
When resistances are connected in series
a) same voltage is applied across all resistors
b) resistances must be same
c) same current flows through all resistances
d) All
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: When resistances are connected in series the net resistance of the circuit gets added up. This is because all the resistances behave like one big resistance and obstruct the flow of current together. Hence using Ohm's law and Kirchhoff’s law of voltages we will determine the current and the voltage in the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us say we connect two resistances in series as shown in the figure.
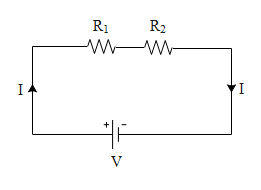
By applying ohm's law to the above circuit we get the potential difference across the resistances is,
$V=IR$ where V is the potential difference across the resistances, I is the current in the circuit and R is the net resistance of the circuit. In series circuit the resistance gets added up i.e. R = R$_1$+R$_2$. Hence the above equation can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& V=I\left( {{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=I{{R}_{1}}+I{{R}_{2}}...(1) \\
\end{align}$
But according to Kirchhoff’s law, the emf V of the battery is equal to the potential difference across both the resistors i.e. $V={{V}_{{{R}_{1}}}}+{{V}_{{{R}_{2}}}}...(2)$ where ${{V}_{{{R}_{1}}}}$ is the potential difference across resistor ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{V}_{{{R}_{2}}}}$ is the potential difference across resistor ${{R}_{2}}$. If we compare equation 1 and 2, we can conclude that the current across the resistors is the same as the current in the overall circuit i.e. $I$. From this we can also conclude that the potential difference across the resistors is different.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
If the resistances in the above circuit were equal, then we can conclude that the potential difference across the two resistors would also have been equal. It is also to be noted that in parallel circuits the current across the resistors is different. But the voltage across each of them is the same.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us say we connect two resistances in series as shown in the figure.

By applying ohm's law to the above circuit we get the potential difference across the resistances is,
$V=IR$ where V is the potential difference across the resistances, I is the current in the circuit and R is the net resistance of the circuit. In series circuit the resistance gets added up i.e. R = R$_1$+R$_2$. Hence the above equation can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& V=I\left( {{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=I{{R}_{1}}+I{{R}_{2}}...(1) \\
\end{align}$
But according to Kirchhoff’s law, the emf V of the battery is equal to the potential difference across both the resistors i.e. $V={{V}_{{{R}_{1}}}}+{{V}_{{{R}_{2}}}}...(2)$ where ${{V}_{{{R}_{1}}}}$ is the potential difference across resistor ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{V}_{{{R}_{2}}}}$ is the potential difference across resistor ${{R}_{2}}$. If we compare equation 1 and 2, we can conclude that the current across the resistors is the same as the current in the overall circuit i.e. $I$. From this we can also conclude that the potential difference across the resistors is different.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
If the resistances in the above circuit were equal, then we can conclude that the potential difference across the two resistors would also have been equal. It is also to be noted that in parallel circuits the current across the resistors is different. But the voltage across each of them is the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




