
$\square XYZW$ is the rectangle. If $XY+YZ=17$ and $XZ+YW=26$ then find $XY$ and $YZ$ (where $XY>YZ$ ).
Answer
623.1k+ views
Hint: For solving this question we should know about the rectangle and how to apply Pythagoras Theorem in right-angled triangles. And by using a simple whole square formula we will solve this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
The polygon $\square XYZW$ is a rectangle as shown in the figure below.
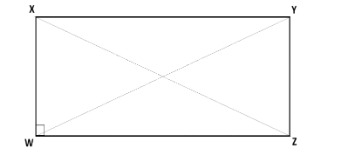
A rectangle is a polygon in which adjacent sides are perpendicular to each other and the length of opposite sides are equal. In other words, for the above rectangle,
\[\angle WXY=\angle XYZ=\angle YZW=\angle ZWX={{90}^{0}}\]
\[XY=WZ\] and \[WX=YZ\]
Now, let $XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$ .
It is given that $XY+YZ=17$ .
Then, we can write, $a+b=17.................\left( equationA \right)$ .
As we have two unknown variables $a$ and $b$ , so we need two different equations to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
We need one more equation in terms of $a$ and $b$ . Before proceeding further just take a look at the result of the Pythagoras Theorem. The Pythagoras Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle as shown below $\Delta ABC$ , the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In the $\Delta ABC$ , $\angle ACB={{90}^{0}}$ and AB is the hypotenuse, BC is the base and AC is the perpendicular. From Pythagoras Theorem, we have:
${{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
Then, we can write, ${{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$ .
If we look at the figure of the $\square XYZW$ , $\Delta XZW$ and $\Delta YZW$ are right-angled triangles and we can apply the result of Pythagoras theorem in both these triangles.
In the $\Delta XZW$ ,
$\angle XWZ={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $XZ$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( XW \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( WZ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $XZ=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}..............(equationB)$ .
Similarly, in the \[\Delta YZW\] ,
$\angle YZW={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $YW$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( YZ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( ZW \right)}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(equationC)$ .
Adding $equationB$ and $equationC$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& XZ+YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow XZ+YW=2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
It is given that, $XZ+YW=26$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=26 \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=13 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{13}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=169..............(equationD) \\
\end{align}$
We will use $equationA$ and $equationD$ to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
As $a$ and $b$ are two positive numbers where $a$ is greater than $b$ . Now, we will use the whole square identities formulae written below:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \\
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \right]+\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \right] \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right] \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right]$ from $equationD$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\times 169 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left( a+b \right)$ from $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( 17 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-289 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{7}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow a-b=7.................(equationE) \\
\end{align}$
Here one point is very important in the above equation that we cannot write $b-a=7$ as we have taken $a>b$ so, the value of $b-a$ will be negative.
From $equationA$ and $equationE$ , we have:
$\begin{align}
& a+b=17 \\
& a-b=7 \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \left( a+b \right)+\left( a-b \right)=17+7 \\
& \Rightarrow 2a=24 \\
& \Rightarrow a=12 \\
\end{align}$
Now put the value of $a$ from the above equation in $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& 12+b=17 \\
& \Rightarrow b=17-12 \\
& \Rightarrow b=5 \\
\end{align}$
Now,
$\because XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$
Thus, $XY=12$ and $YZ=5$ .
Note: For solving this question we have to use the geometrical properties of the rectangle and we should know how to apply Pythagoras Theorem in case of any right-angled triangle and then apply every formula very carefully and find the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
The polygon $\square XYZW$ is a rectangle as shown in the figure below.

A rectangle is a polygon in which adjacent sides are perpendicular to each other and the length of opposite sides are equal. In other words, for the above rectangle,
\[\angle WXY=\angle XYZ=\angle YZW=\angle ZWX={{90}^{0}}\]
\[XY=WZ\] and \[WX=YZ\]
Now, let $XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$ .
It is given that $XY+YZ=17$ .
Then, we can write, $a+b=17.................\left( equationA \right)$ .
As we have two unknown variables $a$ and $b$ , so we need two different equations to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
We need one more equation in terms of $a$ and $b$ . Before proceeding further just take a look at the result of the Pythagoras Theorem. The Pythagoras Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle as shown below $\Delta ABC$ , the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In the $\Delta ABC$ , $\angle ACB={{90}^{0}}$ and AB is the hypotenuse, BC is the base and AC is the perpendicular. From Pythagoras Theorem, we have:
${{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}$
Then, we can write, ${{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$ .
If we look at the figure of the $\square XYZW$ , $\Delta XZW$ and $\Delta YZW$ are right-angled triangles and we can apply the result of Pythagoras theorem in both these triangles.
In the $\Delta XZW$ ,
$\angle XWZ={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $XZ$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( XW \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( WZ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( XZ \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $XZ=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}..............(equationB)$ .
Similarly, in the \[\Delta YZW\] ,
$\angle YZW={{90}^{0}}$ and the side $YW$ is the hypotenuse. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( YZ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( ZW \right)}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{\left( YW \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, $YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}................(equationC)$ .
Adding $equationB$ and $equationC$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& XZ+YW=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow XZ+YW=2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
It is given that, $XZ+YW=26$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=26 \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=13 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{13}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=169..............(equationD) \\
\end{align}$
We will use $equationA$ and $equationD$ to find the values of $a$ and $b$ .
As $a$ and $b$ are two positive numbers where $a$ is greater than $b$ . Now, we will use the whole square identities formulae written below:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \\
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \right]+\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \right] \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right] \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left[ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right]$ from $equationD$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=2\times 169 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting the value of $\left( a+b \right)$ from $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-{{\left( 17 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=338-289 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{7}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow a-b=7.................(equationE) \\
\end{align}$
Here one point is very important in the above equation that we cannot write $b-a=7$ as we have taken $a>b$ so, the value of $b-a$ will be negative.
From $equationA$ and $equationE$ , we have:
$\begin{align}
& a+b=17 \\
& a-b=7 \\
\end{align}$
Adding the above two equations, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \left( a+b \right)+\left( a-b \right)=17+7 \\
& \Rightarrow 2a=24 \\
& \Rightarrow a=12 \\
\end{align}$
Now put the value of $a$ from the above equation in $equationA$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& 12+b=17 \\
& \Rightarrow b=17-12 \\
& \Rightarrow b=5 \\
\end{align}$
Now,
$\because XY=WZ=a$ and $WX=YZ=b$
Thus, $XY=12$ and $YZ=5$ .
Note: For solving this question we have to use the geometrical properties of the rectangle and we should know how to apply Pythagoras Theorem in case of any right-angled triangle and then apply every formula very carefully and find the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed




