
How do you solve $ 2{{\sin }^{2}}x+3\cos x=0 $ on the interval [0,2pi]?
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: We can write $ {{\sin }^{2}}x $ in terms of $ {{\cos }^{2}}x $ we know that $ {{\sin }^{2}}x=1-{{\cos }^{2}}x $ and then the equation will convert into a quadratic equation and we will find the roots it will give us the possible value of cos x.
Complete step by step answer:
The given equation is $ 2{{\sin }^{2}}x+3\cos x=0 $
We can write $ {{\sin }^{2}}x $ as $ 1-{{\cos }^{2}}x $ and it will convert into a quadratic equation
$ 2{{\sin }^{2}}x+3\cos x=2\left( 1-{{\cos }^{2}}x \right)+3\cos x $
Now we can write $ -2{{\cos }^{2}}x+3\cos x+2=0 $
We can multiply -1 in both LHS and RHS
$ \Rightarrow 2{{\cos }^{2}}x-3\cos x-2=0 $
We factorize the equation for factorization we can write $ -3\cos x $ as $ \cos x-4\cos x $
$ \Rightarrow 2{{\cos }^{2}}x+\cos x-4\cos x-2=0 $
We can take cos x common in first half of the equation and -2 common in second half of the equation
$ \Rightarrow \cos x\left( 2\cos x+1 \right)-2\left( 2\cos x+1 \right)=0 $
Now we can take $ 2\cos x+1 $ common
$ \Rightarrow \left( \cos x-2 \right)\left( 2\cos x+1 \right)=0 $
So the value of cos x can be 2 or $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $ we know that range of cosx is -1 to 1
So cosx can not be 2. $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $ is the only possible value of cos x
In the range 0 to $ 2\pi $ the solutions of cos x= $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $ are $ \dfrac{2\pi }{3} $ and $ \dfrac{4\pi }{3} $
We can check that in the graph first we will draw the graph of $ y=\cos x $ and then $ y=-\dfrac{1}{2} $
Then check the intersection point
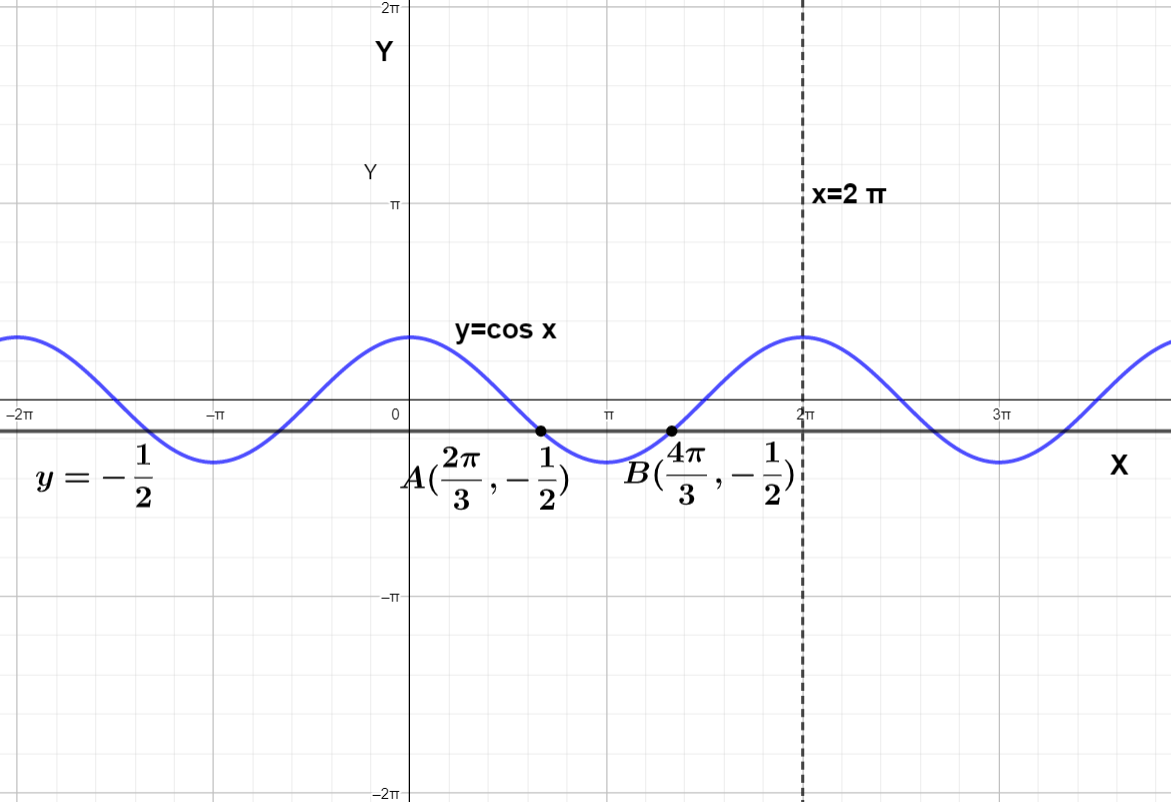
We can see there are 2 solution between x=0 to $ x=2\pi $ one solution is A $ \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3},-\dfrac{1}{2} \right) $ and B $ \left( \dfrac{4\pi }{3},-\dfrac{1}{2} \right) $.
Note:
Whenever there is an equation to solve which has variables in cosx, sinx or log x, etc. form. After solving the equation check the roots are coming in the range of the variable for example there is an equation that has $ {{2}^{x}} $ as a variable and the roots of the equation are -2, -3, 10 then
-2, -3 will not be considered because $ {{2}^{x}} $ is always positive so 10 will be considered.
Complete step by step answer:
The given equation is $ 2{{\sin }^{2}}x+3\cos x=0 $
We can write $ {{\sin }^{2}}x $ as $ 1-{{\cos }^{2}}x $ and it will convert into a quadratic equation
$ 2{{\sin }^{2}}x+3\cos x=2\left( 1-{{\cos }^{2}}x \right)+3\cos x $
Now we can write $ -2{{\cos }^{2}}x+3\cos x+2=0 $
We can multiply -1 in both LHS and RHS
$ \Rightarrow 2{{\cos }^{2}}x-3\cos x-2=0 $
We factorize the equation for factorization we can write $ -3\cos x $ as $ \cos x-4\cos x $
$ \Rightarrow 2{{\cos }^{2}}x+\cos x-4\cos x-2=0 $
We can take cos x common in first half of the equation and -2 common in second half of the equation
$ \Rightarrow \cos x\left( 2\cos x+1 \right)-2\left( 2\cos x+1 \right)=0 $
Now we can take $ 2\cos x+1 $ common
$ \Rightarrow \left( \cos x-2 \right)\left( 2\cos x+1 \right)=0 $
So the value of cos x can be 2 or $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $ we know that range of cosx is -1 to 1
So cosx can not be 2. $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $ is the only possible value of cos x
In the range 0 to $ 2\pi $ the solutions of cos x= $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $ are $ \dfrac{2\pi }{3} $ and $ \dfrac{4\pi }{3} $
We can check that in the graph first we will draw the graph of $ y=\cos x $ and then $ y=-\dfrac{1}{2} $
Then check the intersection point

We can see there are 2 solution between x=0 to $ x=2\pi $ one solution is A $ \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3},-\dfrac{1}{2} \right) $ and B $ \left( \dfrac{4\pi }{3},-\dfrac{1}{2} \right) $.
Note:
Whenever there is an equation to solve which has variables in cosx, sinx or log x, etc. form. After solving the equation check the roots are coming in the range of the variable for example there is an equation that has $ {{2}^{x}} $ as a variable and the roots of the equation are -2, -3, 10 then
-2, -3 will not be considered because $ {{2}^{x}} $ is always positive so 10 will be considered.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




