
Sketch the graph of $PV$ vs $P$ when the temperature of the gas is constant. Here $P$ means pressure and V means volume - showing you the direct relationship b/w P and V (by using pV). How to sketch it?
Answer
496.2k+ views
Hint: We are asked to plot the graph between pV and p when temperature is a constant. We can start to answer this question by taking the ideal gas equation. Once we have done this, we can move onto writing the constants in the equation and finding the relationship between PV and P. This will help us in drawing a PV vs P graph.
Formulas used: The ideal gas equation is given by the formula, \[PV = nRT\]
Where \[V\] is the volume of the gas taken
\[p\] is the pressure of gas taken
\[n\] is the number of moles in the amount of substance
\[R\] is the universal gas constant
\[T\] is the temperature
Complete step by step solution:
Let us start by writing down the ideal gas equation.
The ideal gas equation is as, \[PV = nRT\]
We are given that the temperature of the gas is constant. The universal gas constant is a constant as well, you can see it in the name itself. Then we have the number of moles in the amount of substance, which is also a constant in this case.
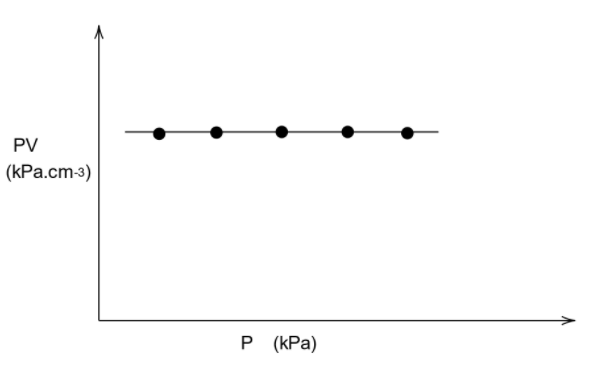
This makes the RHS of the ideal gas equation to be a constant. Let us call this constant “k”. Then we have \[PV = k\]
That is \[PV = \text{constant}\]
We know that if the value in the y axis is a constant, then the graph will be parallel to the x axis. This means that the graph will be parallel to the axis in which only pressure is present, which is the x axis.
Thus, the graph will be as
Note:
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas made up of numerous randomly moving particles which are not subjected to interactions with one another. The motion of these particles will be obeying Newton's laws of motion. This gives rise to the ideal gas equation. The ideal gas law or the ideal gas equation, gives us an idea about various gaseous systems.
Formulas used: The ideal gas equation is given by the formula, \[PV = nRT\]
Where \[V\] is the volume of the gas taken
\[p\] is the pressure of gas taken
\[n\] is the number of moles in the amount of substance
\[R\] is the universal gas constant
\[T\] is the temperature
Complete step by step solution:
Let us start by writing down the ideal gas equation.
The ideal gas equation is as, \[PV = nRT\]
We are given that the temperature of the gas is constant. The universal gas constant is a constant as well, you can see it in the name itself. Then we have the number of moles in the amount of substance, which is also a constant in this case.
This makes the RHS of the ideal gas equation to be a constant. Let us call this constant “k”. Then we have \[PV = k\]
That is \[PV = \text{constant}\]
We know that if the value in the y axis is a constant, then the graph will be parallel to the x axis. This means that the graph will be parallel to the axis in which only pressure is present, which is the x axis.
Thus, the graph will be as

Note:
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas made up of numerous randomly moving particles which are not subjected to interactions with one another. The motion of these particles will be obeying Newton's laws of motion. This gives rise to the ideal gas equation. The ideal gas law or the ideal gas equation, gives us an idea about various gaseous systems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




