
State that $(R) - 2 - chlorobutane$ is represented by:
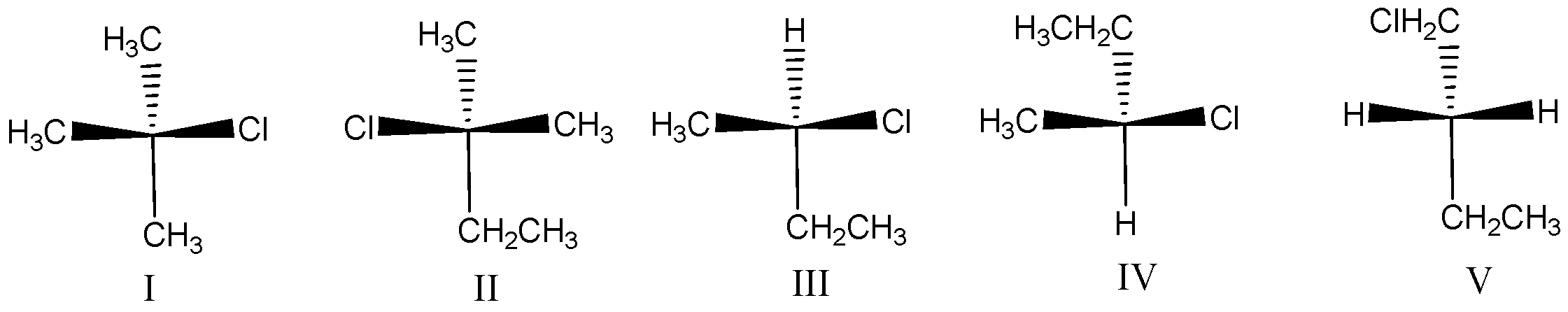
A.$I$
B.$II$
C.$III$
D.$IV$
E.$V$

Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: We need to remember that the $R\& S$ configuration is proposed by three chemists Cahn, Ingold and Prelog, it used to assign a particular configuration in a simpler and more convenient method than drawing a picture. This method is also known as absolute configuration and also called the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the $R\& S$ meanings are right and left, from Latin words Rectus and Sinister. The dashed lines indicate the atoms or group is away from you and behind the plane. Wedged lines indicate atoms are toward you and in front of the plane.
To assign the $R\& S$ configuration for a compound, the compound have more than one chiral carbon atoms and the rules for assigning $R\& S$ configurations are:
a.The atoms attached to the chiral carbon of higher atomic number get higher priority. Hydrogen atoms always get least priority because their atomic number is low among other atoms. Mark a circle from number1 to 4.
b.The above rule is failed to detect a priority of two groups then the priority is decided by comparing the next atom in the group and this is also failed to detect then the comparison may be continued.
c.For doubly and triply bonded atom, the doubly and triply bonded atoms are equivalent to two or three such atoms. For example, a compound contains $ - CHO$ and $ - C{H_2}OH$ , $ - CHO$ gets higher priority.
d.The above rules are done then the next part is assigning a compound. The lowest priority is directed away from us when the molecule is visualized. Determine the direction is clockwise or anticlockwise, if the eye travels in a clockwise then the configuration is said to be specified as $R$ and if it is anticlockwise then the configuration is $S$ .
Let us see the options one by one to find the $(R) - 2 - chlorobutane$ from above rules,
Option I:
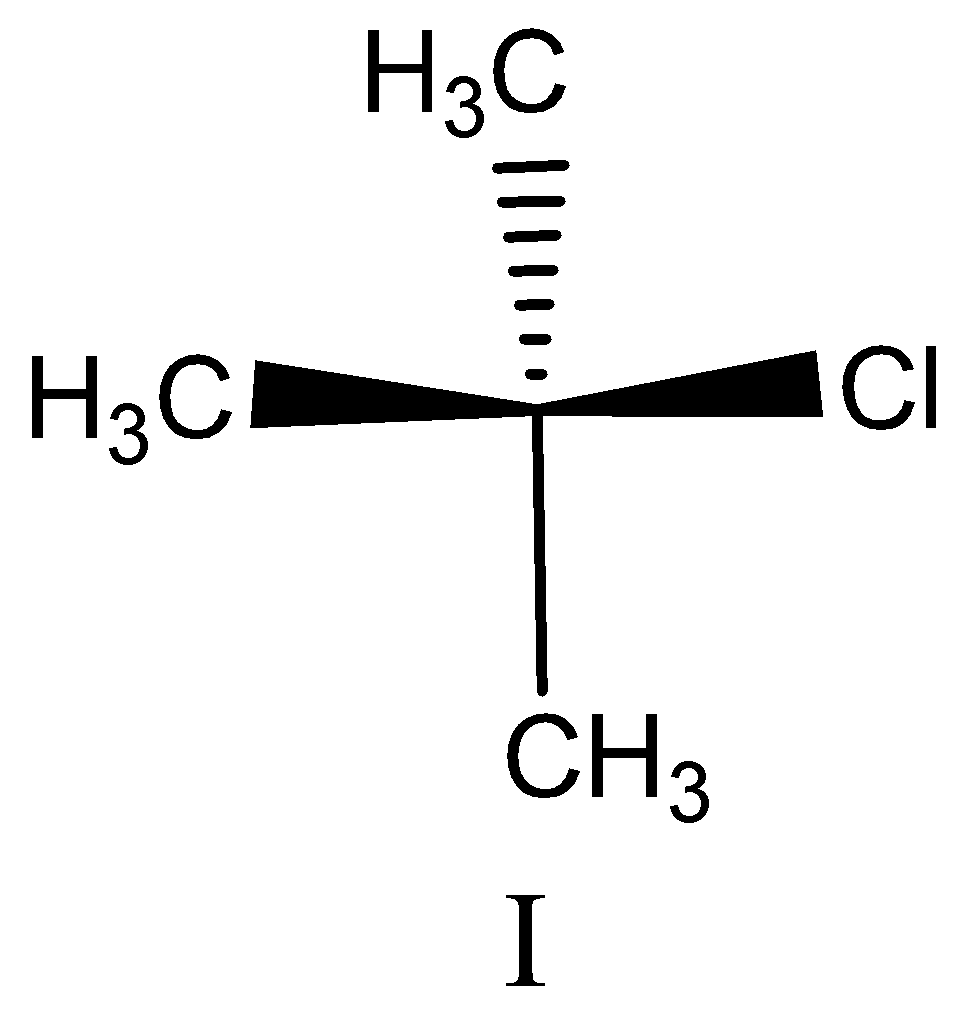
This compound does not contain chiral carbon, because the attached groups are the same so we can’t assign configuration.
Option II:
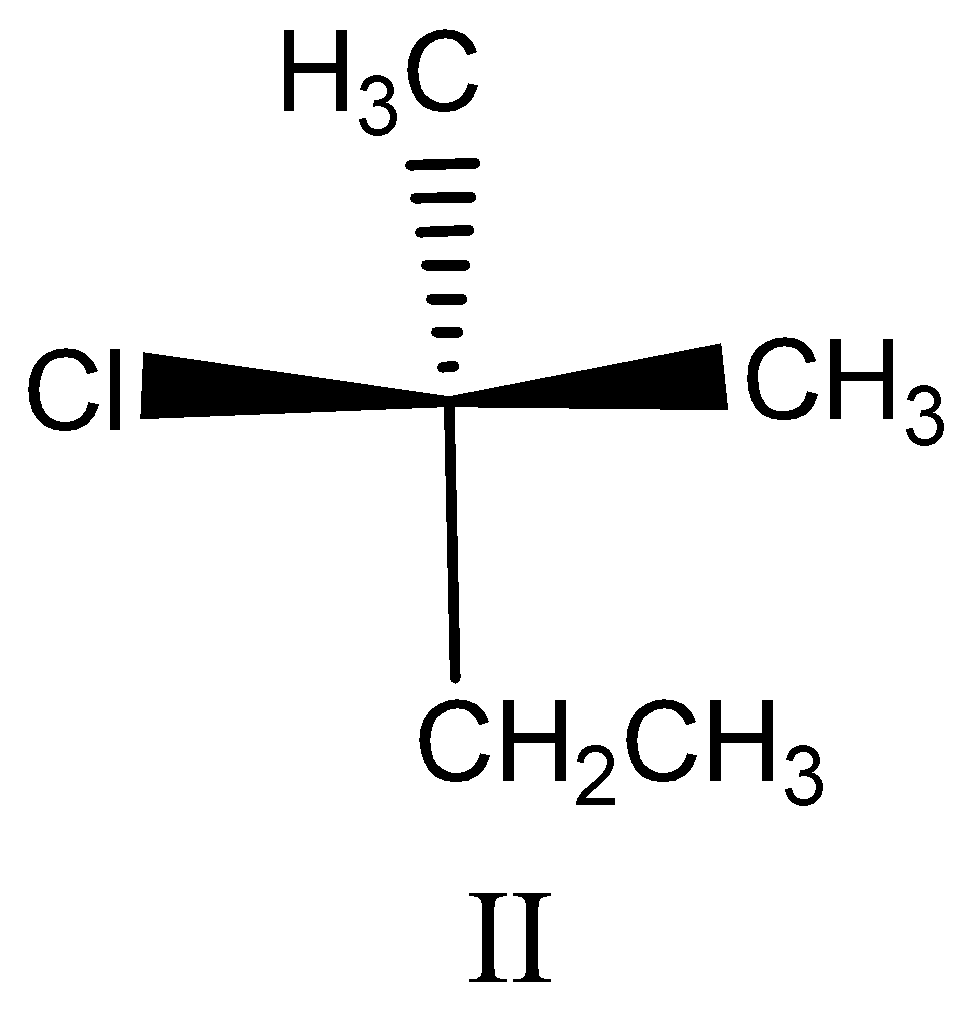
This compound is also not a chiral compound, because the two methyl groups are attached to the central carbon. So this compound is ruled out.
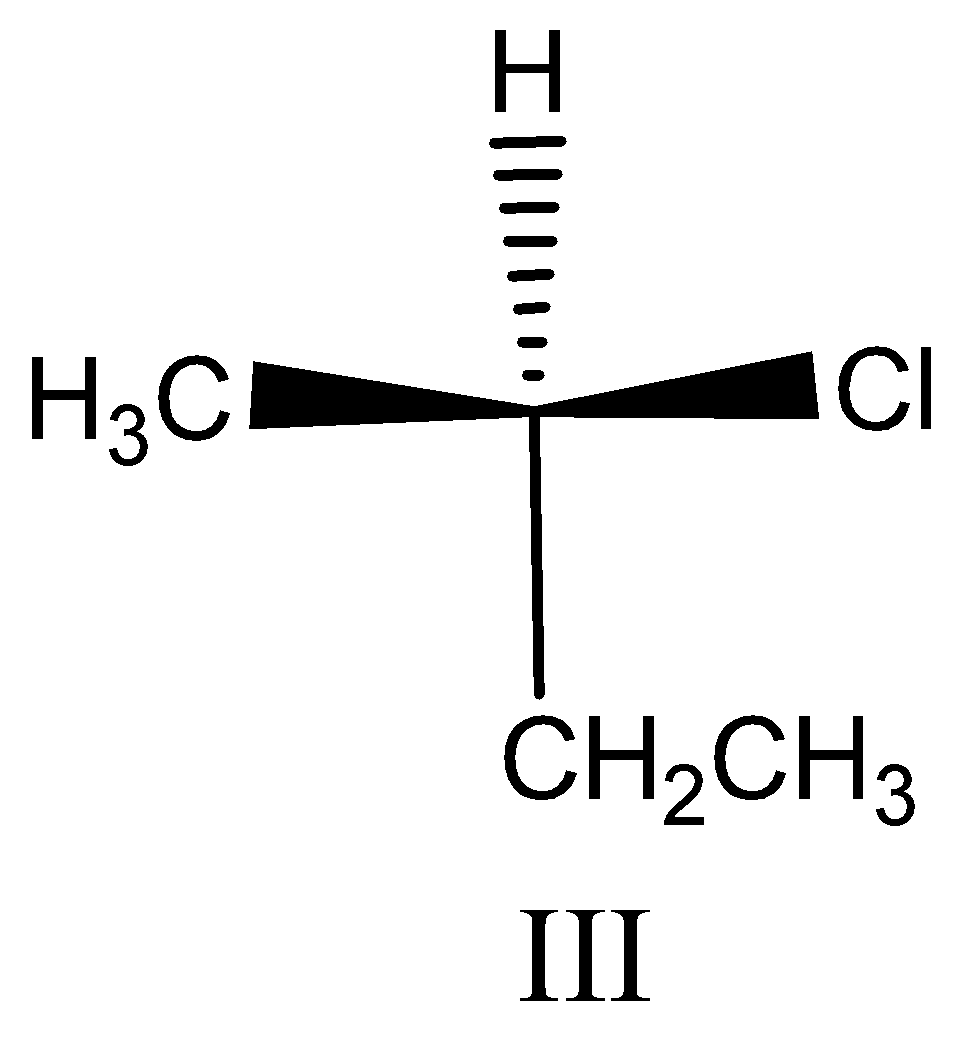
Option III:
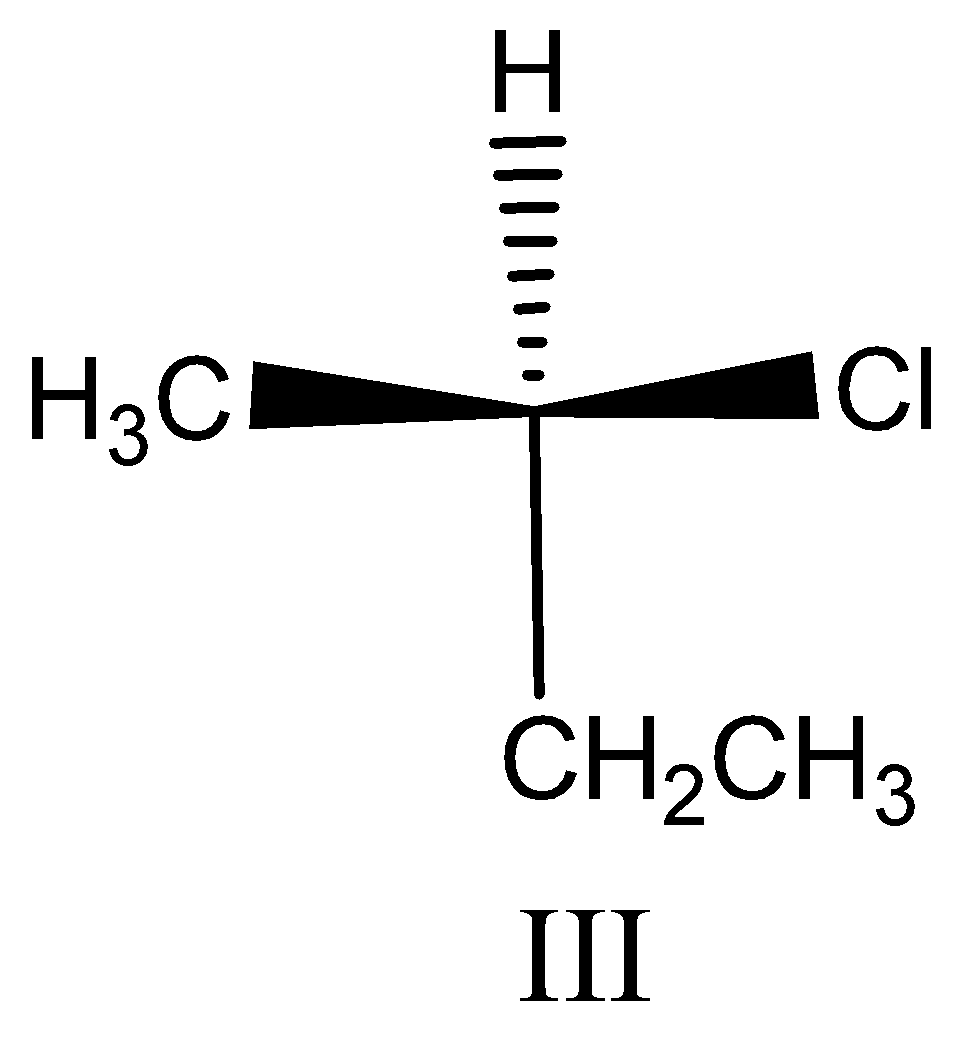
This compound contains chiral carbon so we assign the configuration. First assign the priorities by atomic number.
The priority order is $Cl > C{H_2}C{H_3} > C{H_3} > H$ ,
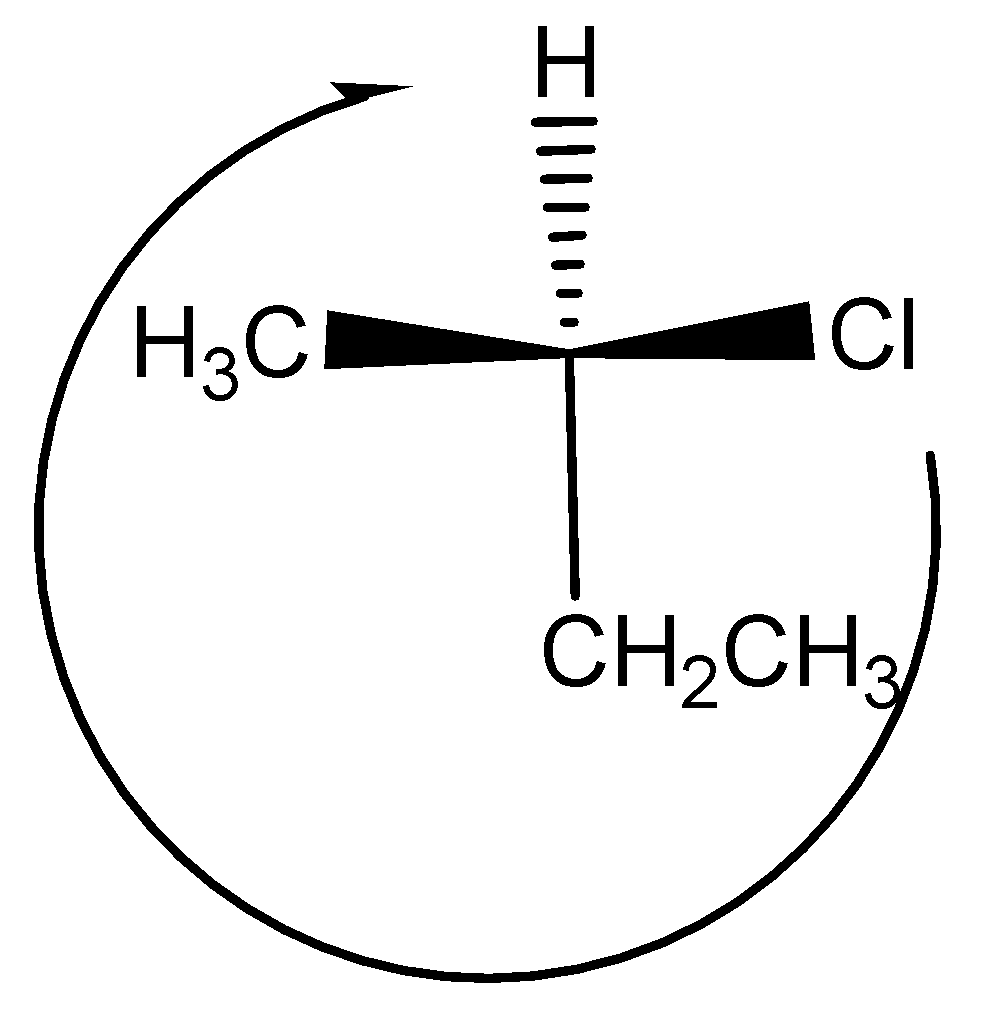
Then we see the direction of the compound, the direction is clockwise. So $R$ configuration and this is $(R) - 2 - chlorobutane$ .
Option IV:
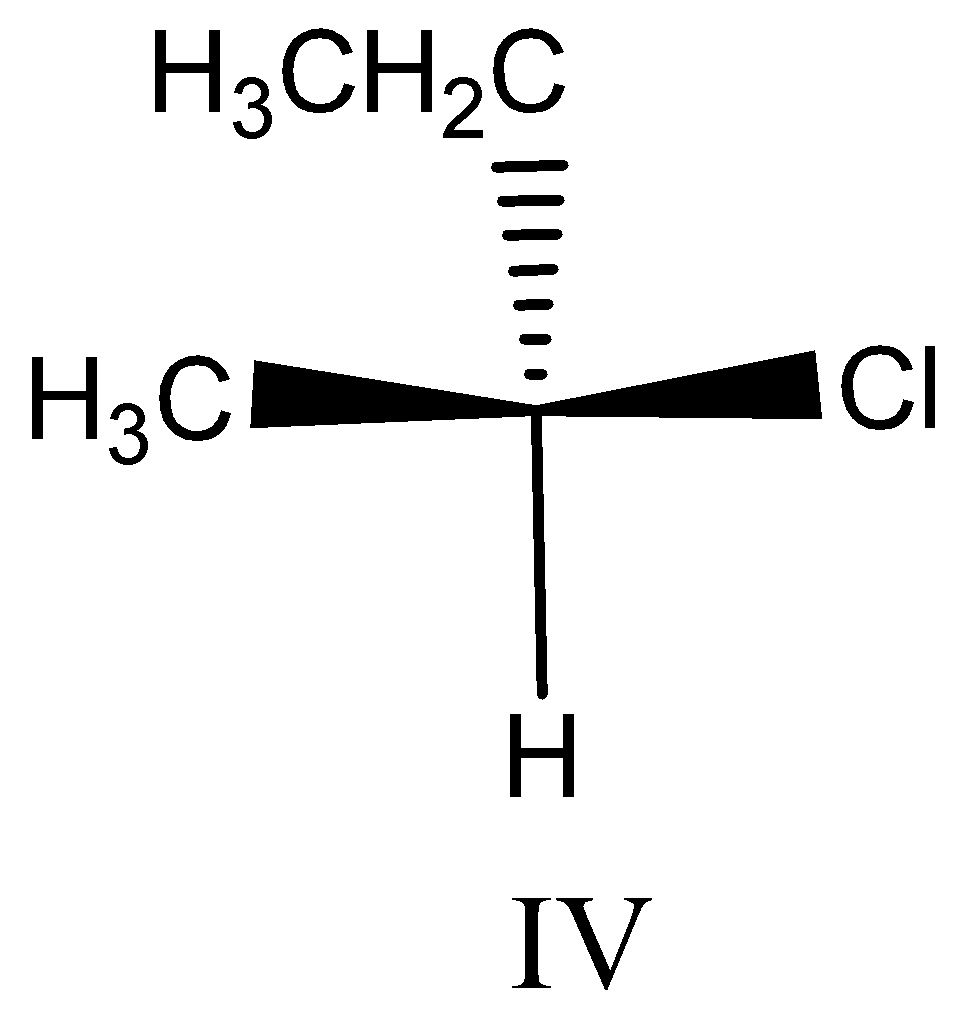
This compound is similar to $III$ , but the $ethyl$ and $hydrogen$ group are interchanged. Option $III$ is $R$ configuration the groups are interchanged so this is $S$ configuration.
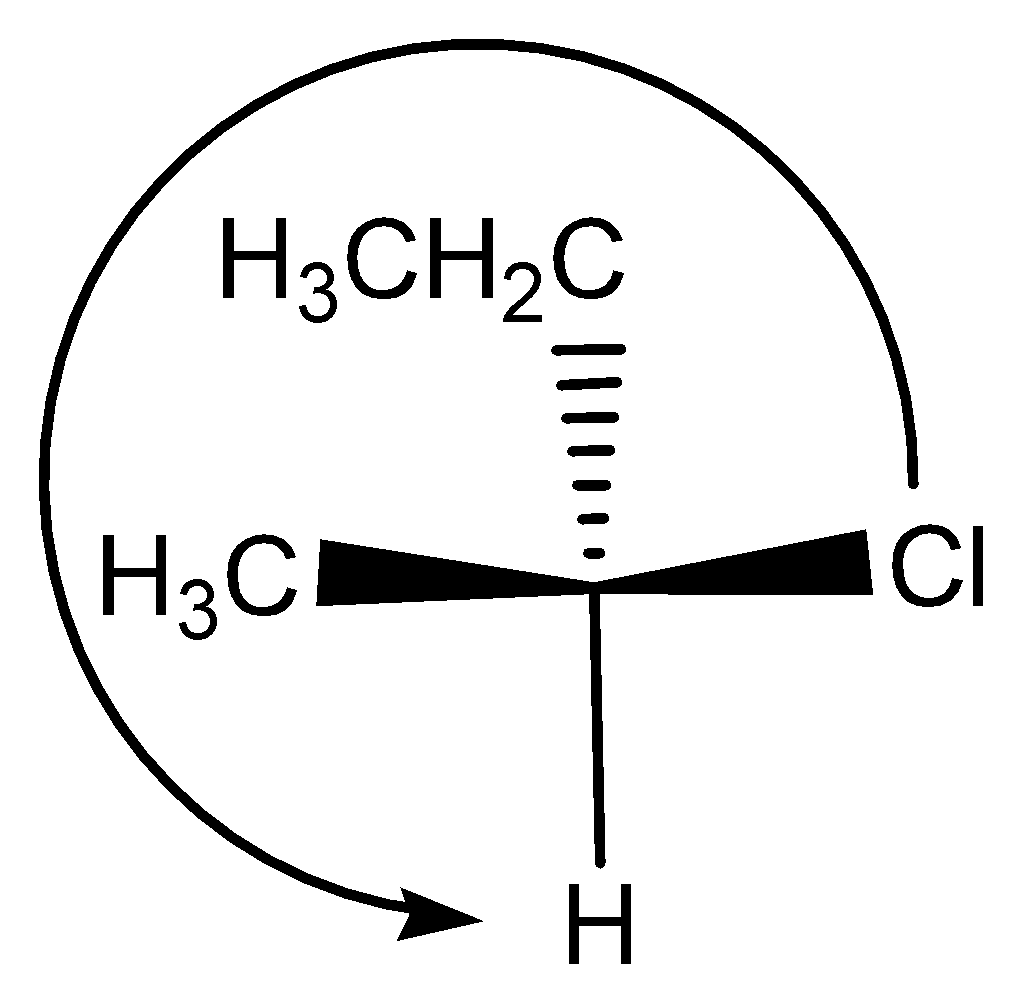
Option V:
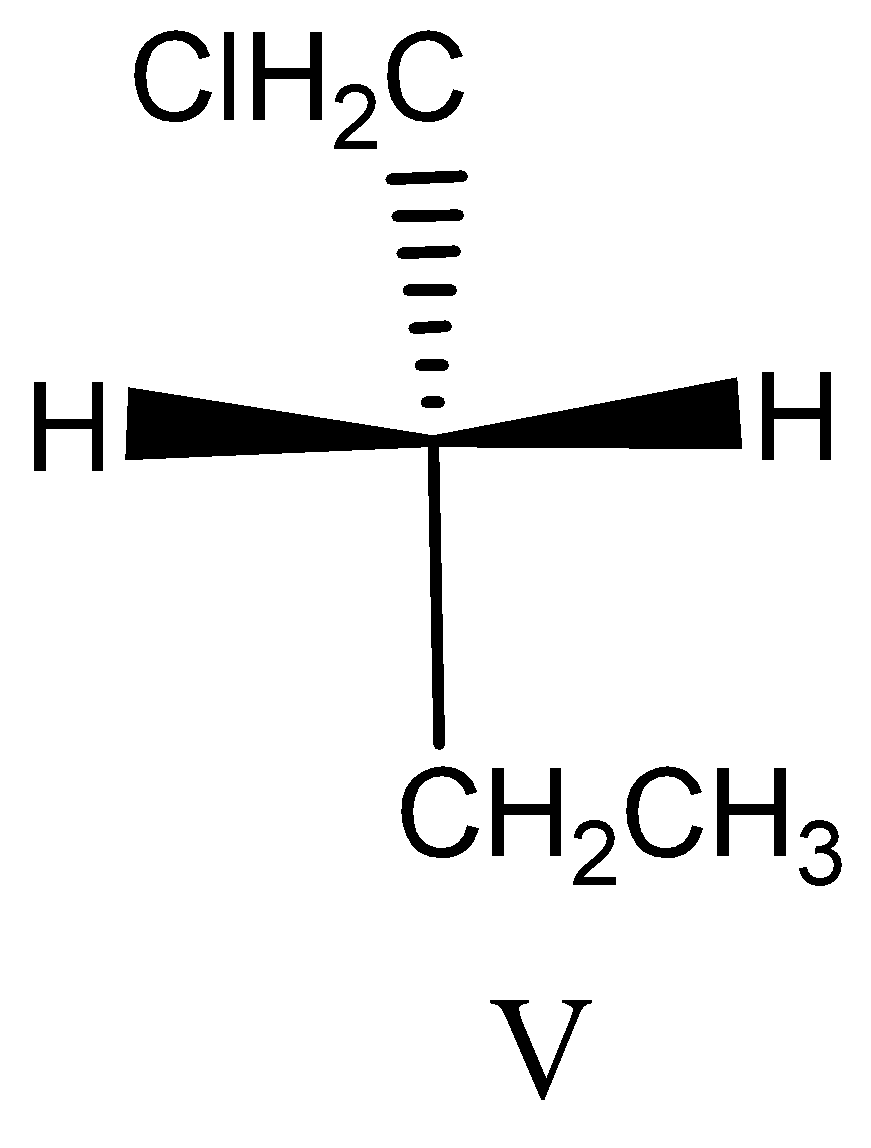
This compound does not have chiral carbon because of the same hydrogen atom attached to the carbon. So this is not applicable for assigning the absolute configuration.
From the above data, $(R) - 2 - chlorobutane$ is represented by
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
We need to know that from $X - $ ray diffraction, the absolute configuration is also determined experimentally, but for non- laboratory purposes we assign $R\& S$ configuration, it is the beneficial one. For an optically active compound, the direction is independent of $R\& S$ configuration of the compound. The prefixes $( + / - )$ are must include with $R\& S$ , for a complete description of an optically active compound.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the $R\& S$ meanings are right and left, from Latin words Rectus and Sinister. The dashed lines indicate the atoms or group is away from you and behind the plane. Wedged lines indicate atoms are toward you and in front of the plane.
To assign the $R\& S$ configuration for a compound, the compound have more than one chiral carbon atoms and the rules for assigning $R\& S$ configurations are:
a.The atoms attached to the chiral carbon of higher atomic number get higher priority. Hydrogen atoms always get least priority because their atomic number is low among other atoms. Mark a circle from number1 to 4.
b.The above rule is failed to detect a priority of two groups then the priority is decided by comparing the next atom in the group and this is also failed to detect then the comparison may be continued.
c.For doubly and triply bonded atom, the doubly and triply bonded atoms are equivalent to two or three such atoms. For example, a compound contains $ - CHO$ and $ - C{H_2}OH$ , $ - CHO$ gets higher priority.
d.The above rules are done then the next part is assigning a compound. The lowest priority is directed away from us when the molecule is visualized. Determine the direction is clockwise or anticlockwise, if the eye travels in a clockwise then the configuration is said to be specified as $R$ and if it is anticlockwise then the configuration is $S$ .
Let us see the options one by one to find the $(R) - 2 - chlorobutane$ from above rules,
Option I:

This compound does not contain chiral carbon, because the attached groups are the same so we can’t assign configuration.
Option II:

This compound is also not a chiral compound, because the two methyl groups are attached to the central carbon. So this compound is ruled out.
Option III:

This compound contains chiral carbon so we assign the configuration. First assign the priorities by atomic number.
The priority order is $Cl > C{H_2}C{H_3} > C{H_3} > H$ ,

Then we see the direction of the compound, the direction is clockwise. So $R$ configuration and this is $(R) - 2 - chlorobutane$ .
Option IV:

This compound is similar to $III$ , but the $ethyl$ and $hydrogen$ group are interchanged. Option $III$ is $R$ configuration the groups are interchanged so this is $S$ configuration.

Option V:

This compound does not have chiral carbon because of the same hydrogen atom attached to the carbon. So this is not applicable for assigning the absolute configuration.
From the above data, $(R) - 2 - chlorobutane$ is represented by

So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
We need to know that from $X - $ ray diffraction, the absolute configuration is also determined experimentally, but for non- laboratory purposes we assign $R\& S$ configuration, it is the beneficial one. For an optically active compound, the direction is independent of $R\& S$ configuration of the compound. The prefixes $( + / - )$ are must include with $R\& S$ , for a complete description of an optically active compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




