
Reaction mechanism of sulphonation of benzene ring using dil. $ HCl $ and $ {H_2}S{O_4} $ around $ {150^ \circ }C $ ?
Answer
501k+ views
Hint: Benzene is an aromatic rings that has high electron density due to the conjugation of double bonds in a cyclic manner inside the ring. Benzene ring tends to undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions that makes the removal of the sulfonic acid group possible.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Benzene can easily undergo a sulphonation reaction in the presence of sulphuric acid. The sulfonic group can be removed by acidic hydrolysis.
Acids like dilute sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid at high temperatures, allow the desulphonation reaction to take place. The water molecule acts as a Bronsted base and abstracts a proton from the acidic medium. Thy hydronium ion formed as a result of acification acts as an electrophile.
The electron rich double bond of benzene gets attacked by the electrophile in such a manner that the hydrogen abstracted from hydronium ions is placed on the carbon atom containing sulfonic acid group and a resonance stabilized carbocation is formed at the adjacent carbon position. Water is formed as a byproduct.
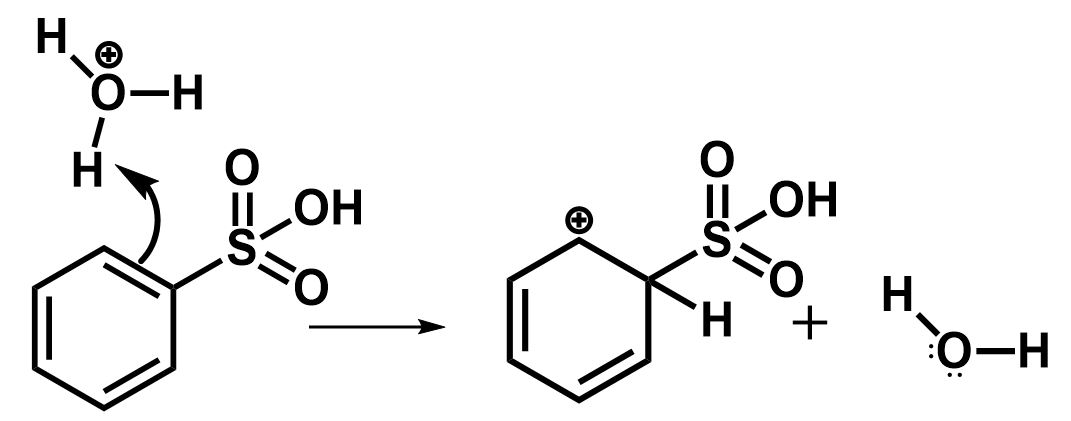
The next step involves the removal of the sulfonic group to regenerate the aromatic character. This is initiated by the nucleophilic attack of water molecules.
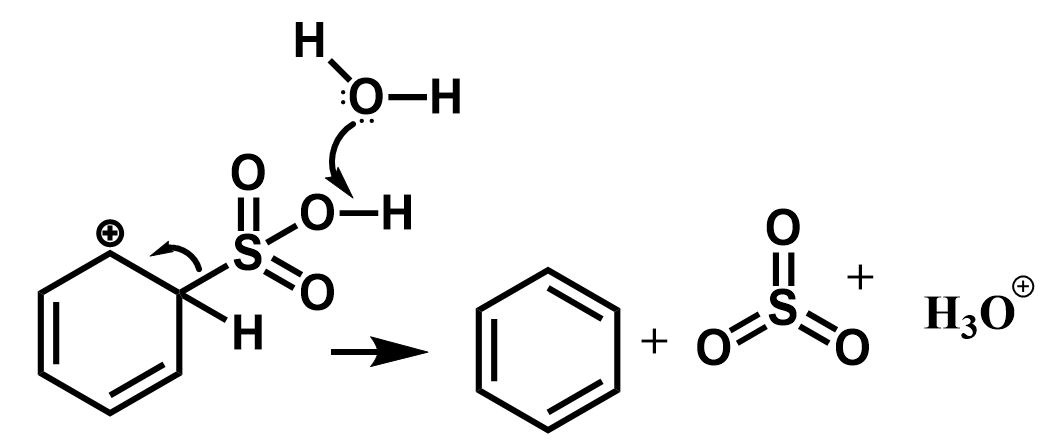
$ \Rightarrow $ As a result, the sulfonic acid group is removed in the form of sulphur trioxide and the benzene ring is regained.
Note:
The Sulphonation process is reversible in nature and therefore it is easy to remove the group. The attack of electrophile specifically shifts the electron density towards the sulfonic group containing carbon as it is an electron withdrawing group and a carbocation is more stable at the adjacent position.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Benzene can easily undergo a sulphonation reaction in the presence of sulphuric acid. The sulfonic group can be removed by acidic hydrolysis.
Acids like dilute sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid at high temperatures, allow the desulphonation reaction to take place. The water molecule acts as a Bronsted base and abstracts a proton from the acidic medium. Thy hydronium ion formed as a result of acification acts as an electrophile.
The electron rich double bond of benzene gets attacked by the electrophile in such a manner that the hydrogen abstracted from hydronium ions is placed on the carbon atom containing sulfonic acid group and a resonance stabilized carbocation is formed at the adjacent carbon position. Water is formed as a byproduct.

The next step involves the removal of the sulfonic group to regenerate the aromatic character. This is initiated by the nucleophilic attack of water molecules.

$ \Rightarrow $ As a result, the sulfonic acid group is removed in the form of sulphur trioxide and the benzene ring is regained.
Note:
The Sulphonation process is reversible in nature and therefore it is easy to remove the group. The attack of electrophile specifically shifts the electron density towards the sulfonic group containing carbon as it is an electron withdrawing group and a carbocation is more stable at the adjacent position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




