
: Resonance is not exhibited by
(A) Phenol
(B) Aniline
(C) Nitrobenzene
(D) Cyclohexane
Answer
524k+ views
Hint: Resonance can be observed in conjugated compounds (compounds having alternate single and multiple bonds). These resonance structures are hypothetical and this phenomenon imparts extra stability to the compound.
Complete step-by-step answer: We can define resonance effect as the delocalization of pi electrons or unshared electrons without shifting any atom.
The actual structure of compound is the resonance hybrid of various possible alternate structures that are known as resonating structures or canonical structures.
The resonance structures of a molecule have the same positions of nuclei and the same number of unpaired electrons. Due to resonance the molecule is planar.
The structures of phenol, aniline, nitrobenzene and cyclohexane are as follows-
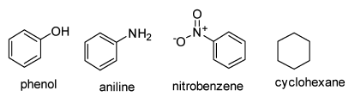
The resonance can be observed in phenol, aniline and nitrobenzene since they have conjugation (alternate single and double bonds) in the molecule. In cyclohexane there is no conjugation. It has only single bonds in this molecule. So resonance effect is absent in cyclohexane. Moreover cyclohexane is not a planar molecule.
Additional information: All resonance structures do not contribute equally to the hybrid. Structures with more covalent bonds are more stable than those with a lesser number of covalent bonds.
There are two types of resonance effect- positive resonance effect and negative resonance effect. In a positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons takes place away from the substituent group attached to the conjugated system. In a negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the substituent group attached to the conjugated system.
Hence,the correct option is (D).
Note: In the given structures the $ - OH, - N{H_2}$ group is an electron releasing group and hence shows a positive resonance effect. They donate the electrons to the ring. The $( - N{O_2})$nitro group is an electron withdrawing group. It withdraws electrons of the ring towards itself. So nitrobenzene shows a negative resonance effect.
Complete step-by-step answer: We can define resonance effect as the delocalization of pi electrons or unshared electrons without shifting any atom.
The actual structure of compound is the resonance hybrid of various possible alternate structures that are known as resonating structures or canonical structures.
The resonance structures of a molecule have the same positions of nuclei and the same number of unpaired electrons. Due to resonance the molecule is planar.
The structures of phenol, aniline, nitrobenzene and cyclohexane are as follows-

The resonance can be observed in phenol, aniline and nitrobenzene since they have conjugation (alternate single and double bonds) in the molecule. In cyclohexane there is no conjugation. It has only single bonds in this molecule. So resonance effect is absent in cyclohexane. Moreover cyclohexane is not a planar molecule.
Additional information: All resonance structures do not contribute equally to the hybrid. Structures with more covalent bonds are more stable than those with a lesser number of covalent bonds.
There are two types of resonance effect- positive resonance effect and negative resonance effect. In a positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons takes place away from the substituent group attached to the conjugated system. In a negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the substituent group attached to the conjugated system.
Hence,the correct option is (D).
Note: In the given structures the $ - OH, - N{H_2}$ group is an electron releasing group and hence shows a positive resonance effect. They donate the electrons to the ring. The $( - N{O_2})$nitro group is an electron withdrawing group. It withdraws electrons of the ring towards itself. So nitrobenzene shows a negative resonance effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




