
What is rectification? Draw the circuit diagram of half wave rectifier and explain its
working. Show the input ac voltage and output voltage waveforms from the rectifier circuit.
Answer
566.1k+ views
Hint:First, understand the meaning of rectification and know how it is related to AC and DC signals. For drawing the circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier check what are the important parts of a half wave rectifier and explain how it works. By understanding the working try to plot the input ac voltage and its output voltage waveforms.
Complete step by step solution:
Rectification is the process in which a rectifier converts alternating current into direct current or in other words it makes current flow only in one direction. A rectifier is an electrical device which consists of one or more diodes which makes current to flow in one direction only.
A half wave rectifier is a rectifier that allows only the positive half cycle of the alternating current to pass and blocks the negative half cycle.
The circuit diagram for half wave rectifier is shown below,
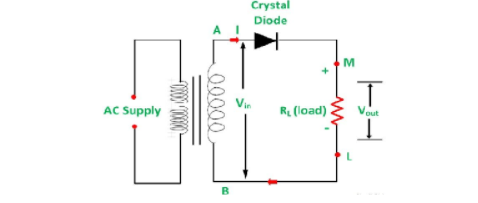
A half wave rectifier mainly consists of three parts; these are a transformer, a resistive load and a diode. AC signal is given to the rectifier through a transformer which can be step up or step down transformer. We know diodes allow the current flow only in one direction or when it is forward biased. When the positive half cycle flows through the circuit, it acts as forward biased and the diode conducts whereas when the negative half cycle passes through the circuit, it acts as reverse biased and the diode doesn’t conduct and blocks the negative half cycle of the ac signal. Therefore, we get output voltage when the positive half cycle of the ac voltage flows through the circuit.
The input ac voltage and output voltage waveforms of a half wave rectifier are shown below.
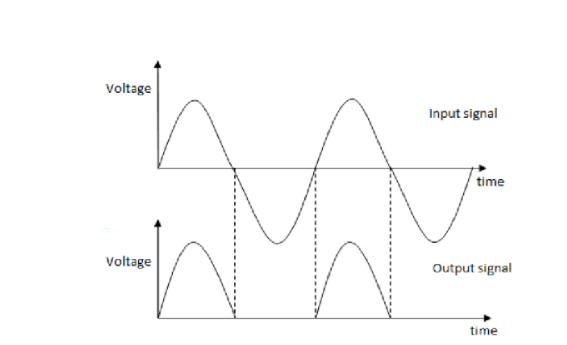
Note:There is one more rectifier which is known as full wave rectifier which is more efficient than half wave rectifier. A half wave rectifier just removes the negative half cycle from the input signal and converts only one half of the input signal whereas a full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and rectifies the negative cycle of the input signal too.
Complete step by step solution:
Rectification is the process in which a rectifier converts alternating current into direct current or in other words it makes current flow only in one direction. A rectifier is an electrical device which consists of one or more diodes which makes current to flow in one direction only.
A half wave rectifier is a rectifier that allows only the positive half cycle of the alternating current to pass and blocks the negative half cycle.
The circuit diagram for half wave rectifier is shown below,

A half wave rectifier mainly consists of three parts; these are a transformer, a resistive load and a diode. AC signal is given to the rectifier through a transformer which can be step up or step down transformer. We know diodes allow the current flow only in one direction or when it is forward biased. When the positive half cycle flows through the circuit, it acts as forward biased and the diode conducts whereas when the negative half cycle passes through the circuit, it acts as reverse biased and the diode doesn’t conduct and blocks the negative half cycle of the ac signal. Therefore, we get output voltage when the positive half cycle of the ac voltage flows through the circuit.
The input ac voltage and output voltage waveforms of a half wave rectifier are shown below.

Note:There is one more rectifier which is known as full wave rectifier which is more efficient than half wave rectifier. A half wave rectifier just removes the negative half cycle from the input signal and converts only one half of the input signal whereas a full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and rectifies the negative cycle of the input signal too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




