
Removal of soil by wind and water is called:
A. Soil conservation
B. Soil binding
C. Soil erosion
D. Mulching
Answer
564.6k+ views
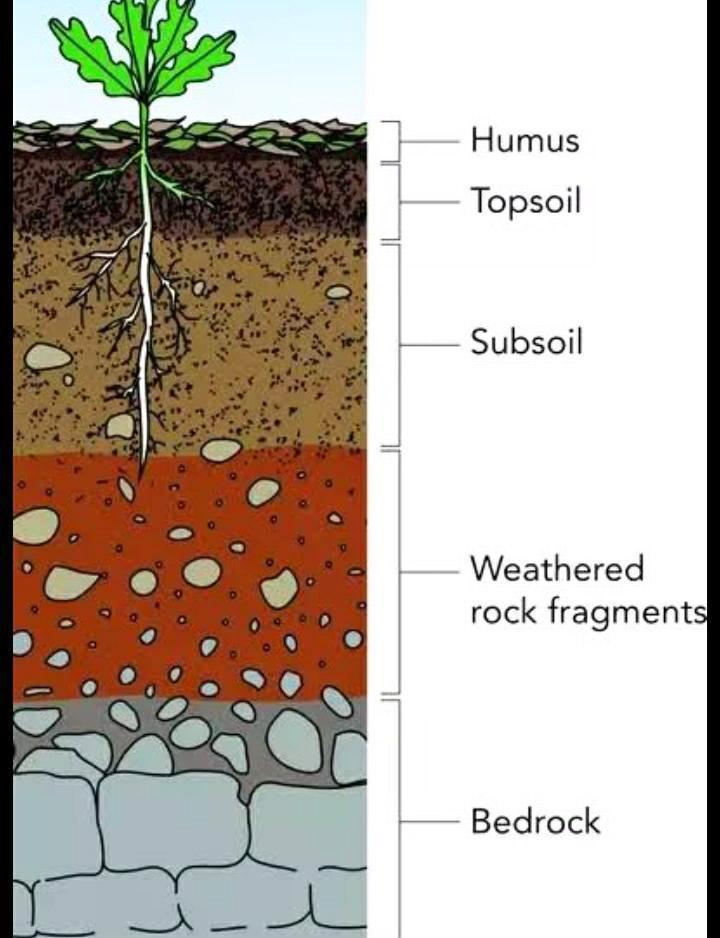
Hint:Topsoil is the upper, peripheral layer of soil, for the most part, the top 5–10 inches (13–25 cm). It has the most noteworthy grouping of natural issues and microorganisms and is the place a large portion of the Earth's organic soil action happens. Topsoil is made out of mineral particles, natural issues, water, and air.
Complete answer:
Soil erosion is the removal of topsoil by the agency like water (water erosion) and wind (wind erosion). Soil erosion is of two kinds i.e., common and anthropogenic. So, option C is correct.
Soil binding is a holding capacity of a plant that forestalls or restrains erosion by giving a ground spread and framing a thick organization of roots that hold the soil. So, option B is incorrect.
Soil Conservation is a blend of practices used to shield the soil from debasement. This implies returning natural issues to the soil on a nonstop premise. So, option A is incorrect.
Mulching is a process in which there is a covering, as of straw, fertilizer, or plastic sheeting, spread on the ground around plants to forestall exorbitant dissipation or erosion, improve the soil, hinder weed development, and so forth. So, option D is incorrect.
Hence, option C) is correct answer.
Note: Soil erosion can be prevented by-
1. Yield Rotation: Rotating in high-buildup crops —, for example, corn, feed, and little grain — can diminish erosion as the layer of buildup shields topsoil from being diverted by wind and water.
2. Conservation Tillage: Conventional culturing produces a smooth surface that leaves soil helpless against erosion.
3. Shape Farming: Planting in column designs that run level around a slope — rather than all over the incline — has appeared to diminish overflow and abate the danger of water erosion.
4. Strip Farming: In zones where a slant is especially steep or there is no elective strategy for forestalling erosion, planting fields in long strips exchanged in a harvest pivot framework (strip cultivating) has demonstrated success.
Complete answer:
Soil erosion is the removal of topsoil by the agency like water (water erosion) and wind (wind erosion). Soil erosion is of two kinds i.e., common and anthropogenic. So, option C is correct.
Soil binding is a holding capacity of a plant that forestalls or restrains erosion by giving a ground spread and framing a thick organization of roots that hold the soil. So, option B is incorrect.
Soil Conservation is a blend of practices used to shield the soil from debasement. This implies returning natural issues to the soil on a nonstop premise. So, option A is incorrect.
Mulching is a process in which there is a covering, as of straw, fertilizer, or plastic sheeting, spread on the ground around plants to forestall exorbitant dissipation or erosion, improve the soil, hinder weed development, and so forth. So, option D is incorrect.

Hence, option C) is correct answer.
Note: Soil erosion can be prevented by-
1. Yield Rotation: Rotating in high-buildup crops —, for example, corn, feed, and little grain — can diminish erosion as the layer of buildup shields topsoil from being diverted by wind and water.
2. Conservation Tillage: Conventional culturing produces a smooth surface that leaves soil helpless against erosion.
3. Shape Farming: Planting in column designs that run level around a slope — rather than all over the incline — has appeared to diminish overflow and abate the danger of water erosion.
4. Strip Farming: In zones where a slant is especially steep or there is no elective strategy for forestalling erosion, planting fields in long strips exchanged in a harvest pivot framework (strip cultivating) has demonstrated success.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




