
What is the role of ${ NAD }^{ + }$ in cellular respiration?
(a) It is a nucleotide source for ATP synthesis.
(b) It functions as an enzyme.
(c) It is the final electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration.
(d) It functions as an electron carrier.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: During cellular respiration, ${ NAD }^{ + }$ becomes NADH which means it is getting reduced. A compound is said to have undergone a reduction reaction when H gets added to it. Or when electrons are added to a compound.
Complete answer:
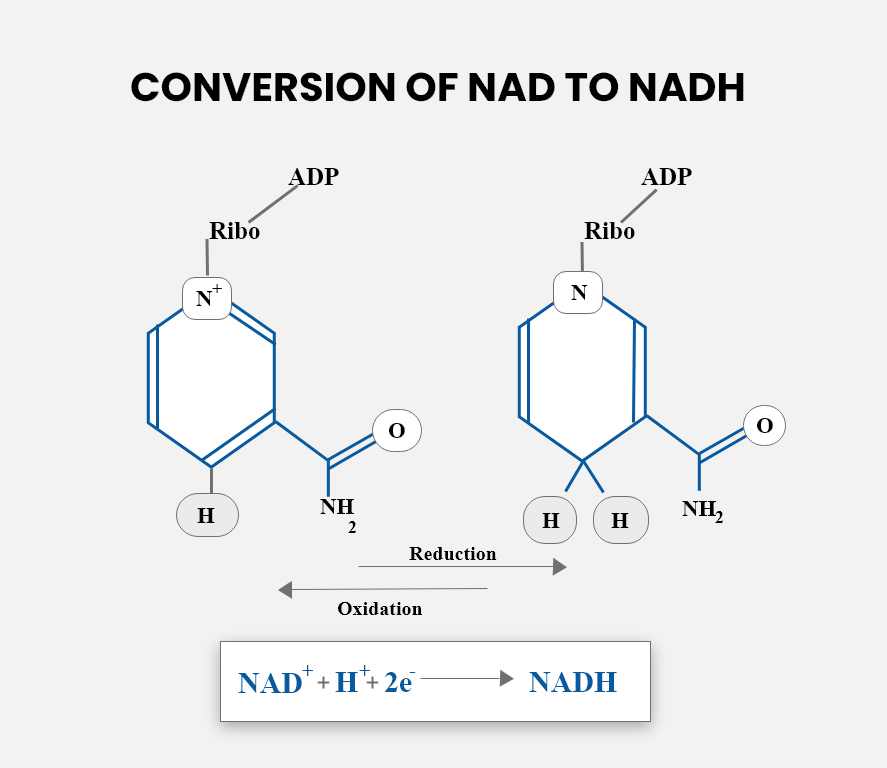
The role of ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is that it acts as an electron carrier. It accepts electrons from compounds by oxidizing them and adds H+ as well to give NADH. NADH is a reducing agent which then gives these electrons at the ETS. These electrons then flow through a series of complexes which result in the production of ATPs. By the process of ETS, 3 ATP molecules are generated by the oxidation of one NADH. This process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
So, the correct answer is the option ‘It functions as an electron carrier’.
Additional information:
Let us know more about this vital compound in our body.
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a coenzyme which means that it helps enzymes function properly. It is present in all living cells and is involved in metabolism. ${ NAD }^{ + }$ has two functions:
- Act as an electron and hydrogen carrier to produce energy from food.
- Act as coenzymes help enzymes catalyze chemical reactions in our bodies.
NAD is formed by simple amino acids like tryptophan, aspartic acid, etc, and a vitamin ${ B }_{ 3 }$ called niacin. It exists in the body as two forms i.e. ${ NAD }^{ + }$ (oxidizing form) and NADH (reducing form). The structure of NAD consists of two nucleotides attached by phosphate groups, hence the name dinucleotide.
Note: Not to be confused with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) which mainly plays a role in photosynthesis. The trick to remember, associate the P of NADP with photosynthesis. In ETS, NADH gives its electrons to Complex-I (NADH dehydrogenase) whereas its contemporary FADH gives its electrons to Complex- II (cytochrome ${ bc }_{ 1 }$).
Complete answer:
The role of ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is that it acts as an electron carrier. It accepts electrons from compounds by oxidizing them and adds H+ as well to give NADH. NADH is a reducing agent which then gives these electrons at the ETS. These electrons then flow through a series of complexes which result in the production of ATPs. By the process of ETS, 3 ATP molecules are generated by the oxidation of one NADH. This process is called oxidative phosphorylation.

So, the correct answer is the option ‘It functions as an electron carrier’.
Additional information:
Let us know more about this vital compound in our body.
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a coenzyme which means that it helps enzymes function properly. It is present in all living cells and is involved in metabolism. ${ NAD }^{ + }$ has two functions:
- Act as an electron and hydrogen carrier to produce energy from food.
- Act as coenzymes help enzymes catalyze chemical reactions in our bodies.
NAD is formed by simple amino acids like tryptophan, aspartic acid, etc, and a vitamin ${ B }_{ 3 }$ called niacin. It exists in the body as two forms i.e. ${ NAD }^{ + }$ (oxidizing form) and NADH (reducing form). The structure of NAD consists of two nucleotides attached by phosphate groups, hence the name dinucleotide.
Note: Not to be confused with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) which mainly plays a role in photosynthesis. The trick to remember, associate the P of NADP with photosynthesis. In ETS, NADH gives its electrons to Complex-I (NADH dehydrogenase) whereas its contemporary FADH gives its electrons to Complex- II (cytochrome ${ bc }_{ 1 }$).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




