
What is the reaction of epoxide with Grignard reagent?
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: Grignard reagents are organometallic compounds having a metal and an organic group along with a halogen, with the formula, RMgX, where R is any alkyl group, Mg is magnesium and X is halogen. They undergo additional reactions with carbonyl groups. Epoxides are tricyclic compounds having one carbonyl group.
Complete answer:
Grignard reagents are highly basic organometallic compounds. They have the tendency to react with any species that donates a proton. Grignard reagents are capable of generating a nucleophile, which can react with electrophiles in addition to reactions. On the other hand, epoxides are tricyclic compounds having 2 carbon and 1 oxygen atoms. They, when undergoes addition with Grignard reagents, leads to the ring opening of the epoxides.
The reaction of epoxide with Grignard reagents leads to the formation of primary alcohols, with two carbons more than the length, due to the ring opening. The reaction of epoxide with Grignard reagents is:
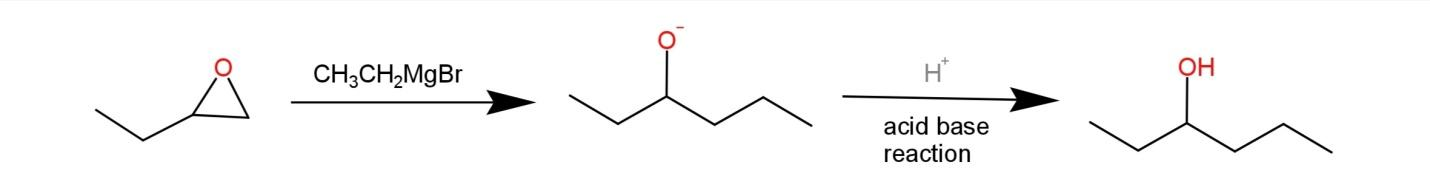
Epoxide opens as the electrophile is generated by the addition of the alkyl group by Grignard reagent on epoxide. This when subjected to acidic conditions leads to the formation of a primary alcohol.
Hence, reaction of epoxides with Grignard reagent generates primary alcohols.
Note:
Epoxides are also called ethylene oxides. The reaction follows the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution, which is ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ type. The strong basic condition of the Grignard reagent is responsible for the opening of the ring of the epoxides. The acid workup is the final step in the reaction of epoxides. Apart from reaction with epoxides, Grignard also reacts with aldehydes, ketones, acid chlorides, etc. compounds with a carbonyl group.
Complete answer:
Grignard reagents are highly basic organometallic compounds. They have the tendency to react with any species that donates a proton. Grignard reagents are capable of generating a nucleophile, which can react with electrophiles in addition to reactions. On the other hand, epoxides are tricyclic compounds having 2 carbon and 1 oxygen atoms. They, when undergoes addition with Grignard reagents, leads to the ring opening of the epoxides.
The reaction of epoxide with Grignard reagents leads to the formation of primary alcohols, with two carbons more than the length, due to the ring opening. The reaction of epoxide with Grignard reagents is:

Epoxide opens as the electrophile is generated by the addition of the alkyl group by Grignard reagent on epoxide. This when subjected to acidic conditions leads to the formation of a primary alcohol.
Hence, reaction of epoxides with Grignard reagent generates primary alcohols.
Note:
Epoxides are also called ethylene oxides. The reaction follows the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution, which is ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ type. The strong basic condition of the Grignard reagent is responsible for the opening of the ring of the epoxides. The acid workup is the final step in the reaction of epoxides. Apart from reaction with epoxides, Grignard also reacts with aldehydes, ketones, acid chlorides, etc. compounds with a carbonyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




