
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: In semiconductors, the forbidden gap between the conduction band and the valence bad is exceedingly small.
Complete step by step solution:
For a semiconductor, resistivity decreases rapidly with increase in temperature. Same current will flow through all the resistors.
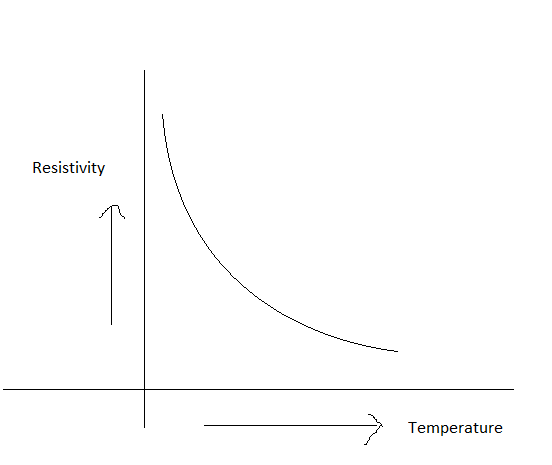
The above graph shows the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
Additional information: Resistivity is known as specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity. It is defined as the intrinsic property of a given material that shows how it opposes the flow of current. In other words, it can also define the resistance offered by the conductor having unit length and unit area of cross section. So, it does not depend upon the length and area of the cross section of a material. But the resistance of a material depends upon the length and area of the cross section of the material.
Silicon is a semiconductor. In semiconductors, the forbidden gap between the conduction band and the valence bad is exceedingly small. At 0 kelvin, the valence band is completely filled, and the conduction band may be empty. But when a small amount of energy is applied, the electrons easily move to the conduction band. Silicon is therefore a good example for semiconductors. Under normal circumstances silicon acts as a poor conductor. Each silicon atom is bonded to 4 other silicon atoms. The bonds between these atoms are covalent bonds where the electrons are in fixed positions.
Note: Before solving the question students need to be well versed with all the properties of semiconductors and also how they change under different circumstances for example pressure and temperature.
Complete step by step solution:
For a semiconductor, resistivity decreases rapidly with increase in temperature. Same current will flow through all the resistors.

The above graph shows the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
Additional information: Resistivity is known as specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity. It is defined as the intrinsic property of a given material that shows how it opposes the flow of current. In other words, it can also define the resistance offered by the conductor having unit length and unit area of cross section. So, it does not depend upon the length and area of the cross section of a material. But the resistance of a material depends upon the length and area of the cross section of the material.
Silicon is a semiconductor. In semiconductors, the forbidden gap between the conduction band and the valence bad is exceedingly small. At 0 kelvin, the valence band is completely filled, and the conduction band may be empty. But when a small amount of energy is applied, the electrons easily move to the conduction band. Silicon is therefore a good example for semiconductors. Under normal circumstances silicon acts as a poor conductor. Each silicon atom is bonded to 4 other silicon atoms. The bonds between these atoms are covalent bonds where the electrons are in fixed positions.
Note: Before solving the question students need to be well versed with all the properties of semiconductors and also how they change under different circumstances for example pressure and temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Draw a diagram to show how hypermetropia is correc class 10 physics CBSE




