
Solve the following
\[\left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|+\left| x+1 \right|=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{\left| x \right|}\]
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: First of all, find those points where modulus function is changing its sign. Now, make various intervals, write the equation accordingly and solve it to find the value of x. That x must lie in the given interval. Also, use \[\left| x \right|=x\text{ for }x\ge 0\text{ and }\left| x \right|=-x\text{ for }x<0\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to solve the equation,
\[\left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|+\left| x+1 \right|=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{\left| x \right|}\]
Let us find the different points at which modulus function is changing its sign.
\[x+1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x=-1\]
and x = 0
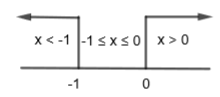
We know if \[x>0,\left| x \right|=x\text{ and }x<0,\left| x \right|=-x\]. Let us consider the equation given in the question,
\[\left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|+\left| x+1 \right|=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{\left| x \right|}\]
In the above equation, we won’t take x = 0 because it is an eliminator.
Let us take x > 0,
For x > 0, x + 1 > 0 and x > 0. So,
\[\dfrac{x+1}{x}>0\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x+1 \right|=\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|=x\]
So, we get,
\[E=\dfrac{\left( x+1 \right)}{x}+\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{x}\]
By multiplying x on both the sides of the above equation, we get,
\[\left( x+1 \right)+x\left( x+1 \right)={{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\]
We know that
\[{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab\]
By using this, we get,
\[\left( x+1 \right)+{{x}^{2}}+x={{x}^{2}}+1+2x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2x+1={{x}^{2}}+1+2x\]
By canceling the like terms, we get,
0 = 0
Hence, LHS = RHS.
So, this equation is true for all values of x > 0.
Now, let us take \[-1\le x<0\]
For, \[-1\le x<0,x+1\ge 0\text{ and }x<0\]
So, \[\dfrac{x+1}{x}\le 0\]
So,
\[\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|=-\left( \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x+1 \right|=\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|=-x\]
So, we get,
\[E=-\left( \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right)+\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{-x}\]
By multiplying x on both the sides of the above equation, we get,
\[\Rightarrow -\left( x+1 \right)+\left( x+1 \right)x=-{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow -x-1+{{x}^{2}}+x=-\left( {{x}^{2}}+1+2x \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-1=-{{x}^{2}}-1-2x\]
\[\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+2x=0\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+x=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x\left( x+1 \right)=0\]
\[x=0;x=1\]
We know that \[x\ne 0\]
So, we get our solution as x = – 1.
Now let us take x < – 1
For, \[x<-1,x+1<0,x<0\]
So, \[\dfrac{x+1}{x}>0\]
So,
\[\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|=-x\]
\[\Rightarrow -\left| x+1 \right|=-\left( x+1 \right)\]
So, we get,
\[E=\dfrac{\left( x+1 \right)}{x}-\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{-x}\]
By multiplying x on both the sides of the above equation, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \left( x+1 \right)-x\left( x+1 \right)=-{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow x+1-{{x}^{2}}-x=-\left( {{x}^{2}}+1+2x \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x+1-{{x}^{2}}=-{{x}^{2}}-1-2x\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x+1=-1-2x\]
\[\Rightarrow 4x+2=0\]
\[x=\dfrac{-2}{4}\]
\[x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\]
This x is greater than – 1, that is it is not in the domain of x < – 1. So, \[x\ne \dfrac{-1}{2}\].
So, we finally get \[x\in \left( -1 \right)\cup \left( 0,\infty \right)\].
Note: Students must note that, whenever we get LHS = RHS after solving the equation, that equation is true for all values of x in the domain of that equation. Also, in the case of a modulus function, observe each point where the function inside the modulus is changing its sign like in the above question, that points are 0 and – 1. Also, in the expression, the denominator can never be 0. So, take care of that while solving the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to solve the equation,
\[\left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|+\left| x+1 \right|=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{\left| x \right|}\]
Let us find the different points at which modulus function is changing its sign.
\[x+1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x=-1\]
and x = 0
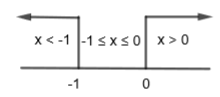
We know if \[x>0,\left| x \right|=x\text{ and }x<0,\left| x \right|=-x\]. Let us consider the equation given in the question,
\[\left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|+\left| x+1 \right|=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{\left| x \right|}\]
In the above equation, we won’t take x = 0 because it is an eliminator.
Let us take x > 0,
For x > 0, x + 1 > 0 and x > 0. So,
\[\dfrac{x+1}{x}>0\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x+1 \right|=\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|=x\]
So, we get,
\[E=\dfrac{\left( x+1 \right)}{x}+\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{x}\]
By multiplying x on both the sides of the above equation, we get,
\[\left( x+1 \right)+x\left( x+1 \right)={{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\]
We know that
\[{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab\]
By using this, we get,
\[\left( x+1 \right)+{{x}^{2}}+x={{x}^{2}}+1+2x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2x+1={{x}^{2}}+1+2x\]
By canceling the like terms, we get,
0 = 0
Hence, LHS = RHS.
So, this equation is true for all values of x > 0.
Now, let us take \[-1\le x<0\]
For, \[-1\le x<0,x+1\ge 0\text{ and }x<0\]
So, \[\dfrac{x+1}{x}\le 0\]
So,
\[\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|=-\left( \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x+1 \right|=\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|=-x\]
So, we get,
\[E=-\left( \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right)+\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{-x}\]
By multiplying x on both the sides of the above equation, we get,
\[\Rightarrow -\left( x+1 \right)+\left( x+1 \right)x=-{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow -x-1+{{x}^{2}}+x=-\left( {{x}^{2}}+1+2x \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-1=-{{x}^{2}}-1-2x\]
\[\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+2x=0\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+x=0\]
\[\Rightarrow x\left( x+1 \right)=0\]
\[x=0;x=1\]
We know that \[x\ne 0\]
So, we get our solution as x = – 1.
Now let us take x < – 1
For, \[x<-1,x+1<0,x<0\]
So, \[\dfrac{x+1}{x}>0\]
So,
\[\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{x+1}{x} \right|=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|=-x\]
\[\Rightarrow -\left| x+1 \right|=-\left( x+1 \right)\]
So, we get,
\[E=\dfrac{\left( x+1 \right)}{x}-\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}{-x}\]
By multiplying x on both the sides of the above equation, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \left( x+1 \right)-x\left( x+1 \right)=-{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow x+1-{{x}^{2}}-x=-\left( {{x}^{2}}+1+2x \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x+1-{{x}^{2}}=-{{x}^{2}}-1-2x\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x+1=-1-2x\]
\[\Rightarrow 4x+2=0\]
\[x=\dfrac{-2}{4}\]
\[x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\]
This x is greater than – 1, that is it is not in the domain of x < – 1. So, \[x\ne \dfrac{-1}{2}\].
So, we finally get \[x\in \left( -1 \right)\cup \left( 0,\infty \right)\].
Note: Students must note that, whenever we get LHS = RHS after solving the equation, that equation is true for all values of x in the domain of that equation. Also, in the case of a modulus function, observe each point where the function inside the modulus is changing its sign like in the above question, that points are 0 and – 1. Also, in the expression, the denominator can never be 0. So, take care of that while solving the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




