
Sieve tube is composed of
(a)Xylem
(b)Cortex
(c)Phloem
(d)Both of xylem and phloem
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: The sieve tube is a part of the tissue of a plant that helps to carry nutrients. They bring foods produced in the leaves to all other parts of the plant. The tube of the sieve is not a part of the tissue that brings water to plants.
Complete answer:
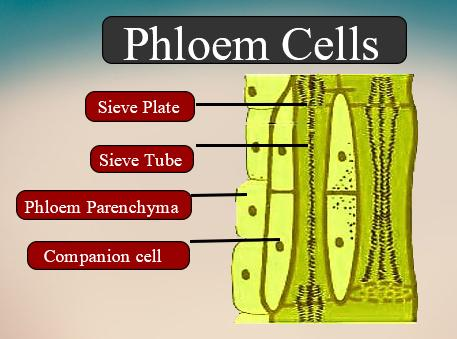
An integral part of the phloem is the sieve tube. They have larger pores and are called sieve plates. They occur end-to-end, forming sieve tubes that allow food to be translocated better.
Sieve components are specialized cells that are vital to the phloem's work, a highly structured tissue that carries organic compounds formed during photosynthesis. Sieve elements are the phloem's main conducting cells.
Sieve tube, elongated living cells (sieve-tube elements) of the phloem in flowering plants, the nuclei of which have broken and vanished, and the transverse end walls of which are pierced by pores (sieve plates) of sievelike groups. These are the means of transporting food (mostly sugar).
Phloem is a complicated permanent tissue of the plant. It consists of sieve tubes, phloem fibers, companion cells, and parenchyma of the phloem. It helps to move leaf-prepared food to different parts of the plant. It can hold food in both upward and downward directions.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Phloem’.
Note: There are distinct structures in the two types of sieve elements, sieve-tube members, and sieve cells. The members of the sieve tube are shorter and wider with a larger nutrient transport area, while the sieve cells appear to be longer and narrower with a narrower nutrient transport area. While the function of each of these sieve element forms is the same, in gymnosperms, non-flowering vascular plants, sieve cells are found, whereas, in angiosperms, flowering vascular plants, sieve-tube members are found.
Complete answer:
An integral part of the phloem is the sieve tube. They have larger pores and are called sieve plates. They occur end-to-end, forming sieve tubes that allow food to be translocated better.
Sieve components are specialized cells that are vital to the phloem's work, a highly structured tissue that carries organic compounds formed during photosynthesis. Sieve elements are the phloem's main conducting cells.
Sieve tube, elongated living cells (sieve-tube elements) of the phloem in flowering plants, the nuclei of which have broken and vanished, and the transverse end walls of which are pierced by pores (sieve plates) of sievelike groups. These are the means of transporting food (mostly sugar).
Phloem is a complicated permanent tissue of the plant. It consists of sieve tubes, phloem fibers, companion cells, and parenchyma of the phloem. It helps to move leaf-prepared food to different parts of the plant. It can hold food in both upward and downward directions.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Phloem’.
Note: There are distinct structures in the two types of sieve elements, sieve-tube members, and sieve cells. The members of the sieve tube are shorter and wider with a larger nutrient transport area, while the sieve cells appear to be longer and narrower with a narrower nutrient transport area. While the function of each of these sieve element forms is the same, in gymnosperms, non-flowering vascular plants, sieve cells are found, whereas, in angiosperms, flowering vascular plants, sieve-tube members are found.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




