
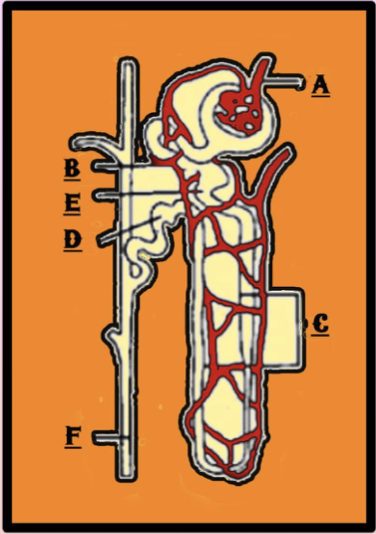
Select the option that correctly identifies the parts labeled from A to Find the given figure of the nephron.
(a) Afferent arteriole PCT Henle’s loop DCT Collecting duct Vasa recta
(b) Efferent arteriole PCT Henle’s loop DCT Collecting duct Vasa recta
(c) Afferent arteriole Peritubular capillaries Henle’s loop DCT PCT Collecting duct
(d) Afferent arteriole Henle’s loop Collecting duct PCT DCT Peritubular capillaries

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The beginning of a renal tubule is formed by a double-walled cup-like structure that is made up of Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus. The glomerulus is formed by the afferent arteriole which then exits the renal corpuscle as a different arteriole.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
A-Afferent arteriole: The afferent arteriole is a thin branch of the renal artery that brings blood towards the nephron and forms glomerulus.
B-Peritubular capillaries: The efferent arteriole that exits the glomerulus forms a fine capillary network around the tubules of the nephron and is known as peritubular capillaries.
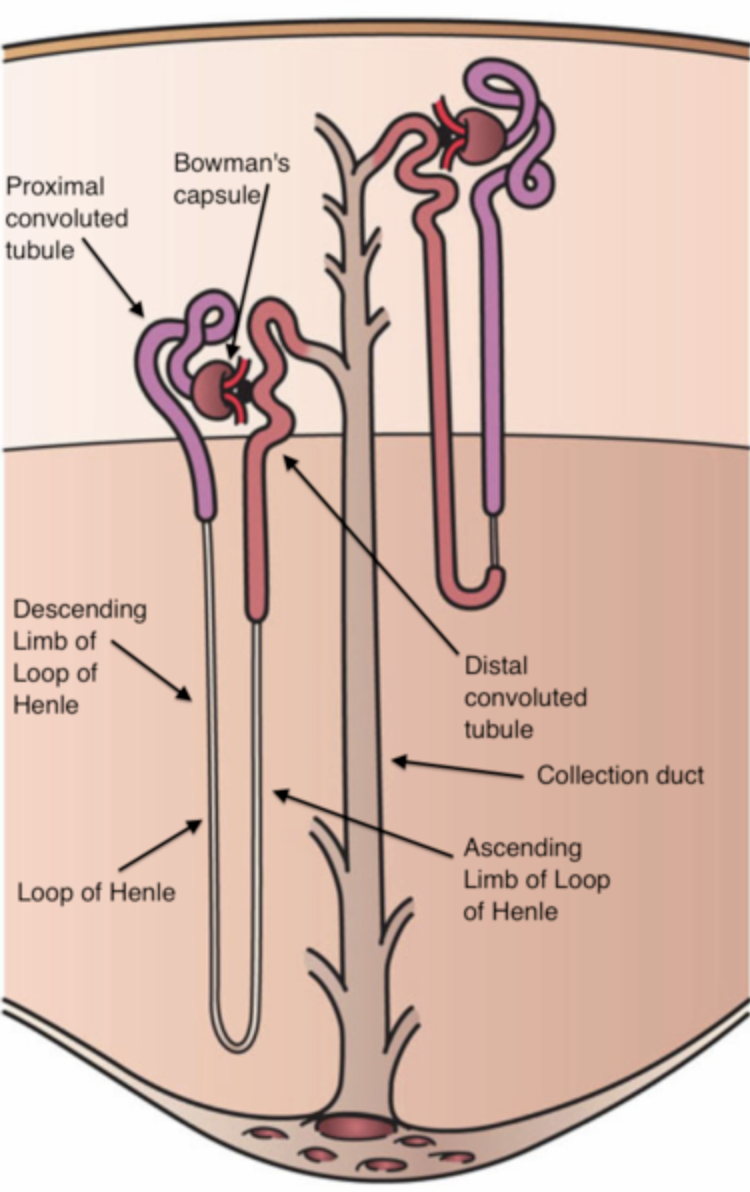
C-Henle’s loop: It is a hairpin-shaped tubule of the nephron which is divided into an ascending and descending limb.
D-DCT: The distant portion of the tubules of nephrons is known as distal convoluted tubule DCT which opens into the collecting duct.
E-PCT: Proximal collecting tubule is the tubule which is just next to the bowman’s capsule and is responsible for absorption.
F-Collecting duct: Collecting ducts are tubules that collect urine from the DCTs of many nephrons.
So, the correct option is ‘Afferent arteriole Peritubular capillaries Henle’s loop DCT PCT Collecting duct’.
Note: There are two types of nephrons on the basis of length of the Loop of Henle i.n. cortical nephrons and juxtaglomerular nephrons. In cortical nephrons, the Loop of Henle is too short and does not reach into the medulla of the kidney. Whereas in the case of juxtamedullary nephrons, the loop of Henle runs deep into the medulla. These nephrons also form the juxtaglomerular apparatus which is responsible for the regulation of the kidney.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
A-Afferent arteriole: The afferent arteriole is a thin branch of the renal artery that brings blood towards the nephron and forms glomerulus.
B-Peritubular capillaries: The efferent arteriole that exits the glomerulus forms a fine capillary network around the tubules of the nephron and is known as peritubular capillaries.
C-Henle’s loop: It is a hairpin-shaped tubule of the nephron which is divided into an ascending and descending limb.
D-DCT: The distant portion of the tubules of nephrons is known as distal convoluted tubule DCT which opens into the collecting duct.
E-PCT: Proximal collecting tubule is the tubule which is just next to the bowman’s capsule and is responsible for absorption.
F-Collecting duct: Collecting ducts are tubules that collect urine from the DCTs of many nephrons.

So, the correct option is ‘Afferent arteriole Peritubular capillaries Henle’s loop DCT PCT Collecting duct’.
Note: There are two types of nephrons on the basis of length of the Loop of Henle i.n. cortical nephrons and juxtaglomerular nephrons. In cortical nephrons, the Loop of Henle is too short and does not reach into the medulla of the kidney. Whereas in the case of juxtamedullary nephrons, the loop of Henle runs deep into the medulla. These nephrons also form the juxtaglomerular apparatus which is responsible for the regulation of the kidney.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




