
What is reflex action? Write its types and two examples of each.
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: When a person touches a hot object unintentionally, without thought, they instinctively jerk their hand away. A reflex does not need the input of any thought. A reflex arc is called the path taken by the nerve impulses in a reflex.
Complete answer:
In response to a stimulus, a reflex action, also known as a reflex, is an automatic and nearly instantaneous reaction.
There are two forms of Reflex Action:
1. Unconditioned reflexes: Inborn reflexes are these. These include knee jerk, peristalsis.
2. Conditioned reflexes: These are acquired after birth and involve some kind of learning. These include playing a musical instrument, driving a car.
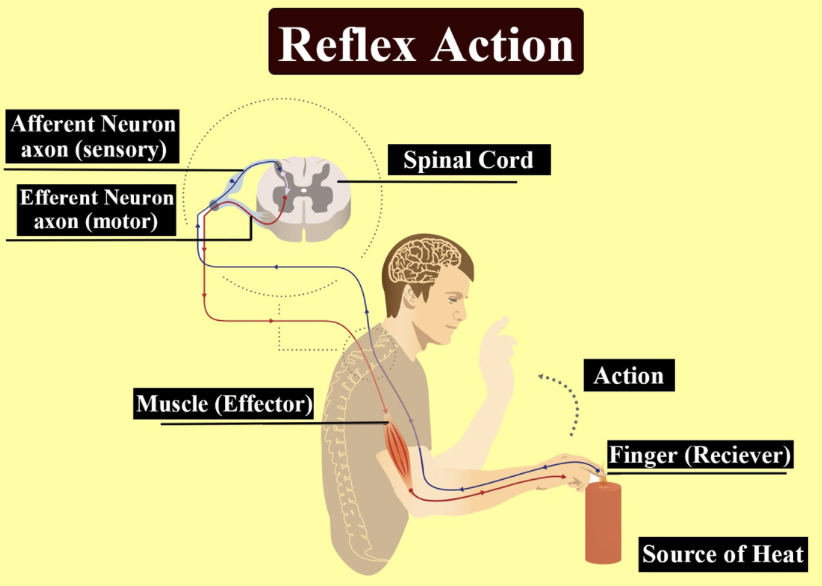
The reflex arc is considered the anatomical pathway of a reflex. It consists of an afferent (or sensory) nerve and an efferent (motor, secretory, or secreto- motor) nerve, usually one or more interneurons inside the central nervous system.
Additional Information:
- The pupillary light reflex is perhaps the best- known reflex.
- The pupils of both eyes contract if a light is flashed close to one eye. Light is the stimulus; impulses through the optic nerve enter the brain; and autonomic nerves that supply the eye relay the response to the pupillary musculature.
- The cough and sneeze reflexes are other reflexes of the midbrain and medulla oblongata.
- An irritant in the trachea triggers the cough reflex and one in the nose triggers the sneeze reflex.
- In both, several muscles are involved in the reflex response; this includes a brief respiration lapse in order to remove the irritant.
Note:
- In the womb, the first reflexes develop.
- The first reflex can be observed at seven and a half weeks after conception; stimulation around the mouth of the fetus causes the lips to be redirected to the stimulus.
Complete answer:
In response to a stimulus, a reflex action, also known as a reflex, is an automatic and nearly instantaneous reaction.

There are two forms of Reflex Action:
1. Unconditioned reflexes: Inborn reflexes are these. These include knee jerk, peristalsis.
2. Conditioned reflexes: These are acquired after birth and involve some kind of learning. These include playing a musical instrument, driving a car.
The reflex arc is considered the anatomical pathway of a reflex. It consists of an afferent (or sensory) nerve and an efferent (motor, secretory, or secreto- motor) nerve, usually one or more interneurons inside the central nervous system.
Additional Information:
- The pupillary light reflex is perhaps the best- known reflex.
- The pupils of both eyes contract if a light is flashed close to one eye. Light is the stimulus; impulses through the optic nerve enter the brain; and autonomic nerves that supply the eye relay the response to the pupillary musculature.
- The cough and sneeze reflexes are other reflexes of the midbrain and medulla oblongata.
- An irritant in the trachea triggers the cough reflex and one in the nose triggers the sneeze reflex.
- In both, several muscles are involved in the reflex response; this includes a brief respiration lapse in order to remove the irritant.
Note:
- In the womb, the first reflexes develop.
- The first reflex can be observed at seven and a half weeks after conception; stimulation around the mouth of the fetus causes the lips to be redirected to the stimulus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




