
State and explain Newton’s law of gravitation force.
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: Newton’s law of gravitation force gives the force which any two particles in this universe apply on each other. This force is always attractive in nature and it resembles the force between two charged particles.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Newton’s law of gravitation states that every object attracts every other object in this universe with a force proportional to product of masses of two objects and inversely proportional to the square of distance between them. This force acts along the line joining the two bodies. This force is always attractive in nature.
If two bodies of masses ${{m}_{1}}$and ${{m}_{2}}$ are kept at a distance $r$ from each other, then the force acting between the two bodies is given by
$F=\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$
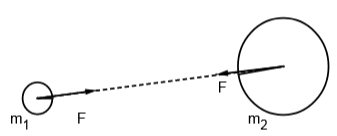
Here G is the universal gravitation constant, and its value is $6.67408\times {{10}^{-11}}$. It's S.I. unit is ${{m}^{3}}k{{g}^{-1}}{{s}^{-2}}$. The value of this constant does not change in any condition. This law was proposed by Isaac Newton in the year 1687 and was used to explain the motion of planets and sun.
Newton’s law of universal gravitation can be expressed in vector form as
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{F}_{21}}}}\,=-\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\, \right|}^{2}}}\overset{\Lambda }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\,\],
Where
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{F}_{21}}}}\,\]is the force applied on body 2 by body 1, G is gravitational constant, \[\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\, \right|\]
(\[\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\, \right|=\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{2}}}}\,-\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{1}}}}\, \right|\], where ${{r}_{2}}$ and ${{r}_{1}}$ are position vectors of body 1 and 2 respectively) is the distance between the two bodies, and \[\overset{\Lambda }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\,\] (\[\overset{\Lambda }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\,=\dfrac{\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{2}}}}\,-\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{1}}}}\,}{\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{2}}}}\,-\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{1}}}}\, \right|}\]) is a unit vector from body 1 to body 2.
Note: Newton’s law of gravitation is very identical to Coulomb’s law of electrical forces between two charges which is proportional to product of charges and inversely proportional to the sure of distance between them.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Newton’s law of gravitation states that every object attracts every other object in this universe with a force proportional to product of masses of two objects and inversely proportional to the square of distance between them. This force acts along the line joining the two bodies. This force is always attractive in nature.
If two bodies of masses ${{m}_{1}}$and ${{m}_{2}}$ are kept at a distance $r$ from each other, then the force acting between the two bodies is given by
$F=\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$

Here G is the universal gravitation constant, and its value is $6.67408\times {{10}^{-11}}$. It's S.I. unit is ${{m}^{3}}k{{g}^{-1}}{{s}^{-2}}$. The value of this constant does not change in any condition. This law was proposed by Isaac Newton in the year 1687 and was used to explain the motion of planets and sun.
Newton’s law of universal gravitation can be expressed in vector form as
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{F}_{21}}}}\,=-\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\, \right|}^{2}}}\overset{\Lambda }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\,\],
Where
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{F}_{21}}}}\,\]is the force applied on body 2 by body 1, G is gravitational constant, \[\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\, \right|\]
(\[\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\, \right|=\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{2}}}}\,-\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{1}}}}\, \right|\], where ${{r}_{2}}$ and ${{r}_{1}}$ are position vectors of body 1 and 2 respectively) is the distance between the two bodies, and \[\overset{\Lambda }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\,\] (\[\overset{\Lambda }{\mathop{{{r}_{12}}}}\,=\dfrac{\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{2}}}}\,-\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{1}}}}\,}{\left| \overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{2}}}}\,-\overset{\to }{\mathop{{{r}_{1}}}}\, \right|}\]) is a unit vector from body 1 to body 2.
Note: Newton’s law of gravitation is very identical to Coulomb’s law of electrical forces between two charges which is proportional to product of charges and inversely proportional to the sure of distance between them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




