
Represent each of the following molecules using Lewis notation:
(A) Bromine gas $\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$
(B) Calcium chloride $\left( {{\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$
(C) Carbon dioxide $\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$
Which of the three molecules listed above contains a double bond?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint:The simplified representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule is known as the Lewis notation. In Lewis notation, each atom of a molecule is shown along with its position in the structure using the chemical symbol of the atom. From the Lewis notations we can determine the molecule that contains the double bond.
Complete step-by-step solution:(A)Bromine gas $\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule as follows:
We know that the valence electrons of bromine are 7. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Br}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {2 \times 7} \right)$
Valence electrons of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 14$
Draw the Lewis notation of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ is:

The two bromine atoms bond with one another forming one bond. As one bond is formed, two electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 14 - 2 = 12$
Place the remaining 12 electrons around the bromine atoms such that all the two bromine atoms complete their octets. Thus,
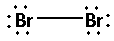
(B)Calcium chloride $\left( {{\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule as follows:
We know that the valence electrons of calcium are 2 and the valence electrons of chlorine are 7. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Ca}}} \right) + \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Cl}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {1 \times 2} \right) + \left( {2 \times 7} \right)$
Valence electrons of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 16$
Draw the Lewis notation of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is:
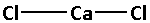
The two chlorine atoms bond with the calcium atom forming two bonds. As two bonds are formed, four electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 16 - 4 = 12$
Place the remaining 12 electrons around the chlorine atoms such that all the two chlorine atoms complete their octets. Thus
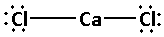
(C) Carbon dioxide $\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule as follows:
We know that the valence electrons of carbon are 4 and the valence electrons of oxygen are 6. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of C}}} \right) + \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {1 \times 4} \right) + \left( {2 \times 6} \right)$
Valence electrons of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 16$
Draw the Lewis notation of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is:
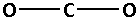
The two oxygen atoms bond with the carbon atom forming two bonds. As two bonds are formed, four electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 16 - 4 = 12$
Place the remaining 12 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the two oxygen atoms complete their octets. Thus,
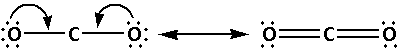
From the Lewis notations, we can see that the molecule that contains double bond is carbon dioxide $\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$.
Note: In the carbon dioxide molecule, the carbon atom shares two of its electrons in the formation of the double bond with one oxygen atom and the other two electrons in the formation of the double bond with the other oxygen atom. Both carbon and oxygen atoms acquire a stable electronic configuration. The valency of carbon is 4 and the valency of oxygen is 6.
Complete step-by-step solution:(A)Bromine gas $\left( {{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule as follows:
We know that the valence electrons of bromine are 7. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Br}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {2 \times 7} \right)$
Valence electrons of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 14$
Draw the Lewis notation of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ is:

The two bromine atoms bond with one another forming one bond. As one bond is formed, two electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 14 - 2 = 12$
Place the remaining 12 electrons around the bromine atoms such that all the two bromine atoms complete their octets. Thus,
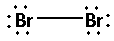
(B)Calcium chloride $\left( {{\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule as follows:
We know that the valence electrons of calcium are 2 and the valence electrons of chlorine are 7. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Ca}}} \right) + \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Cl}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {1 \times 2} \right) + \left( {2 \times 7} \right)$
Valence electrons of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 16$
Draw the Lewis notation of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is:
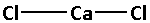
The two chlorine atoms bond with the calcium atom forming two bonds. As two bonds are formed, four electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 16 - 4 = 12$
Place the remaining 12 electrons around the chlorine atoms such that all the two chlorine atoms complete their octets. Thus
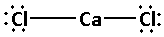
(C) Carbon dioxide $\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule as follows:
We know that the valence electrons of carbon are 4 and the valence electrons of oxygen are 6. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of C}}} \right) + \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {1 \times 4} \right) + \left( {2 \times 6} \right)$
Valence electrons of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 16$
Draw the Lewis notation of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is:
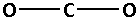
The two oxygen atoms bond with the carbon atom forming two bonds. As two bonds are formed, four electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons $ = 16 - 4 = 12$
Place the remaining 12 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the two oxygen atoms complete their octets. Thus,

From the Lewis notations, we can see that the molecule that contains double bond is carbon dioxide $\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$.
Note: In the carbon dioxide molecule, the carbon atom shares two of its electrons in the formation of the double bond with one oxygen atom and the other two electrons in the formation of the double bond with the other oxygen atom. Both carbon and oxygen atoms acquire a stable electronic configuration. The valency of carbon is 4 and the valency of oxygen is 6.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




