
How much space is filled in cubic close packing?
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint :The 3D Arrangement of different atoms in a row touching each other and forming different layers. When layers containing hexagonal close packing are arranged over each other, two types of arrangement is feasible.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The third layer is formed in such a way that tetrahedral voids are covered. In this way the spheres of the third layer lie directly above those in the first layer. It means the third layer becomes exactly identical to the first layer. If we consider the first layer as A, and second as B, then this type of packing is ABABAB. arrangement and it is known as hexagonal close packing. Examples are Mg, Zn, Cd, Be etc.
If the third layer is formed in such a way that spheres of the third layer must cover octahedral voids. It forms a new third layer. This is ABCABC… arrangement, and is known as cubic close packing.
To find space occupied: we have the formula of packing efficiency:
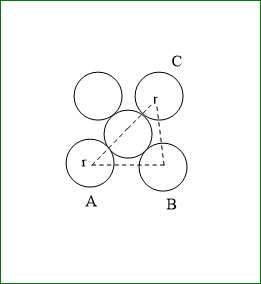
Suppose the edge length of a unit cell is a.
And radius is r
In triangle ABC, $ A{C^2} = B{C^2} + A{B^2} $
$ {a^2} + {a^2} = 2{a^2} $
hence face diagonal $ AC = \sqrt 2 a $
but $ AC = 4r $
therefore, $ 4r = \sqrt 2 a $
hence, volume of unit cell = $ {a^3} = 16\sqrt 2 {r^3} $
as there are a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell.
Packing efficiency: $ = \dfrac{{4 \times \dfrac{{4{\pi ^3}}}{3}}}{{{a^3}or16\sqrt 2 {r^3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 \pi }}{6} = 0.74 $
Hence, % of space occupied $ = 74\% $
Note :
Formation of $ 3^{rd} $ layer over $ 2^{nd} $ : there are two types of voids which are to be covered by the third layer. These are octahedral voids which remain occupied for two consecutive layers and tetrahedral voids forming in the second layer.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The third layer is formed in such a way that tetrahedral voids are covered. In this way the spheres of the third layer lie directly above those in the first layer. It means the third layer becomes exactly identical to the first layer. If we consider the first layer as A, and second as B, then this type of packing is ABABAB. arrangement and it is known as hexagonal close packing. Examples are Mg, Zn, Cd, Be etc.
If the third layer is formed in such a way that spheres of the third layer must cover octahedral voids. It forms a new third layer. This is ABCABC… arrangement, and is known as cubic close packing.
To find space occupied: we have the formula of packing efficiency:

Suppose the edge length of a unit cell is a.
And radius is r
In triangle ABC, $ A{C^2} = B{C^2} + A{B^2} $
$ {a^2} + {a^2} = 2{a^2} $
hence face diagonal $ AC = \sqrt 2 a $
but $ AC = 4r $
therefore, $ 4r = \sqrt 2 a $
hence, volume of unit cell = $ {a^3} = 16\sqrt 2 {r^3} $
as there are a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell.
Packing efficiency: $ = \dfrac{{4 \times \dfrac{{4{\pi ^3}}}{3}}}{{{a^3}or16\sqrt 2 {r^3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 \pi }}{6} = 0.74 $
Hence, % of space occupied $ = 74\% $
Note :
Formation of $ 3^{rd} $ layer over $ 2^{nd} $ : there are two types of voids which are to be covered by the third layer. These are octahedral voids which remain occupied for two consecutive layers and tetrahedral voids forming in the second layer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




