
Secondary constriction II of the chromosome is concerned with the
(a)Synthesis of rRNA
(b)Synthesis of tRNA
(c)Synthesis of mRNA
(d)All of the above
Answer
598.2k+ views
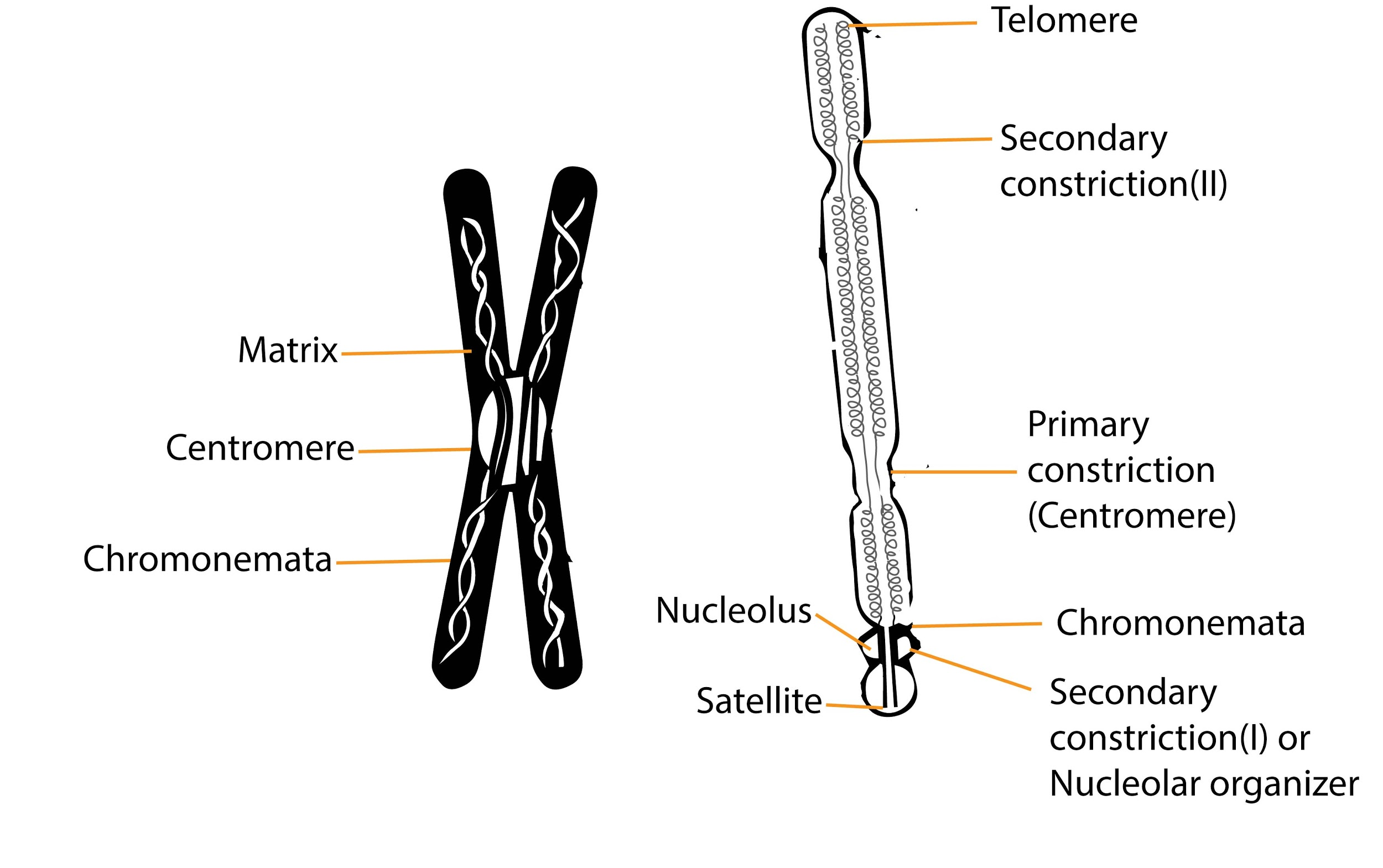
Hint: Secondary constrictions are the constricted or the narrow region found at any point of the chromosome other than that of the centromere, also known as primary constriction.
Complete answer:
Secondary constriction II of the chromosome is generally concerned with the synthesis of rRNA (ribosomal nucleic acid), which is a ribozyme. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), a molecule in cells that forms part of the protein-synthesizing organelle known as a ribosome and that is exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information in messenger RNA (mRNA) into protein, during protein synthesis. The secondary constriction also contains the genes for rRNA synthesis. The difference between the primary and the secondary constrictions can be noticed during the anaphase, as chromosomes can only bend at the site of primary constriction.
Additional Information: -In 1969, Herbert Lubs discovered secondary constriction on the bottom end of the long arm of the X chromosome.
-‘Chromosomal satellite’ is the term given to that part of the end of the chromosome that is separated from the rest of the chromosome by a secondary constriction.
-Secondary constrictions are associated with the nucleolus during interphase of cell division and take part in the reorganization of the nucleolus at the end of the cell division.
-Secondary constrictions are useful in identifying a chromosome from a set of chromosomes.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Synthesis of rRNA.’
Note: The secondary constriction marks the site of a nucleolar organizer region (NOR) (a chromosomal region crucial for the formation of nucleolus), containing multiple copies of the 18S and 28S ribosomal genes that synthesize ribosomal RNA required by ribosomes.
Complete answer:
Secondary constriction II of the chromosome is generally concerned with the synthesis of rRNA (ribosomal nucleic acid), which is a ribozyme. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), a molecule in cells that forms part of the protein-synthesizing organelle known as a ribosome and that is exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information in messenger RNA (mRNA) into protein, during protein synthesis. The secondary constriction also contains the genes for rRNA synthesis. The difference between the primary and the secondary constrictions can be noticed during the anaphase, as chromosomes can only bend at the site of primary constriction.
Additional Information: -In 1969, Herbert Lubs discovered secondary constriction on the bottom end of the long arm of the X chromosome.
-‘Chromosomal satellite’ is the term given to that part of the end of the chromosome that is separated from the rest of the chromosome by a secondary constriction.
-Secondary constrictions are associated with the nucleolus during interphase of cell division and take part in the reorganization of the nucleolus at the end of the cell division.
-Secondary constrictions are useful in identifying a chromosome from a set of chromosomes.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Synthesis of rRNA.’
Note: The secondary constriction marks the site of a nucleolar organizer region (NOR) (a chromosomal region crucial for the formation of nucleolus), containing multiple copies of the 18S and 28S ribosomal genes that synthesize ribosomal RNA required by ribosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




