
What is the R.D.S. of pinacol – pinacolone rearrangement?
A.I step
B.II step
C.III step
D.IV step
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: In pinacol – pinacolone rearrangement reaction, the acids lead to protonation of the hydroxyl group, then removal of water leads to formation of carbocation. Here, 1,2-rearrangement occurs leading to formation of a ketone compound.
Complete answer:
- Pinacol contains alcohol functional group, while pinacolone contains ketone functional group.
- Pinacol is a compound which has two hydroxyl groups each attached to an adjacent carbon atom.
- Pinacolone is an organic compound containing ketone functional groups. It is a colorless liquid and has an odor of peppermint or camphor.
- The pinacol – pinacolone rearrangement reaction is the conversion of an alcohol having two adjacent alcohol groups (pinacol) to a ketone (pinacolone) by the action of an acid (catalyst).
- The reaction mechanism can be explained by the following four steps:
Step 1 – Protonation of a hydroxyl group
In this step, proton or hydrogen ions coming from acid get attached to a hydroxyl group of pinacol.
Step 2 – Loss of water molecule
Here, the water molecule gets detached to give carbocation. The formation of carbocation is slow hence this is rate determining step.
Step 3 – Methyl migration
The methyl group migrates from one carbon to another atom. It gets attached to a positively charged carbon atom of carbocation.
Step 4 – Deprotonation
The proton which got attached in the first step got detached as this proton was generated by an acid catalyst during the reaction. When protons get detached from carbocation, final product pinacolone is formed.
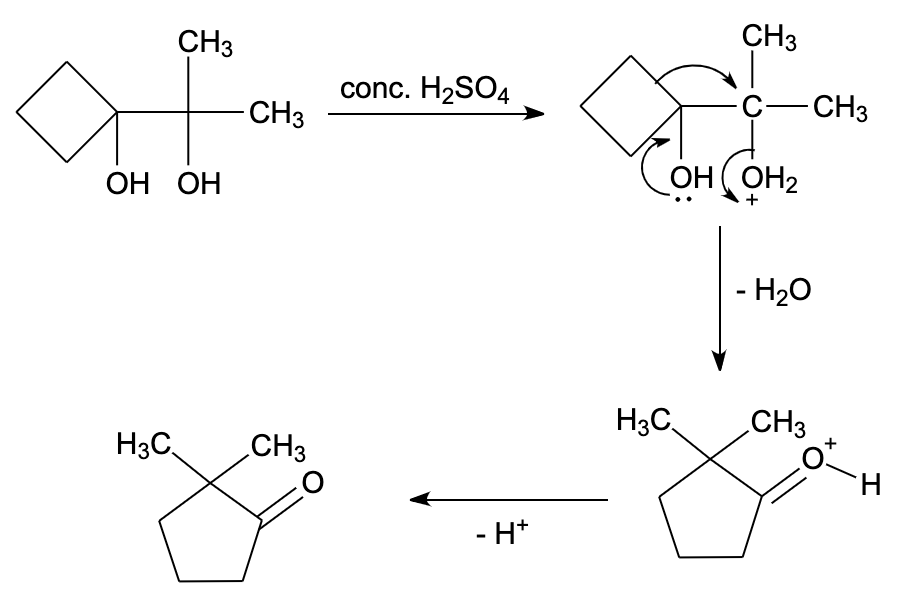
Therefore, the correct option is (B) .
Note:
This rearrangement reaction is regioselective in nature, which means that only the more stable carbocation yields a major product. Also, the rearrangement occurs because of the relative stability of the resulting oxonium ion.
Complete answer:
- Pinacol contains alcohol functional group, while pinacolone contains ketone functional group.
- Pinacol is a compound which has two hydroxyl groups each attached to an adjacent carbon atom.
- Pinacolone is an organic compound containing ketone functional groups. It is a colorless liquid and has an odor of peppermint or camphor.
- The pinacol – pinacolone rearrangement reaction is the conversion of an alcohol having two adjacent alcohol groups (pinacol) to a ketone (pinacolone) by the action of an acid (catalyst).
- The reaction mechanism can be explained by the following four steps:
Step 1 – Protonation of a hydroxyl group
In this step, proton or hydrogen ions coming from acid get attached to a hydroxyl group of pinacol.
Step 2 – Loss of water molecule
Here, the water molecule gets detached to give carbocation. The formation of carbocation is slow hence this is rate determining step.
Step 3 – Methyl migration
The methyl group migrates from one carbon to another atom. It gets attached to a positively charged carbon atom of carbocation.
Step 4 – Deprotonation
The proton which got attached in the first step got detached as this proton was generated by an acid catalyst during the reaction. When protons get detached from carbocation, final product pinacolone is formed.

Therefore, the correct option is (B) .
Note:
This rearrangement reaction is regioselective in nature, which means that only the more stable carbocation yields a major product. Also, the rearrangement occurs because of the relative stability of the resulting oxonium ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




