
What stage of aerobic respiration requires ATP?
Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: Aerobic respiration takes place in cells in the presence of oxygen to produce energy from food. It is common in most of the plants, animals and other mammals. Carbon dioxide and water are produced as end products with the formation of ATP in this respiration. The four stages of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
Complete explanation:
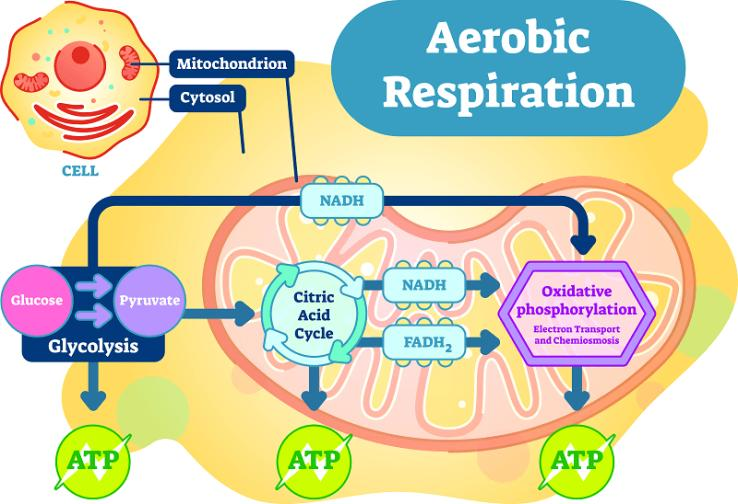
The first half of glycolysis in aerobic respiration needs ATP molecules. Glycolysis, also known as the EMP, takes place in the cytosol of the cells. Glycolysis can be divided into two phases- preparatory phase and payoff phase. Here one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate along with generation of two net molecules of ATP. For one glucose molecule, four ATP molecules are actually produced but two are consumed as part of the preparatory phase of glycolysis.
Preparatory phase is also known as the glucose activation phase. It starts with the phosphorylation of glucose. At the end of this phase, the hexose chain is cleaved into two triose phosphates with the help of two ATP molecules.
Payoff phase is also known as the energy extraction phase. The end reaction of this phase is the conversion of glyceraldehyde-\[3\]-phosphate to pyruvate with liberation of energy. The pyruvate molecule from this phase gets oxidized to form acetyl co A and carbon dioxide by the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Here, one molecule of NADH is also formed.
Note:
The acetyl coA enters the citric acid cycle and gets converted into oxaloacetate. This molecule undergoes a series of events to produce three molecules of NADH, one molecule of \[FADH_2\] and one molecule of ATP or GTP. The NADH enters the electron transport chain and oxidizes to produce a proton gradient. This gradient is used to synthesize ATP with the help of ATP synthase enzymes. At the end of aerobic respiration, \[32\] molecules of ATP would have been produced.
Complete explanation:
The first half of glycolysis in aerobic respiration needs ATP molecules. Glycolysis, also known as the EMP, takes place in the cytosol of the cells. Glycolysis can be divided into two phases- preparatory phase and payoff phase. Here one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate along with generation of two net molecules of ATP. For one glucose molecule, four ATP molecules are actually produced but two are consumed as part of the preparatory phase of glycolysis.
Preparatory phase is also known as the glucose activation phase. It starts with the phosphorylation of glucose. At the end of this phase, the hexose chain is cleaved into two triose phosphates with the help of two ATP molecules.
Payoff phase is also known as the energy extraction phase. The end reaction of this phase is the conversion of glyceraldehyde-\[3\]-phosphate to pyruvate with liberation of energy. The pyruvate molecule from this phase gets oxidized to form acetyl co A and carbon dioxide by the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Here, one molecule of NADH is also formed.

Note:
The acetyl coA enters the citric acid cycle and gets converted into oxaloacetate. This molecule undergoes a series of events to produce three molecules of NADH, one molecule of \[FADH_2\] and one molecule of ATP or GTP. The NADH enters the electron transport chain and oxidizes to produce a proton gradient. This gradient is used to synthesize ATP with the help of ATP synthase enzymes. At the end of aerobic respiration, \[32\] molecules of ATP would have been produced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




