then negated giving a NOR gate, they are equivalent to the AND of the complements of the individual variables.
Thus, the equivalent of the NOR function is a negative AND function,
proving that $\overline {A + B} = \overline A \cdot \overline B $ .
So, from above discussion it could be concluded that a NAND gate is equivalent to a OR gate with inverted inputs. And similarly, a NOR gate is equivalent to a AND gate with inverted inputs.


Note:Do not confuse with De Morgan’s theorem, also present in Sets (Mathematics).
While solving problems on Boolean algebra it is often easier to approach the problem by breaking the longest (uppermost) bar before breaking any bars under it. You must never attempt to break two bars in one step.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




