
What is the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ ?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: To find the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ , we have to rewrite this equation by splitting the constant as combining the terms. We will obtain $\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\left( {{x}^{2}}+2x+1 \right)+1$ . Now, we have to use the algebraic identity to get the result $f\left( x \right)={{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1$ . Now, we have to consider ${{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}$ , which will always be positive. Now, we have to make an inequality whose RHS will be the RHS of the function $f\left( x \right)$ . From this inequality, we can find the range of the given function.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to find the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ . Let us first split the constant as $1+1$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+1+1$
We can group the terms as follows.
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\left( {{x}^{2}}+2x+1 \right)+1$
We can see that the terms inside the parenthesis is of the form ${{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}={{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}$ , where $a=1$ and $b=1$ . Hence, we can write the above equation as
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)={{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1...\left( i \right)$
We know that ${{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}$ will always be positive, that is, greater than or equal to 0, for all $x\in \mathbb{R}$ .
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\ge 0$
Let us add 1 to both the sides to make the LHS of the above equation similar to equation (i).
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1\ge 0+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1\ge 1...\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
We know that the range of a function is the spread of possible y-values (minimum y-value to maximum y-value). Hence, we can write the range of the given function from (ii) as
$y\in \left[ 1,\infty \right)$
Therefore, the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ is $\left[ 1,\infty \right)$ .
Note: Students must know algebraic identities to simplify the equations. We have used a closed interval in the range for 1 and open interval for 0 because from the inequality (ii), we obtained a $\ge $ sign. We can also find the range by substituting different real numbers for x and computing the corresponding y values ( f(x) ). We can then interpret the range from the values of y or from the graph. Let us see the graph of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ , which is a parabola.
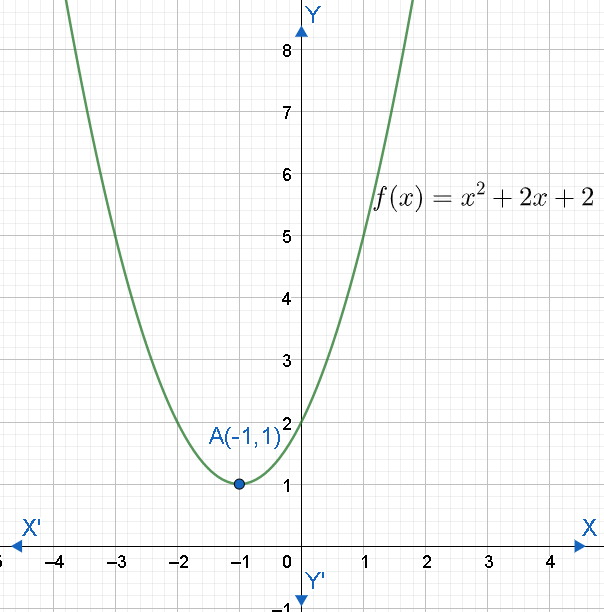
We can see that the minimum value of y is -1 and maximum value is infinity.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to find the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ . Let us first split the constant as $1+1$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+1+1$
We can group the terms as follows.
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\left( {{x}^{2}}+2x+1 \right)+1$
We can see that the terms inside the parenthesis is of the form ${{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}={{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}$ , where $a=1$ and $b=1$ . Hence, we can write the above equation as
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)={{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1...\left( i \right)$
We know that ${{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}$ will always be positive, that is, greater than or equal to 0, for all $x\in \mathbb{R}$ .
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}\ge 0$
Let us add 1 to both the sides to make the LHS of the above equation similar to equation (i).
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1\ge 0+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1\ge 1...\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
We know that the range of a function is the spread of possible y-values (minimum y-value to maximum y-value). Hence, we can write the range of the given function from (ii) as
$y\in \left[ 1,\infty \right)$
Therefore, the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ is $\left[ 1,\infty \right)$ .
Note: Students must know algebraic identities to simplify the equations. We have used a closed interval in the range for 1 and open interval for 0 because from the inequality (ii), we obtained a $\ge $ sign. We can also find the range by substituting different real numbers for x and computing the corresponding y values ( f(x) ). We can then interpret the range from the values of y or from the graph. Let us see the graph of the function $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2x+2$ , which is a parabola.

We can see that the minimum value of y is -1 and maximum value is infinity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




